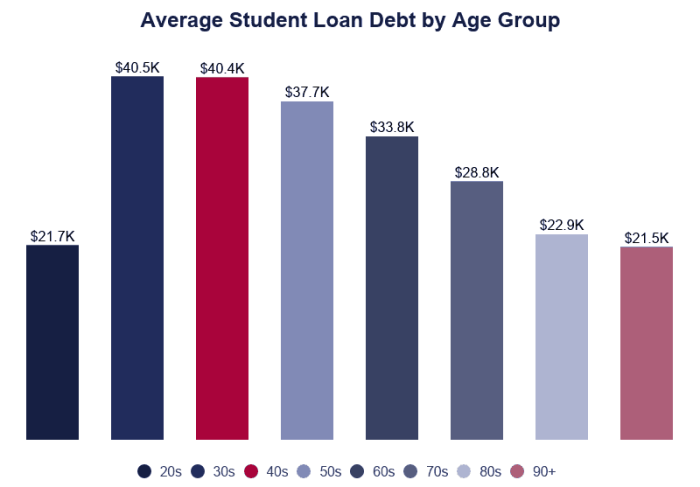
Navigating the complexities of student loan refinancing can feel overwhelming, especially with the fluctuating interest rates and diverse lender options. Understanding the average student loan refinance rate is crucial for making informed decisions and securing the best possible terms for your financial future. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of current market trends, crucial factors influencing rates, and a step-by-step process to help you successfully refinance your student loans.
From exploring the relationship between credit scores and interest rates to comparing fixed versus variable options, we’ll demystify the process. We’ll also examine different lender types, eligibility criteria, and strategies for minimizing fees, empowering you to confidently navigate the refinancing landscape and achieve your financial goals.
Current Market Trends in Student Loan Refinancing
The student loan refinancing market is dynamic, influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors and lender policies. Understanding current trends is crucial for borrowers seeking to lower their monthly payments and potentially save thousands of dollars over the life of their loans. This section will examine current average refinance rates, influential factors, and examples from various lenders.
Currently, average student loan refinance rates are highly competitive, reflecting a generally favorable lending environment for borrowers with strong credit profiles. However, these rates are not static and fluctuate based on various macroeconomic and lender-specific conditions. The rates offered vary significantly depending on factors like credit score, loan amount, and the type of loan (fixed or variable).
Average Student Loan Refinance Rates and Lender Examples
The following table illustrates refinance rates from several prominent lenders. It’s important to note that these rates are subject to change and represent a snapshot in time. Always check directly with the lender for the most up-to-date information.
| Lender | Rate Type | Minimum Credit Score | Loan Amount Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lender A (Example) | Fixed | 680 | $50,000 |
| Lender B (Example) | Variable | 700 | $75,000 |
| Lender C (Example) | Fixed | 660 | $30,000 |
| Lender D (Example) | Variable | 720 | $100,000 |
Factors Influencing Student Loan Refinance Rate Fluctuations
Several key factors contribute to the volatility of average refinance rates. Understanding these factors empowers borrowers to make informed decisions about when to refinance.
Economic conditions play a significant role. For example, during periods of low inflation and stable interest rates set by the Federal Reserve, lenders are often more willing to offer lower refinance rates to attract borrowers. Conversely, during periods of high inflation or rising interest rates, rates tend to increase. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy directly impacts interest rates across the board, including those for student loan refinancing. Changes in the federal funds rate often lead to corresponding adjustments in lending rates.
Furthermore, the performance of the overall economy and the perceived risk associated with lending influence rates. If the economy is strong and unemployment is low, lenders may be more inclined to offer lower rates, reflecting a lower perceived risk of loan defaults. Conversely, during economic downturns, rates may rise to compensate for the increased risk.
Finally, individual borrower characteristics, such as credit score and debt-to-income ratio, heavily influence the specific rate offered. Borrowers with higher credit scores and lower debt-to-income ratios are typically offered more favorable rates, as they represent a lower risk to lenders.
Impact of Credit Score on Refinance Rates
Your credit score is a crucial factor determining the interest rate you’ll receive when refinancing your student loans. Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness – essentially, how likely you are to repay the loan. A higher credit score signals lower risk to the lender, resulting in a more favorable interest rate. Conversely, a lower credit score indicates higher risk, leading to higher interest rates or even loan denial.
