Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can feel like traversing a minefield, especially when understanding how interest rates fluctuate. This guide delves into the often-overlooked world of student loan interest rate variability, exploring the factors that influence these rates, how they change over time, and ultimately, how you can effectively manage your debt in the face of these changes. From fixed versus variable rates to the impact of credit scores, we’ll demystify the process and equip you with the knowledge to make informed financial decisions.
Understanding student loan interest rates is crucial for responsible financial planning. This guide will provide a clear and concise overview of the various types of student loans, the factors influencing their interest rates, and how these rates can change throughout the repayment period. We will also explore strategies for managing your debt effectively, even when faced with fluctuating interest rates.
Types of Student Loans and Interest Rates
Understanding the different types of student loans and their associated interest rates is crucial for responsible borrowing and financial planning. The interest rate significantly impacts the total cost of your education, so careful consideration is essential. This section will Artikel the key differences between federal and private student loans, including typical interest rate ranges and calculation methods.
Federal Student Loans and Interest Rates
Federal student loans are offered by the U.S. government and generally offer more favorable terms than private loans. These loans are categorized into several types, each with its own interest rate structure. The interest rate for federal student loans is typically fixed, meaning it remains constant throughout the loan’s life. This provides borrowers with predictability in their monthly payments.
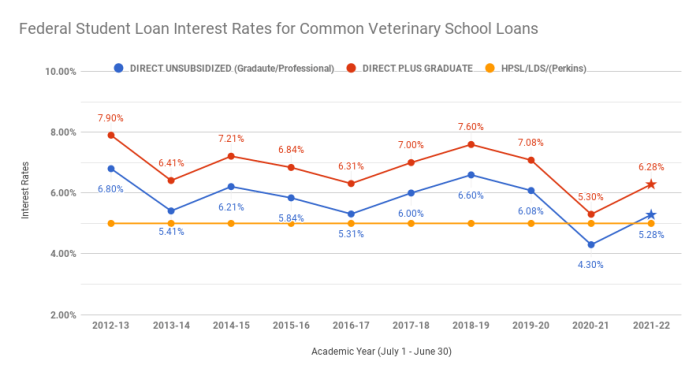
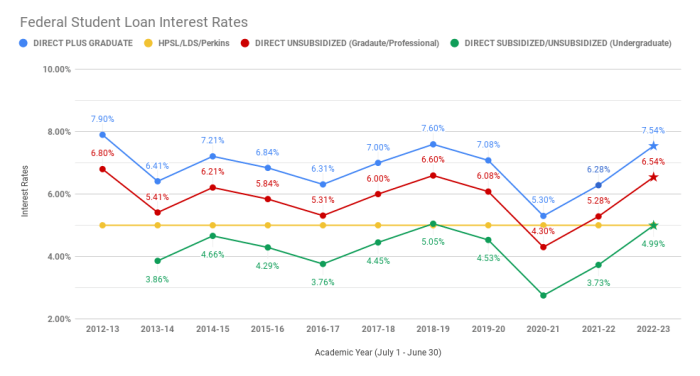
Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans: These loans are awarded based on financial need. The government pays the interest while the borrower is in school at least half-time, during grace periods, and during periods of deferment. Interest rates for these loans are set annually by Congress and are generally lower than unsubsidized loans. For example, the 2023-2024 academic year interest rate was 5.0%.
Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans: These loans are available to students regardless of financial need. Interest begins to accrue immediately, meaning interest is added to the principal balance from the time the loan is disbursed. The interest rate is also set annually by Congress and is usually slightly higher than subsidized loans. For example, the 2023-2024 academic year interest rate was 5.0%.
Federal PLUS Loans: These loans are available to graduate and professional students, as well as parents of undergraduate students. Interest rates are typically higher than Stafford loans. Interest begins to accrue immediately. The 2023-2024 academic year interest rate was 7.5% for graduate PLUS loans and 8.05% for parent PLUS loans.
