
Navigating the complex world of student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, especially with the myriad of options and lenders available. This guide aims to simplify the process, helping you understand the nuances of federal versus private loans, various repayment plans, and the crucial factors to consider when refinancing. We’ll explore government programs offering loan forgiveness, provide practical strategies for debt management, and equip you with the knowledge to avoid potential scams.
From understanding income-driven repayment plans to comparing refinancing offers from different lenders, we’ll cover everything you need to make informed decisions about your student loan debt. This comprehensive resource will empower you to take control of your financial future and find the best path towards repayment.
Understanding Student Loan Repayment Options

Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, but understanding the different options available is crucial for managing your debt effectively. This section will clarify the distinctions between federal and private loans and detail the various repayment plans, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Federal vs. Private Student Loans
Federal student loans are offered by the U.S. government and generally offer more borrower protections than private loans. These protections include income-driven repayment plans, loan forgiveness programs, and deferment or forbearance options during times of financial hardship. Private student loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. They typically have less flexible repayment options and fewer borrower protections. Interest rates and terms are determined by the lender’s assessment of the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Student Loan Repayment Plans
Several repayment plans are available for federal student loans, each with its own set of features and implications. Choosing the right plan depends on your individual financial circumstances and long-term goals.
Standard Repayment Plan
This plan involves fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period. It’s a straightforward option, but the monthly payments can be substantial, especially for borrowers with significant loan balances.
Graduated Repayment Plan
This plan starts with lower monthly payments that gradually increase over time. While initially more affordable, the payments become significantly higher in later years.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
These plans (such as ICR, PAYE, REPAYE, andIBR) base your monthly payment on your income and family size. Payments are typically lower than under standard repayment, and any remaining balance may be forgiven after 20 or 25 years, depending on the plan. However, this forgiveness is considered taxable income.
Extended Repayment Plan
This plan allows you to spread your payments over a longer period (up to 25 years), resulting in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid.
Pros and Cons of Repayment Plans
Each repayment plan presents a unique balance of advantages and disadvantages. The optimal choice depends on individual financial situations and long-term objectives. For instance, income-driven plans offer lower monthly payments but may result in a larger total repayment amount due to prolonged interest accrual. Conversely, standard repayment plans involve higher initial payments but lead to faster debt elimination.
Comparison of Repayment Plans
| Plan Name | Monthly Payment Example | Interest Accrual Details | Forgiveness Eligibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Repayment | Varies based on loan amount and interest rate; example: $500 | Interest accrues throughout the repayment period. | No |
| Graduated Repayment | Starts low, increases over time; example: $300-$700 over 10 years | Interest accrues throughout the repayment period. | No |
| Income-Driven Repayment (e.g., PAYE, REPAYE) | Based on income and family size; example: $200-$400 | Interest may accrue depending on payment amount. | Yes, after 20 or 25 years (taxable income) |
| Extended Repayment | Lower than standard; example: $300 over 25 years | Interest accrues over a longer period, resulting in higher total interest paid. | No |
Factors Influencing the “Best” Place to Refinance Student Loans
Choosing the right lender to refinance your student loans can significantly impact your overall repayment experience. Several key factors must be carefully considered to ensure you secure the most advantageous terms and minimize potential risks. This section will explore those crucial factors, helping you make an informed decision.
Interest Rates and Fees
Interest rates are the cornerstone of any loan refinancing decision. Lower interest rates translate directly into lower monthly payments and less overall interest paid over the life of the loan. However, it’s crucial to look beyond the advertised rate. Many lenders charge various fees, such as origination fees, prepayment penalties, or late payment fees. These fees can add up and offset the benefits of a slightly lower interest rate. A thorough comparison of the annual percentage rate (APR), which incorporates these fees, is essential for a true apples-to-apples comparison. For example, a lender advertising a 4% interest rate with a 2% origination fee might end up being more expensive than a lender offering 4.5% with no origination fee.
Eligibility Requirements
Eligibility criteria vary significantly between lenders. These typically involve factors like credit score, credit history, debt-to-income ratio, and the type and amount of student loan debt you possess. Some lenders are more lenient than others, making them potentially suitable for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit. Understanding your own credit profile and the eligibility requirements of different lenders is vital to avoid wasted time applying to lenders you’re unlikely to qualify with. A borrower with a low credit score might need to explore lenders specializing in borrowers with less-than-stellar credit, even if the interest rates might be slightly higher.