Lenders consider various aspects of your credit history when calculating your credit score, including payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, credit mix, and new credit. Each of these components contributes to your overall score, impacting the interest rate you qualify for. Understanding this relationship is vital for securing the best possible terms on your student loan refinance.
Credit Score Ranges and Refinance Rates
The relationship between credit score and refinance rate is generally inverse; higher credit scores correspond to lower rates. While specific rates vary based on lender, loan amount, and other factors, the following table provides a general illustration of how credit score ranges might influence refinance rates. Remember that these are examples and actual rates may differ.
| Credit Score Range | Approximate Refinance Rate Range (Example) |
|---|---|
| 750-850 (Excellent) | 3.00% – 5.00% |
| 700-749 (Good) | 5.00% – 6.50% |
| 650-699 (Fair) | 6.50% – 8.00% |
| Below 650 (Poor) | 8.00% + or Loan Denial |
Improving Credit Score for Better Rates
Improving your credit score before applying for student loan refinancing can significantly impact the interest rate you obtain. Several strategies can help you boost your score.
Taking proactive steps to improve your creditworthiness can lead to substantial savings over the life of your loan. Even a small improvement in your credit score can translate into a lower interest rate and significant cost savings. For instance, a 1% reduction in your interest rate on a $50,000 loan could save you thousands of dollars over the repayment period.
Comparison of Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates

Choosing between a fixed and variable interest rate when refinancing your student loans is a crucial decision that significantly impacts your monthly payments and overall repayment cost. Understanding the nuances of each option is vital for making an informed choice aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. This section will Artikel the key differences between fixed and variable rate loans, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each.
The primary difference between fixed and variable interest rates lies in their predictability. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan’s term, providing borrowers with predictable monthly payments. Conversely, a variable interest rate fluctuates based on an underlying benchmark index, such as the prime rate or LIBOR (although LIBOR is being phased out). This fluctuation introduces an element of uncertainty into your monthly payments.
Fixed Interest Rate Loans
Fixed-rate loans offer the stability of consistent monthly payments. This predictability makes budgeting easier and reduces the risk of unexpected increases in your repayment burden. However, if interest rates fall significantly after you refinance with a fixed rate, you may miss out on potential savings.
Variable Interest Rate Loans
Variable-rate loans offer the potential for lower initial interest rates, leading to potentially lower monthly payments in the early stages of repayment. However, this advantage is offset by the risk of rising interest rates, which can substantially increase your monthly payments over the life of the loan. The unpredictability of variable rates can make long-term financial planning more challenging.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Variable Rate Loans
Understanding the core differences is essential for making an informed decision. The following points summarize the key distinctions:
- Interest Rate: Fixed rates remain constant throughout the loan term; variable rates fluctuate based on a benchmark index.
- Monthly Payments: Fixed rates provide predictable monthly payments; variable rates result in fluctuating monthly payments.
- Risk: Fixed rates offer lower risk but potentially higher overall cost; variable rates offer higher risk but potentially lower initial cost.
- Predictability: Fixed rates provide greater predictability and budgeting ease; variable rates introduce uncertainty into budgeting.
- Long-Term Cost: The long-term cost of a fixed-rate loan is predictable; the long-term cost of a variable-rate loan is uncertain.
Scenarios Favoring Fixed vs. Variable Rates
The best choice depends on individual circumstances and risk tolerance.
Scenarios Favoring a Fixed Rate: A fixed rate is generally preferable for borrowers who prioritize predictability and stability. This is particularly true for those with a low risk tolerance or those who prefer to avoid the uncertainty associated with fluctuating payments. For example, a borrower with a stable income and a preference for predictable budgeting would likely find a fixed-rate loan more suitable. They value the peace of mind that comes with knowing exactly how much they’ll owe each month, even if it means potentially paying slightly more in interest over the long term.
Scenarios Favoring a Variable Rate: A variable rate might be more beneficial for borrowers who are comfortable with some risk and anticipate potentially lower interest rates in the future. This strategy could be advantageous for borrowers with a higher risk tolerance who are confident in their ability to manage fluctuating payments. For instance, a borrower expecting a significant income increase in the near future might opt for a variable rate, hoping to capitalize on lower initial interest rates. However, they need to be prepared for the possibility of higher payments if interest rates rise.