Interest Calculation Example (Federal Loans): Let’s say a student borrows $10,000 in an unsubsidized Stafford loan with a 5% annual interest rate. If no payments are made during the first year, the interest accrued would be $500 ($10,000 x 0.05). This $500 is added to the principal, resulting in a new balance of $10,500. The next year’s interest will be calculated on this increased amount.
Private Student Loans and Interest Rates
Private student loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. Unlike federal loans, interest rates on private student loans are variable, meaning they can fluctuate over time based on market conditions, or fixed. This makes it more difficult to predict the total cost of the loan. Creditworthiness significantly impacts the interest rate offered; borrowers with strong credit histories typically qualify for lower rates.
Variable Interest Rates: These rates adjust periodically based on an underlying index, such as the prime rate or LIBOR. This can lead to unpredictable monthly payments. For example, a loan might start at 7% but increase to 9% if market interest rates rise.
Fixed Interest Rates: These rates remain constant throughout the loan’s repayment period, offering predictability in monthly payments. However, they may be higher than the initial rate of a comparable variable-rate loan.
Interest Calculation Example (Private Loans): Suppose a student takes out a $10,000 private loan with a 7% fixed annual interest rate. Similar to federal loans, the interest accrued during the first year would be $700 ($10,000 x 0.07). This is added to the principal, leading to a balance of $10,700 for the next year’s interest calculation. With a variable rate, this calculation would change each year based on the fluctuating interest rate.
Comparison of Student Loan Interest Rates
| Loan Type | Interest Rate Type | Typical Interest Rate Range (2023-2024) | Example Interest Calculation (on $10,000) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidized Federal Stafford Loan | Fixed | 5.0% | Year 1: $500 (if no payments) |
| Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loan | Fixed | 5.0% | Year 1: $500 (if no payments) |
| Federal Grad PLUS Loan | Fixed | 7.5% | Year 1: $750 (if no payments) |
| Federal Parent PLUS Loan | Fixed | 8.05% | Year 1: $805 (if no payments) |
| Private Student Loan (Fixed) | Fixed | 6% – 12% (depending on creditworthiness) | Year 1: $600 – $1200 (if no payments) |
| Private Student Loan (Variable) | Variable | 5% – 10% (subject to change) | Year 1: Varies depending on market conditions |
Factors Influencing Student Loan Interest Rates
Several key factors interact to determine the interest rate a student receives on their loan. Understanding these factors can help students make informed decisions about borrowing and repayment. These factors influence the lender’s assessment of risk, directly impacting the interest rate offered.
Credit History
A strong credit history is crucial in securing favorable student loan interest rates. Lenders use credit scores and reports to assess the borrower’s creditworthiness. A higher credit score generally indicates a lower risk of default, leading to a lower interest rate. Conversely, a poor or nonexistent credit history, characterized by missed payments, bankruptcies, or high debt-to-income ratios, often results in higher interest rates or even loan denial. For example, a borrower with a credit score above 750 might qualify for a significantly lower interest rate compared to a borrower with a score below 600. The difference can amount to several percentage points over the life of the loan, leading to substantial savings or increased costs.
Loan Repayment Period
The length of the loan repayment period directly impacts the total interest paid. Longer repayment periods, while resulting in lower monthly payments, ultimately lead to significantly higher overall interest costs. This is because interest accrues over a longer duration. For instance, a 10-year loan will accrue less interest than a 20-year loan with the same principal and interest rate. The longer the repayment period, the more time the borrower has to pay interest on the principal balance.
Examples of Credit Score Impact on Interest Rates
To illustrate the impact of credit scores, consider these hypothetical examples: A borrower with an excellent credit score (780) might receive a federal student loan with a 4.5% interest rate, while a borrower with a fair credit score (680) might receive the same loan with a 6.5% interest rate. A borrower with a poor credit score (below 600) may face significantly higher rates or may even be denied a loan. These examples demonstrate the substantial financial implications of creditworthiness on student loan costs.