Credit Score and Credit History
Your credit score and credit history are paramount in the refinancing process. Lenders use these factors to assess your creditworthiness and determine the interest rate and terms they’ll offer. A higher credit score generally translates to more favorable loan terms, including lower interest rates. Building and maintaining a good credit history through responsible financial practices is therefore crucial before applying for refinancing. A consistent history of on-time payments and responsible credit utilization will significantly improve your chances of securing a better interest rate. Conversely, a poor credit history may limit your options or result in higher interest rates.
Benefits and Risks of Refinancing
Refinancing student loans can offer significant benefits, such as lower monthly payments, a shorter repayment term, or a switch from variable to fixed interest rates. However, refinancing also carries potential risks. You might lose access to federal student loan protections, such as income-driven repayment plans or forbearance options. Additionally, if interest rates rise after refinancing, you might not be able to benefit from lower rates in the future. Careful consideration of your personal financial situation and long-term goals is essential before making a decision. For example, if you anticipate potential job loss or significant financial hardship, the loss of federal protections could be a substantial risk.
Comparison of Lenders
Before choosing a lender, it’s wise to compare offers from at least three different lenders. This allows you to assess the interest rates, fees, eligibility requirements, and customer service provided by each lender. Remember that the “best” lender will depend on your individual circumstances.
- Lender A: May offer highly competitive interest rates for borrowers with excellent credit, but may have stricter eligibility requirements and higher fees for those with less-than-perfect credit. They might also offer a streamlined online application process.
- Lender B: Might have more flexible eligibility criteria, potentially catering to borrowers with lower credit scores. However, they may offer slightly higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk. They may also prioritize personalized customer service over online efficiency.
- Lender C: Could provide a balance between competitive interest rates and flexible eligibility. Their fees might be moderate, and they might offer a variety of loan terms to suit different borrower needs. They may focus on a hybrid approach, combining online tools with responsive customer support.
Government Programs and Loan Forgiveness
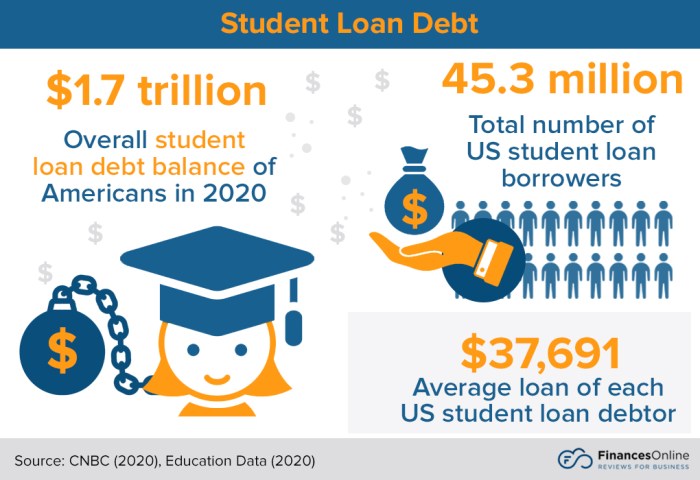
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be daunting, but several government programs offer pathways to loan forgiveness or reduced repayment burdens. Understanding these programs and their eligibility requirements is crucial for borrowers seeking to manage their student loan debt effectively. This section details key federal programs and their implications.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program offers complete forgiveness of remaining federal student loan debt after 120 qualifying monthly payments under an income-driven repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying government or non-profit organization. Eligibility hinges on several factors, including the type of loan, repayment plan, and employer.
Eligibility Criteria: Borrowers must have Direct Loans (not Federal Family Education Loans or Perkins Loans) and be employed full-time by a qualifying government or not-for-profit organization. They must also be enrolled in an income-driven repayment plan. Consistent, on-time payments are critical for maintaining eligibility. Any missed payments could delay or prevent forgiveness.
Application Process: The application process involves verifying employment and loan information through the PSLF Help Tool. Borrowers must submit an Employment Certification form annually to their loan servicer, confirming their qualifying employment. The entire process can take several years to complete, and careful documentation is essential.
Impact on Long-Term Repayment Costs: Successful completion of the PSLF program results in the complete elimination of remaining federal student loan debt, significantly reducing long-term repayment costs. For example, a borrower with $50,000 in remaining debt would save the entire amount after 10 years of qualifying payments. However, it’s crucial to remember that the program requires consistent, qualifying payments over a decade.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program
The Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program offers forgiveness of up to $17,500 in federal student loan debt for teachers who have completed five years of full-time teaching in a low-income school or educational service agency. This program targets educators in underserved communities, aiming to incentivize and support their work.