Types of Student Loan Refinancing Lenders
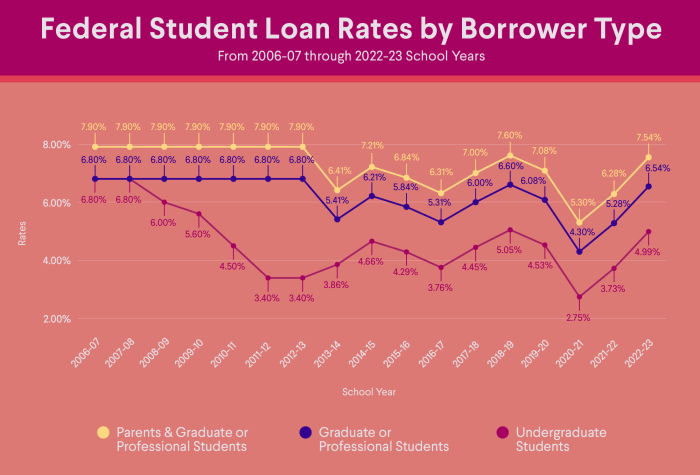
Choosing the right lender for student loan refinancing is crucial, as it directly impacts your interest rate, repayment terms, and overall borrowing experience. Different lenders offer varying benefits and drawbacks, making careful comparison essential before making a decision. Understanding the landscape of available lenders will help you navigate this process effectively.
Several types of financial institutions offer student loan refinancing options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These include banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Each lender type caters to different borrower profiles and offers a unique set of services and features.
Lender Types and Their Offerings
The following table compares the offerings of three distinct lender types: Banks, Credit Unions, and Online Lenders. Note that these are general comparisons and individual lender offerings may vary.
| Feature | Banks | Credit Unions | Online Lenders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loan Terms (e.g., repayment periods) | Typically offer a range of terms, often aligning with standard loan structures. May offer shorter or longer terms depending on the applicant’s creditworthiness and loan amount. | May offer flexible terms, potentially including options tailored to individual member needs. Often focus on building relationships with members and providing personalized service. | Often provide a wide range of loan terms, sometimes offering more flexibility than traditional lenders. Terms are often clearly Artikeld online. |
| Fees (origination fees, prepayment penalties, etc.) | Generally charge origination fees, and may have prepayment penalties. Specific fees vary widely between banks. | May have lower or waived fees compared to banks, reflecting their member-focused approach. Fees are often transparent and disclosed upfront. | Fees vary significantly between online lenders. Some may have no origination fees, while others may charge higher fees to offset lower interest rates. It’s crucial to compare fees across lenders. |
| Customer Service Features | Offer various customer service channels, including phone, email, and in-person support at branches. However, the level of personalized service may vary. | Often emphasize personalized service and strong member relationships. May provide more accessible and responsive customer service than larger banks. | Primarily rely on online and phone support. The quality of customer service can vary widely, with some online lenders known for responsive support while others struggle to provide timely assistance. |
Evaluating Lenders Based on Offerings and Customer Reviews
Evaluating different lenders requires a thorough assessment of their offerings and a review of customer experiences. Begin by comparing interest rates, loan terms, and fees across multiple lenders. Use online comparison tools to streamline this process. Then, delve into customer reviews on platforms like Trustpilot, Yelp, and the Better Business Bureau. Look for consistent patterns in feedback regarding customer service responsiveness, loan processing efficiency, and overall satisfaction. Pay close attention to negative reviews to identify potential red flags. By carefully analyzing both quantitative data (rates, fees) and qualitative data (customer reviews), you can make an informed decision about which lender best suits your needs and financial circumstances. Remember that the lowest interest rate isn’t always the best option; consider the overall package of fees, terms, and customer service quality.
Factors Affecting Eligibility for Refinancing
Securing approval for student loan refinancing hinges on several key factors that lenders carefully assess. Understanding these criteria is crucial for borrowers hoping to achieve lower interest rates and more manageable repayment terms. Meeting these requirements significantly increases your chances of a successful refinance application.
Lenders evaluate applicants based on a combination of financial health and creditworthiness. A strong application demonstrates responsible financial behavior and reduces the lender’s perceived risk. Failing to meet certain criteria can lead to rejection, higher interest rates, or less favorable loan terms.
