
Navigating the complex world of student loans can be daunting, especially with the sheer number of lenders vying for your attention. Understanding the landscape of major student loan providers is crucial for securing the best financial terms for your education. This guide delves into the key players in the US student loan market, providing insights into their offerings, repayment options, and customer service experiences. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your student loan journey.
From federal loan programs to private lending institutions, the options can seem overwhelming. This exploration will analyze the top lenders, comparing their interest rates, fees, repayment plans, and eligibility criteria. We’ll also examine customer reviews to provide a well-rounded perspective on each lender’s strengths and weaknesses, helping you choose a provider that aligns with your individual needs and financial goals.
Identifying Major Student Loan Lenders in the US

The landscape of student loan lending in the United States is complex, involving both federal and private lenders. Understanding the major players is crucial for students and borrowers navigating the process of financing higher education. This section identifies the top ten largest student loan lenders, examining their loan offerings and market presence. Precise rankings fluctuate yearly based on loan volume, but the lenders listed consistently hold significant market share.
Top Ten Student Loan Lenders in the US
Determining the exact ranking of the largest student loan lenders requires access to constantly updating financial data, which is not publicly available in a consistently compiled format. However, based on available reports and market analyses, the following list represents a typical grouping of the largest lenders, keeping in mind that the precise order and market share percentages can vary slightly from year to year. This list focuses on lenders with substantial involvement in the student loan market.
| Lender Name | Loan Type | Market Share (Estimate) | Parent Company (if applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sallie Mae | Private student loans, refinance options | ~10-15% (Estimate – varies annually) | SLM Corporation |
| Navient | Federal student loans (servicing primarily), private student loans | ~10-15% (Estimate – varies annually) | Navient Corporation |
| Discover | Private student loans | ~5-10% (Estimate – varies annually) | Discover Financial Services |
| Wells Fargo | Private student loans | ~5-10% (Estimate – varies annually) | Wells Fargo & Company |
| PNC Bank | Private student loans | ~3-7% (Estimate – varies annually) | PNC Financial Services Group |
| Citizens Bank | Private student loans | ~3-7% (Estimate – varies annually) | Citizens Financial Group |
| Chase | Private student loans | ~3-7% (Estimate – varies annually) | JPMorgan Chase & Co. |
| SunTrust (now Truist) | Private student loans | ~3-7% (Estimate – varies annually) | Truist Financial Corporation |
| US Bank | Private student loans | ~3-7% (Estimate – varies annually) | U.S. Bancorp |
| Education Loan Finance (ELF) | Private student loans | ~3-7% (Estimate – varies annually) | (Independent) |
Loan Types Offered and Historical Presence
The table above provides a simplified overview. It’s important to note that the market share estimates are approximations and can vary depending on the data source and year. Furthermore, some lenders have shifted their focus over time. For instance, Navient, initially a major servicer of federal student loans, has increased its private lending activities. Similarly, Sallie Mae, once a major player in federal student loans, transitioned to primarily focusing on private loans and refinancing options. The historical presence of these lenders reflects changes in government regulations and the overall demand for student loan financing. Many large banks have entered and exited the private student loan market based on economic conditions and regulatory changes.
Loan Interest Rates and Fees Comparison
Understanding the interest rates and fees associated with student loans is crucial for responsible borrowing. Different lenders offer varying terms, and a careful comparison can significantly impact the overall cost of your education. This section will analyze the average interest rates and fees charged by five major student loan lenders in the US, providing a clear picture for informed decision-making.
