Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, particularly when understanding the nuances of interest rates. In 2023, the landscape of federal student loan interest rates presents both challenges and opportunities for borrowers. This guide aims to clarify the key aspects of these rates, empowering you to make informed decisions about your financial future.
From understanding the different types of federal loans and their associated interest rates to exploring strategies for minimizing debt accumulation, we will delve into the practical implications of these rates on your repayment journey. We will examine the impact of various repayment plans and explore how economic factors influence these rates. This comprehensive overview will equip you with the knowledge necessary to effectively manage your student loan debt.
Understanding the 2023 Student Loan Interest Rate Landscape
Navigating the complexities of student loan interest rates can be daunting, particularly given the variations in loan types and the factors influencing their costs. This section provides a clear overview of the 2023 interest rate landscape for federal student loans, offering essential information for borrowers to make informed financial decisions.
Federal Student Loan Types and 2023 Interest Rates
The federal government offers several types of student loans, each with its own interest rate. These rates are fixed for the life of the loan, meaning they don’t change over time. Understanding the distinctions between these loan types is crucial for effective financial planning. The rates listed below represent the fixed interest rates for the 2023-2024 academic year and are subject to change in subsequent years. It’s important to check the official Federal Student Aid website for the most up-to-date information.
Factors Influencing Federal Student Loan Interest Rates
Several factors contribute to the determination of federal student loan interest rates. These rates are not arbitrarily set but are influenced by broader economic conditions. The most significant factor is the 10-year Treasury note yield, which serves as a benchmark for government borrowing costs. Other factors, while less prominent, can also play a role, including the loan’s repayment period and the borrower’s creditworthiness (although credit history does not directly affect federal student loan interest rates). Changes in government policy can also impact interest rates.
Subsidized vs. Unsubsidized Loan Interest Rates
A key distinction lies between subsidized and unsubsidized federal student loans. Subsidized loans are need-based and the government pays the interest while the borrower is in school at least half-time, during grace periods, and during periods of deferment. Unsubsidized loans, on the other hand, accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed, regardless of the borrower’s enrollment status. This means borrowers are responsible for all accrued interest on unsubsidized loans. Consequently, the effective cost of an unsubsidized loan will be higher than a subsidized loan with the same interest rate due to compounding interest. For 2023-2024, the interest rate difference between subsidized and unsubsidized loans of the same type was minimal, but this can vary from year to year.
Graduate vs. Undergraduate Loan Interest Rates in 2023
Interest rates for graduate and undergraduate federal student loans can differ. Graduate students often face slightly higher interest rates compared to undergraduates, reflecting the generally higher loan amounts borrowed for graduate studies. This reflects the increased borrowing risk associated with larger loan amounts and longer repayment periods for graduate education. However, the specific interest rate still depends on the type of loan (subsidized or unsubsidized) and the year the loan was disbursed.
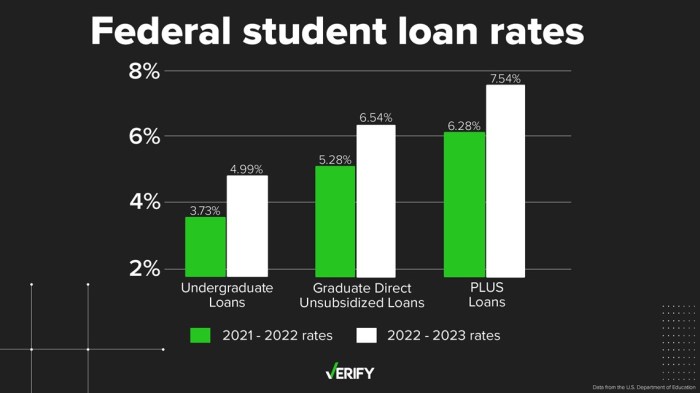
Summary of 2023 Federal Student Loan Interest Rates
| Loan Type | Interest Rate (2023-2024) | Subsidized/Unsubsidized | Loan Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Subsidized Loan | 4.99% | Subsidized | Undergraduate |
| Direct Unsubsidized Loan | 4.99% | Unsubsidized | Undergraduate |
| Direct Subsidized Loan | 6.54% | Subsidized | Graduate |
| Direct Unsubsidized Loan | 6.54% | Unsubsidized | Graduate |
Impact of Interest Rates on Repayment Plans

Understanding the interplay between student loan interest rates and repayment plans is crucial for borrowers seeking to minimize their long-term debt burden. The rate significantly impacts the total amount repaid, influencing both the overall cost and the length of the repayment period. This section will explore how different interest rates affect various repayment strategies.