Flowchart Illustrating Interest Rate Determination
The following flowchart visually represents the interplay of factors determining student loan interest rates:
[Start] –> [Credit Score Assessment] –> [Credit History Review (including payment history, debt-to-income ratio)] –> [Loan Type Selection (Federal vs. Private)] –> [Repayment Period Selection] –> [Interest Rate Calculation (based on risk assessment)] –> [Loan Approval/Denial] –> [End]
How Interest Rates Change Over Time

Student loan interest rates, whether fixed or variable, can fluctuate, impacting borrowers’ monthly payments and overall loan costs. Understanding these changes is crucial for effective financial planning. This section explores how interest rates on existing student loans can change, the reasons behind these adjustments, and the resulting effects on repayment schedules.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates and Their Behavior
The primary factor determining how a student loan’s interest rate changes over time is whether the loan has a fixed or variable interest rate. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan’s life. This provides predictability and allows borrowers to accurately budget their monthly payments. Conversely, a variable interest rate is tied to an underlying benchmark index, such as the prime rate or LIBOR (though LIBOR is being phased out). This means the interest rate can fluctuate up or down periodically, leading to changes in the monthly payment amount.
Circumstances Leading to Interest Rate Adjustments
For variable-rate loans, the lender adjusts the interest rate based on movements in the benchmark index to which it is tied. For example, if the prime rate increases, the interest rate on a variable-rate student loan will likely increase as well. The frequency of these adjustments varies depending on the loan terms; some loans might adjust monthly, while others might adjust quarterly or annually. It’s important to note that fixed-rate loans are not subject to these adjustments; their interest rate remains unchanged.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Monthly Payments
Changes in interest rates directly affect the monthly payment amount. An increase in the interest rate leads to a higher monthly payment, while a decrease results in a lower payment. Consider this example: A borrower with a $50,000 variable-rate loan at 5% might have a monthly payment of approximately $268. If the interest rate rises to 7%, the monthly payment could increase to roughly $337, a significant difference of almost $70 per month. Conversely, a decrease in the interest rate would result in a lower monthly payment. The exact impact will depend on the loan’s principal, term, and the magnitude of the interest rate change.
Potential Scenarios of Interest Rate Fluctuations
Understanding the potential scenarios of interest rate fluctuations is vital for responsible financial planning.
- Scenario 1: Variable Rate Increase: If the benchmark interest rate rises, the borrower’s monthly payment on a variable-rate loan will increase. This could necessitate adjustments to the borrower’s budget to accommodate the higher payment.
- Scenario 2: Variable Rate Decrease: If the benchmark interest rate falls, the borrower’s monthly payment on a variable-rate loan will decrease. This can provide some financial relief, but it’s important to remember that the total interest paid over the life of the loan may still be higher than with a fixed-rate loan.
- Scenario 3: Fixed Rate Remains Constant: Borrowers with fixed-rate loans will not experience any changes in their monthly payments due to interest rate fluctuations. This predictability offers stability in their repayment plan.
- Scenario 4: Refinancing Opportunity: If interest rates significantly decrease, borrowers with variable-rate loans or even those with fixed-rate loans might consider refinancing to secure a lower interest rate and reduce their monthly payments. However, refinancing involves its own costs and considerations.
Understanding the Loan’s Terms and Conditions
Before you sign on the dotted line for any student loan, meticulously reviewing the loan agreement is paramount. Understanding the terms and conditions, particularly those related to interest rates, is crucial for managing your debt effectively and avoiding unexpected financial burdens. Failing to do so could lead to higher repayment costs and prolonged debt repayment periods.
Understanding the intricacies of your loan agreement empowers you to make informed financial decisions and effectively manage your student loan debt. This section details how to interpret the interest rate information within your loan documents and provides guidance on managing potential interest rate changes.
Interest Rate Information in Loan Agreements
Loan agreements typically include a dedicated section outlining the interest rate applicable to your loan. This section usually specifies the interest rate type (fixed or variable), the annual percentage rate (APR), and any potential for future adjustments. The APR represents the total cost of borrowing, including fees and interest, expressed as a yearly percentage. It’s vital to differentiate between the nominal interest rate (the stated rate) and the APR, as the APR provides a more comprehensive picture of the actual cost of borrowing. Look for clear definitions of these terms within the agreement. Furthermore, the agreement should clearly state how the interest is calculated (e.g., simple interest or compound interest) and when interest capitalization occurs (if applicable). Capitalization is when accrued interest is added to the principal loan amount, increasing the total amount owed.
