
Navigating the complexities of student loan debt can feel overwhelming, but understanding your options is the first step towards financial freedom. Refinancing your student loans, specifically through a citizen student loan refinance program, offers a potential path to lower monthly payments and reduced overall interest costs. This guide delves into the intricacies of this process, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your financial future.
We’ll explore the mechanics of refinancing, eligibility requirements, and the key factors to consider when comparing lenders. We’ll also analyze the potential benefits and drawbacks, providing real-world examples to illustrate the impact of refinancing on various financial situations. By the end, you’ll possess a clearer understanding of whether refinancing is the right choice for you and how to proceed confidently.
Understanding Citizen Student Loan Refinancing
Refinancing your student loans with Citizen One can potentially save you money by lowering your interest rate and simplifying your monthly payments. This process involves replacing your existing federal or private student loans with a new loan from a private lender, Citizen One in this case. Understanding the mechanics, eligibility, and comparison with other lenders is crucial before making a decision.
Citizen Student Loan Refinancing Mechanics
Citizen One’s refinancing process involves applying online, providing necessary documentation (such as income verification and student loan details), and undergoing a credit check. Once approved, your new loan from Citizen One will pay off your existing student loans, and you’ll begin making payments on the new, refinanced loan. The key benefit is the potential for a lower interest rate, resulting in lower monthly payments and reduced overall interest paid over the life of the loan. This is particularly advantageous for borrowers with good credit scores. The process typically takes several weeks, depending on the volume of applications and the speed of documentation verification.
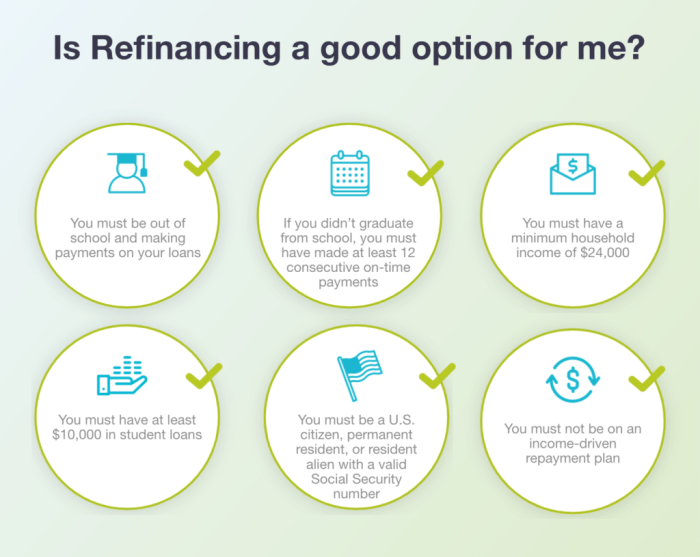
Citizen Student Loan Refinancing Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for Citizen One’s student loan refinancing program, borrowers generally need to meet several criteria. These typically include having a good credit score (often above 660), a stable income, and a minimum amount of student loan debt. Specific requirements regarding the type of loans that can be refinanced (federal, private, or a combination) and the minimum loan amount may vary. Co-signers may be required for borrowers with lower credit scores or less stable income. It’s essential to review Citizen One’s specific eligibility requirements on their website before applying.
Comparison of Citizen Student Loan Refinancing Lenders
Several lenders offer student loan refinancing options. Comparing Citizen One to other major lenders requires considering several factors, including interest rates, fees, repayment terms, and customer service. While specific rates and fees fluctuate based on market conditions and individual borrower profiles, a general comparison can help inform your decision. It’s crucial to compare offers from multiple lenders before making a final choice. Consider factors such as loan term options, the availability of various repayment plans, and any potential penalties for early repayment.
Applying for Citizen Student Loan Refinancing: A Step-by-Step Guide
The application process for Citizen One student loan refinancing is generally straightforward. First, you’ll need to gather your necessary documents, including proof of income, student loan details, and personal identification. Next, you’ll complete the online application, providing accurate and complete information. Citizen One will then review your application and conduct a credit check. If approved, you’ll receive a loan offer outlining the terms and conditions. After reviewing and accepting the offer, you’ll need to sign the loan documents electronically. Finally, Citizen One will disburse the funds to pay off your existing loans, and you’ll begin making payments on your refinanced loan.