Eligibility Criteria: Teachers must teach full-time for five consecutive academic years in a low-income school or educational service agency. They must also meet specific loan requirements and have received a direct subsidized or unsubsidized loan. The program has specific requirements about the type of school and the teacher’s role.
Application Process: The application process involves completing a Teacher Loan Forgiveness application and providing documentation of employment and loan information. This includes official transcripts showing teaching experience and verification from the school district confirming low-income status and full-time employment.
Impact on Long-Term Repayment Costs: Successful completion of this program can significantly reduce a teacher’s student loan debt, freeing up financial resources for other needs. For a teacher with $50,000 in loans, the forgiveness of $17,500 represents a substantial reduction in their long-term repayment burden. However, the eligibility requirements necessitate a five-year commitment to teaching in a qualifying environment.
Illustrative Flowchart: Applying for PSLF
The following flowchart Artikels the steps involved in applying for the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program:
[Flowchart Description]: The flowchart would begin with a “Start” box. The next box would be “Confirm Eligibility: Direct Loans, Income-Driven Repayment Plan, Qualifying Employer.” A “Yes” branch would lead to “Make 120 Qualifying Payments.” A “No” branch would lead to “Ineligible.” The “Make 120 Qualifying Payments” box would branch to “Complete and Submit Employment Certification Form Annually.” This would lead to “Submit PSLF Application.” A final box would indicate “Loan Forgiveness.” The entire flowchart would visually represent the sequential steps in the application process.
Managing Student Loan Debt Effectively
Successfully navigating student loan debt requires a proactive and organized approach. Understanding your repayment options, creating a realistic budget, and prioritizing financial literacy are crucial steps towards responsible debt management and ultimately, financial freedom. This section will Artikel practical strategies and resources to help you effectively manage your student loans.
Effective student loan management hinges on a combination of budgeting, financial literacy, and the utilization of available resources. By understanding your income, expenses, and loan repayment terms, you can create a manageable repayment plan and avoid the pitfalls of accumulating unnecessary debt or falling behind on payments. This involves developing responsible borrowing habits from the outset, and continuing to refine your financial strategies as your circumstances evolve.
Budgeting and Managing Student Loan Payments
Creating a detailed budget is essential for incorporating student loan payments into your overall financial plan. A budget allows you to visualize your income and expenses, ensuring you allocate sufficient funds for loan repayments while still meeting your other financial obligations. Failing to budget effectively can lead to missed payments, late fees, and ultimately, a negative impact on your credit score. Tracking your spending habits is a key first step. Consider using budgeting apps or spreadsheets to monitor your income and expenses, and adjust your spending as needed to prioritize your loan payments.
A well-structured budget should clearly Artikel all income sources and expenses, allocating sufficient funds for essential needs and loan repayments. Unexpected expenses should also be factored in, with a contingency fund established to handle these situations without jeopardizing your loan payments.
The Importance of Financial Literacy and Responsible Borrowing Practices
Financial literacy is paramount in managing student loan debt effectively. Understanding interest rates, repayment plans, and the long-term implications of borrowing are crucial for making informed decisions. Responsible borrowing involves carefully considering your financial capacity before taking out loans, and only borrowing the amount you truly need. This includes researching different loan options, comparing interest rates, and understanding the terms and conditions before signing any loan agreements.
Responsible borrowing also entails regularly reviewing your loan statements, actively monitoring your credit score, and seeking professional financial advice when needed. Financial literacy empowers you to make informed decisions about your financial future, minimizing the risks associated with student loan debt.
Resources Available to Students Seeking Help with Managing Student Loan Debt
Numerous resources are available to students seeking assistance with managing their student loan debt. These resources provide valuable information, guidance, and support to help students navigate the complexities of loan repayment. Government agencies, non-profit organizations, and financial institutions offer various programs and services designed to assist students in managing their debt effectively. These may include debt counseling, loan consolidation programs, and income-driven repayment plans.
It’s crucial to utilize these resources proactively to access personalized support and avoid potential pitfalls associated with student loan debt. Don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance; many resources are available at no or low cost.
Sample Budget Incorporating Student Loan Payments
The following sample budget demonstrates how student loan payments can be integrated into a realistic financial plan. Remember that this is a template, and your actual budget will depend on your individual circumstances and income.