Interpreting Interest Rate Adjustments
Variable interest rate loans are subject to change over time, typically based on an index rate (such as the prime rate or LIBOR). The loan agreement will Artikel the mechanism for these adjustments, specifying how often the rate can be changed (e.g., annually, semiannually) and the limits on how much the rate can change at any given time. For instance, the agreement might state that the rate can change by a maximum of 1% per year or within a specified range. Understanding these limits is crucial for budgeting and financial planning. Fixed-rate loans, on the other hand, maintain a constant interest rate throughout the loan term, providing greater predictability in repayment costs.
Implications of Interest Rate Changes
Changes in interest rates directly impact your monthly payments and the total amount you pay over the life of the loan. An increase in the interest rate will result in higher monthly payments and a greater total repayment amount. Conversely, a decrease in the interest rate will lower monthly payments and reduce the overall repayment amount. To understand these implications, consider using online student loan calculators that allow you to input different interest rates and loan terms to see how changes affect your repayment schedule and total cost. This proactive approach helps you prepare for potential rate fluctuations and adjust your budget accordingly.
Sample Loan Agreement Excerpt
Interest Rate: The initial interest rate for this loan is 6.5% per annum, fixed for the first five years. After the initial five-year period, the interest rate will become variable and will be adjusted annually based on the one-year Treasury Bill rate plus 2.5 percentage points. The rate will not exceed 10% per annum. The interest rate will be reviewed and adjusted on the anniversary date of the loan origination. The lender will provide written notice of any interest rate changes at least 30 days prior to the effective date of the change.
Managing Student Loan Debt with Changing Interest Rates
Navigating the fluctuating landscape of student loan interest rates requires a proactive approach to minimize financial strain. Understanding various strategies and implementing effective budgeting techniques can significantly impact your ability to manage and ultimately pay off your debt. This section will explore practical methods to mitigate the effects of interest rate changes and achieve financial stability.
Strategies for Minimizing the Impact of Interest Rate Changes
Effective management of student loan debt in the face of fluctuating interest rates hinges on a multi-pronged strategy. Prioritizing higher-interest loans for extra payments is a crucial step. This approach maximizes savings by focusing on the debts accumulating interest most rapidly. Another important strategy is to maintain consistent, on-time payments, even if the payment amount remains the same. This demonstrates responsible borrowing and can positively impact your credit score, potentially opening doors to better refinancing options down the line. Regularly reviewing your loan terms and exploring available options, such as refinancing or income-driven repayment plans, is also vital to ensuring you’re utilizing the most beneficial repayment strategies available.
Benefits of Making Extra Payments to Reduce Principal
Making extra payments on your student loans, even small ones, offers substantial long-term benefits. Each extra payment directly reduces the principal balance, thus lowering the overall amount of interest accrued over the life of the loan. This translates to significant savings. For example, consider a $30,000 loan with a 6% interest rate over 10 years. Making an extra $100 payment each month would shorten the repayment period and reduce the total interest paid by approximately $3,000. This simple strategy can dramatically accelerate debt reduction and lead to substantial financial savings.
Budgeting Techniques to Manage Loan Payments Effectively
Creating a detailed budget is fundamental to effective student loan management. Begin by tracking all income and expenses to identify areas for potential savings. Categorize your expenses – necessities, wants, and debt payments – to clearly visualize your financial picture. Allocate a specific amount each month towards your student loan payments, treating it as a non-negotiable expense. Consider utilizing budgeting apps or spreadsheets to automate tracking and facilitate efficient financial management. For example, allocating a portion of any unexpected income, such as a bonus or tax refund, directly to loan payments can expedite debt repayment.
Refinancing to Potentially Lower Interest Rates
Refinancing your student loans can be a powerful tool for lowering your interest rate, particularly if rates have fallen since you initially took out your loans. This involves consolidating multiple loans into a single loan with a new lender offering a lower interest rate. However, it’s crucial to carefully compare offers from different lenders to secure the most favorable terms. Factors such as credit score, loan amount, and repayment term all influence the interest rate offered. For instance, someone with an excellent credit score might qualify for a significantly lower interest rate compared to someone with a lower score. Before refinancing, carefully evaluate all fees and terms to ensure the overall cost savings outweigh any associated expenses.