Credit Score Requirements
Your credit score is a cornerstone of the refinancing process. Lenders use it to gauge your creditworthiness and predict the likelihood of repayment. A higher credit score generally translates to more favorable loan terms, including lower interest rates. Specific minimum credit score requirements vary by lender, but scores above 670 are often preferred for the best rates.
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) represents the proportion of your monthly income dedicated to debt payments. Lenders examine this ratio to determine your capacity to handle additional debt. A lower DTI indicates a greater ability to manage monthly payments, improving your chances of approval. A high DTI may result in rejection or less favorable terms. For example, a DTI of 40% might be acceptable, while a DTI exceeding 50% could raise concerns.
Income and Employment Stability
Consistent income and stable employment are essential for demonstrating your ability to repay the refinanced loan. Lenders prefer applicants with a proven history of stable income and employment. Self-employment or inconsistent income may require more stringent documentation or lead to less favorable loan terms. For instance, a lender may require tax returns or bank statements to verify income for self-employed individuals.
Loan Amount and Type
The type and amount of student loans you wish to refinance also impact eligibility. Lenders may have preferences for specific loan types (e.g., federal vs. private) and minimum loan amounts. Additionally, the total loan amount influences the lender’s risk assessment. Refinancing a smaller loan amount might be easier than refinancing a large sum.
Remaining Loan Balance
The remaining balance on your existing student loans plays a significant role. Lenders typically prefer applicants with a substantial remaining balance to justify the refinancing process. Refinancing a small balance might not be cost-effective for the lender, potentially leading to rejection or less favorable terms.
Understanding Loan Terms and Fees
Refinancing your student loans can offer significant savings, but it’s crucial to understand the associated terms and fees to make an informed decision. Ignoring these details could negate any potential benefits. This section clarifies common loan terms and fees, empowering you to compare offers effectively and choose the best option for your financial situation.
Loan Term Length
The loan term length refers to the period you have to repay your loan. Shorter loan terms typically result in higher monthly payments but lower overall interest paid due to less time accruing interest. Longer terms mean lower monthly payments, but you’ll pay significantly more in interest over the life of the loan. For example, a $50,000 loan refinanced at 6% interest will cost approximately $60,000 over 10 years, while the same loan over 15 years will cost approximately $75,000. Choosing the right term involves balancing affordability with long-term cost savings.
Interest Capitalization
Interest capitalization occurs when accrued interest is added to the principal loan balance. This increases the amount you owe, leading to higher future interest payments. It’s common in federal student loans but may also be a feature of some private refinance loans. For instance, if you defer payments for a period, interest continues to accrue and will be capitalized at the end of the deferment period, increasing your principal balance. Understanding capitalization is essential for accurate budgeting and repayment planning.
Prepayment Penalties
Prepayment penalties are fees charged for paying off your loan early. While uncommon in student loan refinancing, it’s crucial to check the loan agreement. If a prepayment penalty exists, it could offset any savings from refinancing if you anticipate paying off the loan quickly. For example, a penalty of 2% on a $40,000 loan would cost $800 if you paid it off early. Always verify the absence of prepayment penalties before signing a loan agreement.
Examples of Refinancing Fees
Several fees can be associated with student loan refinancing. These include origination fees (a percentage of the loan amount), application fees, and potentially late payment fees. Origination fees are most common and typically range from 0% to 2% of the loan amount. Application fees can be a flat rate or a percentage of the loan amount. Late payment fees are penalties for missed payments. These fees, while seemingly small individually, can accumulate and significantly impact the overall cost of the loan over time. A 1% origination fee on a $30,000 loan would cost $300 upfront.
Strategies for Minimizing Fees
Understanding and implementing strategies to minimize fees is key to maximizing the benefits of refinancing.
- Shop around and compare offers: Different lenders offer varying fees and terms. Comparing multiple offers helps you identify the most cost-effective option.
- Look for lenders with low or no fees: Some lenders advertise no origination fees or application fees, significantly reducing the overall cost.
- Maintain a good credit score: A higher credit score often qualifies you for lower interest rates and potentially lower fees.
- Make on-time payments: Avoiding late payment fees is crucial for keeping your overall costs low.
- Read the loan agreement carefully: Thoroughly review all terms and conditions before signing to avoid unexpected fees.
The Refinancing Process
Refinancing your student loans can significantly impact your monthly payments and overall interest paid. Understanding the process is crucial to securing the best possible terms. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the entire journey, from initial research to final loan disbursement. Careful planning and preparation will greatly increase your chances of a successful refinance.