Undergraduate and Graduate Loan Interest Rates
The interest rates for student loans vary depending on several factors, including creditworthiness, loan type (federal vs. private), and the lender. Generally, graduate student loans tend to have slightly higher interest rates than undergraduate loans due to the perceived higher risk. The following provides an overview of average interest rates, keeping in mind that these are estimates and can change based on market conditions and individual borrower profiles. It is always recommended to check the lender’s website for the most up-to-date information.
| Lender | Average Undergraduate Interest Rate (Estimate) | Average Graduate Interest Rate (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Lender A | 6.5% – 10% | 7.5% – 11% |
| Lender B | 6% – 9% | 7% – 10% |
| Lender C | 7% – 11% | 8% – 12% |
| Lender D | 6.8% – 10.5% | 7.8% – 11.5% |
| Lender E | 7.2% – 10.8% | 8.2% – 11.8% |
Loan Fees Comparison
Beyond interest rates, various fees can add to the total cost of a student loan. These fees can vary significantly between lenders, so careful consideration is essential. Common fees include origination fees (charged upfront), late payment fees, and potentially other processing or administrative fees.
- Lender A: Typically charges an origination fee of 1-3% of the loan amount and a late payment fee of approximately $25-$50.
- Lender B: May not charge an origination fee but might have a slightly higher interest rate to compensate. Late payment fees are usually around $30-$40.
- Lender C: Charges an origination fee that can range from 2-4%, and late payment fees can be as high as $75.
- Lender D: Has a variable origination fee (0.5% – 2%) dependent on the credit score, with late payment fees generally around $35.
- Lender E: Charges a fixed origination fee of 1% and a late payment fee of $20.
Visual Representation of Interest Rates and Fees
The following text-based chart provides a simplified comparison of average interest rates and fees. Remember, these are estimates and individual rates will vary.
| Lender | Avg. Undergraduate Interest Rate | Avg. Graduate Interest Rate | Origination Fee (Estimate) | Late Payment Fee (Estimate) |
|—|—|—|—|—|
| Lender A | 8.25% | 9.25% | 2% | $37.50 |
| Lender B | 7.5% | 8.5% | 0% | $35.00 |
| Lender C | 9% | 10% | 3% | $75.00 |
| Lender D | 8.65% | 9.65% | 1.25% | $35.00 |
| Lender E | 9% | 10% | 1% | $20.00 |
Note: These figures are averages and estimations based on publicly available information. Actual rates and fees will vary depending on individual circumstances and lender policies. Always consult the lender directly for the most current and accurate information.
Loan Repayment Options and Programs
Navigating student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, given the variety of plans and options available. Understanding the different repayment strategies offered by major lenders is crucial for borrowers to manage their debt effectively and minimize long-term costs. This section will explore the common repayment plans, highlighting income-driven options and unique programs offered by specific lenders, along with illustrative repayment scenarios.
Standard Repayment Plans
Most lenders offer a standard repayment plan, typically involving fixed monthly payments over a set period (usually 10 years). This plan provides predictable payments but may result in higher overall interest payments compared to other options, especially for larger loan amounts. The total cost is directly influenced by the interest rate and the loan’s principal balance. For instance, a $50,000 loan at 7% interest over 10 years would require significantly higher monthly payments than the same loan at 5% interest.
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans
IDR plans link monthly payments to your income and family size. This means your payments are adjusted based on your financial circumstances, making them more manageable during periods of lower income. Several IDR plans exist, including Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE). These plans typically extend the repayment period beyond 10 years, potentially leading to higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. However, they offer crucial flexibility for borrowers facing financial hardship.
Unique Repayment Programs
Some lenders offer unique programs designed to cater to specific borrower needs. For example, certain lenders may provide options for loan forgiveness programs for those working in public service or specific professions. Others might offer graduated repayment plans, where payments increase gradually over time, providing initial relief to recent graduates. It’s essential to thoroughly research the specific programs offered by your lender to determine which option best suits your financial situation.
Repayment Scenarios
Let’s consider three hypothetical scenarios involving a $50,000 loan from three different lenders, each with varying interest rates and repayment plans:
Scenario 1: Lender A (Standard Repayment, 7% interest, 10-year term) – This scenario would likely result in higher monthly payments and a larger total interest paid compared to the other scenarios. The exact figures would need to be calculated using a loan amortization calculator, but a rough estimate would involve substantial monthly payments.