This example illustrates a monthly budget. Adjust categories and amounts to reflect your specific financial situation. Remember to account for unexpected expenses with a dedicated contingency fund.
| Category | Allocation |
|---|---|
| Income (Net Pay) | $3000 |
| Student Loan Payment | $500 |
| Rent/Mortgage | $1000 |
| Utilities (Electricity, Water, Gas) | $200 |
| Groceries | $300 |
| Transportation | $200 |
| Healthcare | $100 |
| Savings (Emergency Fund & Other Goals) | $200 |
| Entertainment & Miscellaneous | $500 |
Avoiding Student Loan Scams
Navigating the world of student loans can be complex, and unfortunately, this complexity makes it a fertile ground for scams. Predatory lenders and fraudulent schemes target students and their families, promising unrealistic benefits or employing deceptive tactics to exploit their financial vulnerability. Understanding how these scams operate and how to protect yourself is crucial to securing a financially responsible future.
Scammers often use high-pressure tactics, promising quick loan approvals with minimal documentation or exceptionally low interest rates. They may impersonate legitimate government agencies or well-known lending institutions, creating a sense of urgency to pressure victims into acting before they can verify the information. Other scams involve loan forgiveness programs that don’t exist or require upfront fees for services that are either unnecessary or never delivered.
Common Student Loan Scams and Fraudulent Practices
Several types of student loan scams are prevalent. One common tactic involves unsolicited phone calls, emails, or text messages promising loan forgiveness or debt consolidation. These communications often contain misleading information or outright lies, designed to trick individuals into providing personal financial information. Another common scam involves fake websites or applications that mimic legitimate lenders or government agencies. These fraudulent sites may request sensitive information, such as Social Security numbers and bank account details, which are then used for identity theft or financial fraud. Finally, some scams involve upfront fees for services that are never provided, such as loan application assistance or debt consolidation services. Victims pay for a service that never materializes, leaving them financially worse off.
Warning Signs of Student Loan Scams
Identifying potential scams requires vigilance. Be wary of unsolicited offers promising unusually low interest rates, quick loan approvals without proper verification, or loan forgiveness without meeting the established government criteria. If a lender or servicer demands upfront fees for services that should be included in the loan terms, it’s a significant red flag. Similarly, pressure tactics or requests for personal information through unofficial channels (such as email or text message) should be treated with extreme caution. Always independently verify any information received through these channels using official websites or direct contact with legitimate institutions. If something feels too good to be true, it probably is.
Reporting Suspected Student Loan Scams
If you suspect you’ve encountered a student loan scam, report it immediately to the appropriate authorities. Contact the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to file a complaint. The FTC is the primary agency responsible for investigating and addressing consumer fraud, including student loan scams. You should also report the scam to your state’s attorney general’s office, and if you provided personal information, consider contacting your bank or credit card company to report potential identity theft. Finally, if the scam involved a specific lender or servicer, contact that institution directly to report the incident. Document all communication and transactions related to the suspected scam, including emails, text messages, and financial records. This documentation will be invaluable when filing a report.
Characteristics of Legitimate Student Loan Lenders and Servicers
It’s crucial to be able to differentiate between legitimate and fraudulent entities. Legitimate lenders and servicers will exhibit certain characteristics:
- They will clearly identify themselves and their contact information.
- They will never request personal information through unsolicited emails, text messages, or phone calls.
- They will provide detailed information about loan terms, interest rates, and repayment options.
- They will not require upfront fees for services that are part of the standard loan process.
- They will have a physical address and a verifiable online presence.
- They will be transparent about their fees and charges.
- They will be registered and licensed to operate in your state.
Last Point

Successfully managing student loan debt requires careful planning, understanding of available options, and proactive steps to minimize long-term costs. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of different repayment plans and lenders, utilizing available government programs, and practicing responsible financial habits, you can navigate the complexities of student loan repayment effectively. Remember, seeking professional financial advice can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between federal and private student loans?
Federal loans are offered by the government and typically have more flexible repayment options and protections for borrowers. Private loans are from banks and credit unions, often with higher interest rates and fewer protections.
How can I improve my chances of getting a lower interest rate on refinancing?
A higher credit score and a strong credit history significantly improve your chances of securing a lower interest rate. Also, shop around and compare offers from multiple lenders.
What happens if I miss a student loan payment?
Missing payments can negatively impact your credit score, lead to late fees, and potentially result in loan default, which has serious financial consequences.
Are there any penalties for paying off my student loans early?
Generally, there are no penalties for paying off student loans early, but it’s always best to check your loan agreement to confirm.