Varying interest rates directly influence the total cost of borrowing. A higher interest rate means more money is paid in interest over the life of the loan, increasing the total amount repaid beyond the principal loan amount. Conversely, lower interest rates reduce the overall interest paid, leading to lower total repayment costs and potentially shorter repayment periods.
Effects of Interest Rates on Standard Repayment Plans
The standard repayment plan typically involves fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period. However, the monthly payment amount and the total interest paid are heavily influenced by the interest rate. A higher interest rate necessitates a larger monthly payment to meet the repayment schedule within the 10-year timeframe. For example, a $50,000 loan with a 5% interest rate will result in significantly lower total interest paid and smaller monthly payments compared to the same loan with a 7% interest rate. The difference can amount to thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
Effects of Interest Rates on Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-driven repayment plans (IDR) adjust monthly payments based on the borrower’s income and family size. While the monthly payment is lower compared to standard plans, the repayment period is typically extended to 20 or 25 years. Even though the monthly payments are smaller, higher interest rates still increase the total interest paid over the extended repayment period. The longer repayment term magnifies the impact of even small interest rate differences. A borrower might end up paying considerably more in interest despite having lower monthly payments.
Comparative Analysis of Repayment Plans and Interest Rates
The following analysis compares the long-term cost implications of different repayment plans under varying interest rate assumptions for a hypothetical $30,000 loan. These figures are for illustrative purposes and may vary based on individual loan terms and circumstances.
It is important to note that these are simplified examples and do not include factors like fees or potential changes in interest rates during the repayment period. Actual repayment amounts and timelines may differ.
| Repayment Plan | Interest Rate (Annual Percentage Rate) | Approximate Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid (Estimated) | Loan Payoff Timeline (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 5% | $316 | $11,400 | 10 years |
| Standard | 7% | $344 | $15,800 | 10 years |
| Income-Driven (20-year plan) | 5% | $180 | $16,000 | 20 years |
| Income-Driven (20-year plan) | 7% | $195 | $21,000 | 20 years |
Interest Rate Changes and Their Implications
Understanding the potential shifts in student loan interest rates is crucial for borrowers to effectively manage their debt. Future rate adjustments depend on a complex interplay of economic factors and government policy decisions. This section explores these factors and their impact on borrowers.
Potential Scenarios for Future Interest Rate Adjustments
Several scenarios could unfold regarding future student loan interest rate adjustments. For instance, continued high inflation could lead to further interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve, indirectly impacting student loan rates if the government ties them to market indices. Conversely, a significant economic downturn might prompt the government to lower rates to stimulate borrowing and economic activity. A third scenario involves the government making independent adjustments to student loan interest rates, potentially decoupling them from broader market trends, based on political or social considerations. These scenarios highlight the uncertainty inherent in predicting future rate changes.
Impact of Economic Factors on Student Loan Interest Rates
Economic factors like inflation and interest rate hikes significantly influence student loan interest rates. High inflation typically prompts the Federal Reserve to increase the federal funds rate, the target rate for overnight lending between banks. This increase ripples through the financial system, affecting various borrowing costs, including student loans, particularly those tied to market-based indices. Conversely, during periods of low inflation or economic recession, interest rates tend to fall, potentially leading to lower student loan interest rates. For example, the significant interest rate cuts implemented during the 2008 financial crisis resulted in lower rates for many federal student loans.