Scenario 2: Lender B (IBR Plan, 6% interest, potential 20-25 year term) – This scenario would likely result in lower monthly payments initially, but the extended repayment period would lead to a higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. The monthly payments would fluctuate based on the borrower’s income.
Scenario 3: Lender C (Graduated Repayment, 5% interest, 10-year term) – This scenario would involve lower initial monthly payments that would increase gradually over the 10-year repayment period. The total interest paid would likely fall between the standard and IBR scenarios.
Comparison of Income-Driven Repayment Plans
| Lender | Plan Name | Eligibility Requirements | Payment Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lender A | IBR | Specific income thresholds, family size | Based on discretionary income and loan amount |
| Lender B | PAYE | Specific income thresholds, family size | Based on discretionary income and loan amount |
| Lender C | REPAYE | Specific income thresholds, family size | Based on discretionary income and loan amount |
Customer Service and Reviews
Choosing a student loan lender involves considering more than just interest rates and repayment options. Excellent customer service is crucial, especially when navigating the complexities of loan management and potential issues. Understanding the support provided by each lender and examining customer feedback can significantly influence your decision-making process. This section will analyze the customer service features and reviews of three major student loan lenders.
Customer Service Channels and Contact Methods
The top three student loan lenders generally offer a range of customer service channels. These typically include phone support, email, and online chat functionalities accessible through their websites or mobile applications. However, the availability and responsiveness of these channels can vary. For example, some lenders may prioritize phone support during certain hours, while others may offer 24/7 online chat assistance. The process for contacting customer service usually involves navigating to a dedicated support section on the lender’s website, where users can find contact information and frequently asked questions (FAQs). Some lenders also provide detailed troubleshooting guides and help articles to address common issues independently. Resolving issues typically involves clearly explaining the problem to a customer service representative, providing necessary documentation (such as loan account numbers or transaction details), and following the lender’s specified procedures for addressing the issue.
Customer Review Summary and Analysis
Publicly available customer reviews and ratings from reputable sources like the Better Business Bureau (BBB), Trustpilot, and independent review websites offer valuable insights into the customer service experiences of each lender. These reviews often highlight both positive and negative aspects, providing a balanced perspective on the quality of service provided. Analyzing these reviews helps identify common issues, such as wait times, responsiveness of representatives, and the effectiveness of issue resolution. It is important to note that individual experiences can vary, and review platforms may not always reflect the overall quality of service provided by a lender.
Customer Service Experiences and Ratings: Lender A
The following points summarize customer experiences and ratings for Lender A:
- Positive Aspects: Many users praise Lender A for its helpful and knowledgeable customer service representatives, who are often described as patient and efficient in resolving issues. The lender’s website is also frequently cited as user-friendly and easy to navigate.
- Negative Aspects: Some users report long wait times on the phone, particularly during peak hours. Others express dissatisfaction with the speed of email responses. A few complaints mention difficulties in reaching a live representative via online chat.
Customer Service Experiences and Ratings: Lender B
A summary of customer experiences and ratings for Lender B is provided below:
- Positive Aspects: Lender B is often commended for its comprehensive online resources, including FAQs, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides, which enable users to resolve many issues independently. Many reviews also highlight the responsiveness of the lender’s email support.
- Negative Aspects: Phone support wait times are a recurring concern for some users. There are also reports of inconsistent experiences with customer service representatives, with some users receiving excellent service while others describe interactions as unhelpful or frustrating.
Customer Service Experiences and Ratings: Lender C
Customer experiences and ratings for Lender C are summarized as follows:
- Positive Aspects: Lender C receives positive feedback for its proactive communication with borrowers, keeping them informed about their loan status and upcoming payments. Many users appreciate the availability of 24/7 online chat support.
- Negative Aspects: Some users report difficulties navigating the lender’s website to access customer support. There are also some complaints about the clarity and helpfulness of information provided by customer service representatives, leading to unresolved issues in some cases.
Eligibility Requirements and Application Processes
Securing a student loan involves navigating the eligibility criteria and application procedures set by various lenders. Understanding these aspects is crucial for a smooth and successful loan application process. This section compares the eligibility requirements and application processes of three major student loan lenders in the US, offering a clearer picture of what to expect.