Pre-Refinancing Preparation
Before you begin the formal application process, several preparatory steps are essential. This includes checking your credit report for accuracy, understanding your current loan details (interest rates, balances, lenders), and researching different refinancing lenders and their offered rates. It’s also wise to determine your desired loan term and payment amount to help you narrow your options. This phase ensures you enter the application process informed and prepared to make sound financial decisions.
Choosing a Lender and Comparing Offers
With your preparation complete, the next step is to choose a lender and compare their offers. Several online lenders specialize in student loan refinancing. Each lender will have different eligibility criteria, interest rates, and loan terms. Carefully compare interest rates, fees, and repayment terms to determine which lender offers the most favorable conditions for your unique financial situation. Consider using a loan comparison tool to streamline this process.
Completing the Application
Once you’ve selected a lender, you’ll need to complete their application. This typically involves providing personal information, employment details, and information about your student loans. Be accurate and thorough in your application to avoid delays. Many lenders offer online applications, simplifying the process. It’s important to review all the information before submitting to ensure accuracy.
Document Submission and Verification
After submitting your application, the lender will verify the information you provided. This may involve requesting supporting documentation, such as tax returns or pay stubs. Providing these documents promptly is crucial for a smooth and efficient process. Delays in document submission can significantly extend the overall refinancing timeline.
Loan Approval and Rate Lock
Following the verification process, the lender will review your application and determine your eligibility for refinancing. If approved, you’ll be offered a specific interest rate and loan terms. Many lenders offer a rate lock, securing your interest rate for a specific period, protecting you from potential rate increases. This is a crucial step in securing favorable terms.
Loan Closing and Disbursement
Upon accepting the loan offer, you’ll proceed with the loan closing process. This may involve e-signing documents or receiving physical documents to sign and return. Once the closing is complete, the lender will disburse the funds, paying off your existing student loans. The timeline for disbursement varies depending on the lender and the complexity of the process. After disbursement, you will begin making payments according to your new loan terms.
Last Point
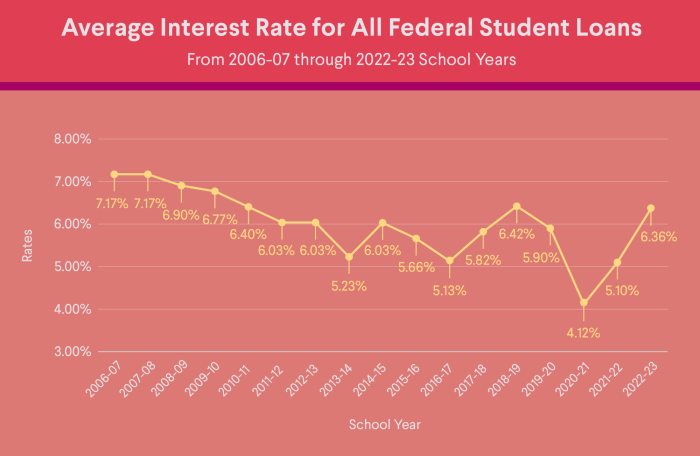
Refinancing your student loans can significantly impact your financial well-being, offering the potential for lower monthly payments and substantial long-term savings. By carefully considering the factors discussed—market trends, credit scores, interest rate types, lender options, and eligibility requirements—you can make an informed decision that aligns with your individual circumstances. Remember to thoroughly research lenders, compare offers, and understand all associated fees before committing to a refinance plan. Taking a proactive approach to this process can lead to substantial financial benefits.
Top FAQs
What is the impact of prepayment on my refinance loan?
Most lenders do not charge prepayment penalties on student loan refinancing, but it’s always best to check your loan agreement. Prepaying can save you money on interest in the long run.
How long does the refinance process typically take?
The entire process, from application to disbursement, usually takes between 4 to 8 weeks, but it can vary depending on the lender and your individual circumstances.
Can I refinance federal and private student loans together?
Some lenders allow refinancing of both federal and private loans, while others only refinance private loans. Check lender eligibility requirements carefully.
What happens if I am denied for a refinance?
If denied, review the reasons provided by the lender. Improving your credit score, reducing your debt-to-income ratio, or waiting until your financial situation improves may increase your chances of approval in the future.