Government Setting of Student Loan Interest Rates
The U.S. government sets interest rates for federal student loans through a combination of statutory provisions and administrative decisions. For some loan programs, rates are fixed by law for specific periods. Others, like some unsubsidized loans, are tied to market-based indices, such as the 10-year Treasury note, plus a fixed margin. The government may adjust the margin or choose a different index, but the underlying principle is to reflect prevailing market conditions. This approach aims to balance the cost of borrowing for the government with affordability for students. Changes in government policy, budget priorities, or economic forecasts can all affect the setting of these rates.
Effects of Interest Rate Fluctuations on Borrowers’ Monthly Payments
Fluctuations in interest rates directly impact borrowers’ monthly payments. A higher interest rate increases the total interest accrued over the loan’s life and results in higher monthly payments for the same loan amount. Conversely, lower interest rates decrease the total interest paid and reduce monthly payments. Consider two scenarios: a $100,000 loan at 5% interest versus the same loan at 7%. The higher interest rate would lead to significantly larger monthly payments and a substantially higher total repayment amount. This illustrates the importance of understanding the impact of even small interest rate changes on long-term borrowing costs.
Visual Representation of Interest Rates and Loan Repayment Burden
Imagine a graph with the horizontal axis representing interest rates (ranging from, say, 2% to 10%) and the vertical axis representing monthly payments (in dollars). For a fixed loan amount (e.g., $50,000), we can plot points representing the monthly payment at each interest rate. The resulting line will be an upward-sloping curve, demonstrating a direct positive correlation: as interest rates increase, so do monthly payments. A steeper slope would indicate a greater sensitivity of monthly payments to interest rate changes. This visualization clearly shows how even small increases in interest rates can dramatically increase the total repayment burden over the loan’s lifespan.
Strategies for Managing Student Loan Debt with High Interest Rates
Navigating high student loan interest rates can feel daunting, but proactive strategies can significantly reduce your overall debt burden and accelerate your repayment journey. Understanding your options and implementing effective strategies is key to minimizing the long-term financial impact of these loans. This section Artikels several approaches to help you manage your debt effectively.
Minimizing Interest Accumulation on Student Loans
Several strategies can help minimize the accumulation of interest on your student loans. Prioritizing higher-interest loans for extra payments is crucial. Exploring options like income-driven repayment plans can temporarily lower monthly payments, though it often extends the repayment period and increases total interest paid over the life of the loan. Careful budgeting and identifying areas for savings can free up additional funds for loan repayment. Additionally, consistent on-time payments avoid late fees which can quickly add to your debt.
Refinancing Student Loans to Lower Interest Rates
Refinancing your student loans can be a powerful tool for lowering your interest rate and monthly payments. By consolidating multiple loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate, you can significantly reduce the total interest paid over the life of the loan. However, it’s important to carefully compare offers from different lenders to secure the best rate and terms. Eligibility criteria vary among lenders, so it’s crucial to check your credit score and financial history before applying. A lower interest rate translates directly to less money paid in interest over the loan’s lifetime, freeing up funds for other financial goals.
Impact of Extra Principal Payments on Total Interest Paid
Making extra payments towards the principal of your student loans can substantially reduce the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Even small, consistent extra payments can make a significant difference over time. For example, paying an extra $100 per month on a $30,000 loan with a 7% interest rate could save thousands of dollars in interest and shorten the repayment period considerably. This strategy accelerates the repayment process and minimizes the overall cost of borrowing. Consider this an investment in your financial future, offering substantial long-term savings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Exploring Loan Refinancing Options
- Check your credit score: Lenders use your credit score to determine your eligibility and interest rate. A higher score generally leads to better terms.
- Research lenders: Compare interest rates, fees, and repayment terms offered by various lenders specializing in student loan refinancing.
- Gather necessary documents: Prepare your income verification, student loan details, and other supporting documents required by lenders.