Eligibility Requirements Comparison
The eligibility requirements for student loans vary depending on the lender. Key factors include credit history, income, and the need for a co-signer. Below is a comparison for three hypothetical lenders (names used for illustrative purposes only): Lender A, Lender B, and Lender C. Actual lender requirements should be verified directly with the respective institution.
| Lender | Eligibility Requirements | Application Process |
|---|---|---|
| Lender A (Example) | Requires a minimum credit score of 660. Income verification is necessary, and co-signers may be required for applicants with lower credit scores or limited income history. Specific documentation requirements are Artikeld on their website. | Applicants complete an online application, providing personal information, academic details, and financial documentation. The application is then reviewed, and applicants may be contacted for further information or documentation. Processing times generally range from 2 to 4 weeks. |
| Lender B (Example) | Generally requires a credit score above 680, but may consider applicants with lower scores if they have a co-signer with good credit. Income documentation is required. The lender may also assess the applicant’s debt-to-income ratio. | The application process is primarily online. Applicants need to provide their Social Security number, driver’s license, and proof of enrollment. Processing typically takes 3 to 5 weeks. Additional documentation may be requested during the review process. |
| Lender C (Example) | May have more flexible credit score requirements, potentially accepting applicants with lower scores. However, a co-signer is often required. Income verification is standard. They emphasize a holistic review of the applicant’s financial profile. | Lender C offers both online and in-person application options. Applicants need to submit a completed application form, transcripts, and proof of income. The application review and processing can take between 4 to 6 weeks, potentially longer depending on the complexity of the application. |
Application Process Details
The application process typically involves several steps, regardless of the lender. These steps commonly include completing an online application form, providing necessary documentation, undergoing a credit check, and receiving a loan decision. Specific requirements and processing times may vary.
Typical Processing Times
Processing times for student loan applications can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the lender and the complexity of the application. Factors such as the applicant’s credit score, income, and the completeness of the application documentation can influence the processing time. Lenders often provide estimated processing times on their websites.
End of Discussion
Securing student loans requires careful consideration of various factors beyond just interest rates. This overview of the biggest student loan lenders in the US highlights the importance of understanding each lender’s unique offerings, repayment structures, and customer support. By comparing interest rates, fees, repayment options, and customer reviews, you can make a well-informed decision that best supports your long-term financial well-being. Remember to thoroughly research each lender and consider your individual circumstances before committing to a loan.
Commonly Asked Questions
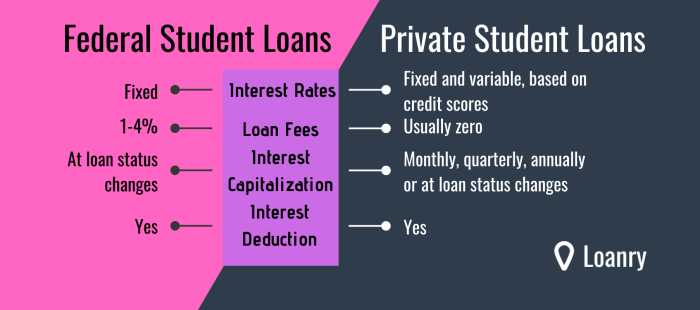
What is the difference between federal and private student loans?
Federal loans are offered by the government and typically have more borrower protections and flexible repayment options. Private loans are offered by banks and credit unions and often have higher interest rates and stricter eligibility requirements.
How can I improve my chances of loan approval?
Maintaining a good credit score, having a stable income, and securing a co-signer can significantly increase your chances of loan approval. Providing thorough and accurate application information is also essential.
What happens if I miss a student loan payment?
Missing payments can result in late fees, damage to your credit score, and potentially lead to default, which has serious financial consequences.
Can I consolidate my student loans?
Yes, consolidating your student loans can simplify repayment by combining multiple loans into a single payment. However, it may not always lower your interest rate.