Resources for Understanding Interest Rate Changes

Navigating the complexities of student loan interest rates requires access to reliable information. Understanding where to find accurate and up-to-date data is crucial for making informed decisions about your loan repayment strategy. This section Artikels key resources and provides guidance on evaluating the credibility of information sources.
Reputable sources provide crucial information regarding student loan interest rates, enabling borrowers to make informed decisions and manage their debt effectively. Government websites offer official data and guidelines, while financial institutions provide details on specific loan programs. Critically evaluating online information ensures accuracy and protects against misinformation.
Government Websites as Information Sources
Government websites, particularly those of the Department of Education, are primary sources for accurate information on federal student loan interest rates. These sites typically provide details on current interest rates for various federal loan programs, including subsidized and unsubsidized loans, as well as loan consolidation options. They also often include information on how interest rates are determined, and may offer tools and calculators to help estimate repayment costs under different scenarios. For example, the Federal Student Aid website (studentaid.gov) is an excellent resource for understanding the nuances of federal student loan interest rates. This website provides detailed information on current rates, rate changes over time, and repayment options.
Information from Financial Institutions
Private lenders, such as banks and credit unions, also offer student loans. Their websites usually provide information about the interest rates they offer, as well as the terms and conditions of their loans. This information often varies depending on the borrower’s creditworthiness and other factors. It’s important to compare interest rates from multiple lenders to find the most favorable option. However, always be aware that the information presented on these websites reflects the lender’s specific offerings and may not represent the overall market.
Evaluating the Credibility of Online Information
The internet offers a vast amount of information, but not all of it is accurate or reliable. When researching student loan interest rates online, it is essential to evaluate the credibility of the source. Look for websites affiliated with reputable organizations, government agencies, or well-established financial institutions. Check the website’s “About Us” section to learn more about its mission and authority. Be wary of websites with biased information or those promoting specific products without clearly disclosing any potential conflicts of interest. Always cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Look for evidence of fact-checking or citations supporting the information presented.
Helpful Websites and Organizations
The following table lists some helpful websites and organizations that provide information on student loan interest rates:
| Website/Organization | Description |
|---|---|
| studentaid.gov | The official website of the U.S. Department of Education’s Federal Student Aid office, providing comprehensive information on federal student loans. |
| Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) | Offers resources and tools to help consumers understand and manage their finances, including student loans. |
| National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC) | A non-profit organization that provides financial education and counseling services, including assistance with managing student loan debt. |
| Your Lender’s Website | Check your specific lender’s website for information about your loan terms, including interest rates and repayment options. |
Concluding Remarks
Successfully managing student loan debt requires a proactive and informed approach. By understanding the intricacies of interest rate fluctuations, the various loan types, and the strategies available for minimizing their impact, borrowers can navigate the repayment process with greater confidence and financial security. Remember to always review your loan documents carefully, utilize available resources, and consider seeking professional financial advice if needed. Taking control of your student loan debt empowers you to build a brighter financial future.
Helpful Answers
What happens if I refinance my student loans?
Refinancing can potentially lower your interest rate, resulting in lower monthly payments and reduced overall interest paid. However, it’s important to carefully compare offers and understand the terms before refinancing.
Can I pay off my student loans faster?
Yes, making extra payments towards your principal balance can significantly reduce the total interest paid and shorten your repayment period. Even small extra payments can make a substantial difference over time.
Where can I find trustworthy information about student loan interest rates?
Reliable sources include the Federal Student Aid website (for federal loans), your loan servicer’s website, and reputable financial institutions. Always be wary of information from unknown or unverified sources.
What is the difference between a fixed and variable interest rate?
A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term, while a variable interest rate can fluctuate based on market conditions. Fixed rates offer predictability, while variable rates could potentially result in lower initial payments but higher payments later on.