- Compare loan offers: Carefully review the terms of multiple loan offers before making a decision. Pay close attention to the interest rate, fees, and repayment period.
- Apply for refinancing: Once you’ve chosen a lender, complete the application process and provide all the required information.
- Review loan documents: Before finalizing the refinancing, carefully review all loan documents to ensure you understand the terms and conditions.
Resources and Further Information for Borrowers
Navigating the complexities of student loan interest rates can be challenging. Fortunately, numerous resources are available to help borrowers understand their options and manage their debt effectively. This section provides a comprehensive overview of government websites, contact information for relevant agencies, and links to reputable financial websites offering guidance on student loan management. Understanding these resources is crucial for making informed decisions about your student loan repayment.
The federal government provides a wealth of information and support for student loan borrowers. Several key agencies offer resources, tools, and direct assistance. Additionally, many reputable financial websites provide valuable, independent advice and tools to help you manage your student loans effectively.
Government Resources and Websites
The U.S. Department of Education’s Federal Student Aid website is the primary source of information for federal student loans. This website provides detailed information on interest rates, repayment plans, loan forgiveness programs, and other relevant topics. It offers tools to calculate your monthly payments, explore repayment options, and manage your loans online. The site also includes a comprehensive FAQ section addressing common questions from borrowers. Another valuable resource is the StudentAid.gov website, which allows borrowers to access their loan information, make payments, and manage their accounts.
Contact Information for Relevant Agencies and Servicers
Direct contact with the appropriate agencies and servicers is crucial for resolving issues and accessing personalized assistance. While specific contact details may vary, the Federal Student Aid website provides a comprehensive directory of student loan servicers, allowing borrowers to easily find the contact information for their specific loan servicer. This directory usually includes phone numbers, email addresses, and mailing addresses. For general inquiries about federal student aid, borrowers can contact the Federal Student Aid Information Center.
Reputable Financial Websites Offering Guidance
Numerous reputable financial websites offer valuable guidance on student loan management. These websites often provide articles, calculators, and other tools to help borrowers understand their options, plan for repayment, and manage their debt effectively. For instance, some websites offer detailed comparisons of different repayment plans, helping borrowers choose the option that best suits their financial situation. Other websites provide budgeting tools and financial advice to help borrowers manage their overall finances while repaying their student loans. These independent resources supplement the information provided by government agencies.
Key Resources and Contact Information
| Resource | Website | Phone Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Student Aid | [Website address would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Phone number would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Email address would go here – this is a placeholder] |
| StudentAid.gov | [Website address would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Phone number would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Email address would go here – this is a placeholder] |
| [Example Financial Website 1] | [Website address would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Phone number would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Email address would go here – this is a placeholder] |
| [Example Financial Website 2] | [Website address would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Phone number would go here – this is a placeholder] | [Email address would go here – this is a placeholder] |
Final Wrap-Up
Successfully managing student loan debt requires a proactive approach and a clear understanding of the interest rate dynamics at play. By understanding the factors that influence interest rates, exploring various repayment options, and employing effective debt management strategies, borrowers can significantly reduce their overall repayment burden and achieve long-term financial stability. Remember to utilize the available resources and seek professional guidance when needed to navigate this crucial financial aspect of your life.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between subsidized and unsubsidized loans?
Subsidized loans do not accrue interest while you’re in school, during grace periods, or during deferment. Unsubsidized loans accrue interest throughout your entire loan term.
Can I refinance my student loans to a lower interest rate?
Yes, refinancing can lower your interest rate, but it often involves private lenders and may affect your eligibility for federal repayment programs.
What happens if I don’t make my student loan payments?
Failure to make payments can lead to delinquency, negatively impacting your credit score and potentially resulting in wage garnishment or tax refund offset.
Where can I find my student loan interest rate information?
Your loan servicer’s website and your monthly statements will provide details about your interest rate and loan balance.
How are student loan interest rates determined?
Interest rates for federal student loans are set by the government and are often tied to market conditions and the 10-year Treasury note.