Comparison of Student Loan Refinancing Lenders
The following table provides a sample comparison of interest rates, fees, and repayment terms from three major lenders. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual rates and terms may vary depending on individual circumstances and market conditions. Always check the lender’s website for the most up-to-date information.
| Lender | Interest Rate (Example) | Fees (Example) | Repayment Terms (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citizen One | 6.5% – 15% (Variable) | Origination Fee (Variable) | 5-15 years |
| Lender B | 7% – 16% (Variable) | Origination Fee (Variable) | 5-20 years |
| Lender C | 6% – 14% (Fixed/Variable) | No Origination Fee (Potential Other Fees) | 7-10 years |
Benefits and Drawbacks of Refinancing
Refinancing your student loans can be a complex decision with significant long-term financial implications. Understanding the potential advantages and disadvantages is crucial before proceeding. While refinancing can offer substantial savings, it’s essential to weigh these benefits against the risks involved. This section will explore both sides of the coin, providing you with a clearer picture to inform your decision.
Potential Benefits of Refinancing Citizen Student Loans
Refinancing your student loans with a private lender like Citizen One can offer several key advantages. Primarily, many borrowers secure lower interest rates compared to their federal loans. This translates to lower monthly payments and significant savings over the life of the loan. Furthermore, refinancing can simplify your repayment process by consolidating multiple loans into a single, manageable payment. This streamlined approach can make budgeting easier and reduce the administrative burden of managing several different loan accounts. The potential for a shorter repayment term is another benefit, allowing for quicker debt elimination.
Potential Drawbacks of Refinancing Citizen Student Loans
While refinancing offers attractive benefits, it’s vital to consider the potential downsides. The most significant drawback is the loss of federal student loan protections. Federal loans often come with benefits such as income-driven repayment plans, deferment options, and forgiveness programs for specific professions. These protections are typically lost upon refinancing with a private lender. Additionally, interest rates on private loans can fluctuate, and if rates rise after refinancing, your monthly payments could increase unexpectedly. It’s also important to note that if you have multiple loans with different interest rates, refinancing might not always result in a lower overall interest rate, especially if the new rate is close to the weighted average of your existing rates.
Long-Term Financial Implications of Refinancing
The long-term financial impact of refinancing depends heavily on individual circumstances and market conditions. A lower interest rate will generally lead to substantial savings over the loan’s lifetime. However, the loss of federal protections could prove costly in unforeseen circumstances, such as job loss or unexpected medical expenses. Careful consideration should be given to your personal financial stability and risk tolerance before deciding to refinance. For example, a borrower with a stable income and a low risk tolerance might benefit more from keeping their federal loans, even with slightly higher interest rates, to retain the safety net of federal protections. Conversely, a borrower with a high income and a higher risk tolerance might find that the savings from a lower interest rate outweigh the risk of losing federal protections.
Real-World Examples of Refinancing Outcomes
One individual, let’s call him John, successfully refinanced his student loans with Citizen One, reducing his interest rate by 2% and saving approximately $10,000 over the life of his loan. He had a stable job and felt confident in his ability to manage his payments. Conversely, Sarah, who experienced a job loss shortly after refinancing, struggled to make her payments and regretted losing access to federal income-driven repayment plans. Her situation highlights the importance of considering potential risks.
Pros and Cons of Refinancing Citizen Student Loans
Before making a decision, it’s helpful to summarize the key advantages and disadvantages:
- Pros: Lower interest rates, simplified repayment, potentially shorter repayment term, lower monthly payments.
- Cons: Loss of federal student loan protections, potential for higher interest rates if rates rise, increased risk if unexpected financial hardship occurs.
Factors Influencing Refinancing Decisions
Refinancing your student loans can be a smart financial move, but it’s crucial to carefully consider several factors before making a decision. The right choice depends on your individual financial circumstances and goals. Understanding these influencing factors will help you determine if refinancing is the best option for you.
Credit Score’s Influence on Refinancing
Your credit score significantly impacts your eligibility for refinancing and the interest rate you’ll receive. Lenders use credit scores to assess your creditworthiness – essentially, how likely you are to repay the loan. A higher credit score generally translates to better loan terms, including lower interest rates and potentially more favorable repayment options. For example, a borrower with a credit score above 750 might qualify for a significantly lower interest rate compared to someone with a score below 670. Conversely, a low credit score may result in rejection of your application or significantly higher interest rates, potentially negating the benefits of refinancing.
Debt Amount and Income’s Role in Refinancing
The amount of student loan debt you have and your income are key factors in determining your eligibility and the terms of your refinanced loan. Lenders assess your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), which compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. A lower DTI generally indicates a lower risk to the lender, leading to better loan offers. For instance, someone with a high income and relatively low student loan debt will likely have a favorable DTI, making them a more attractive candidate for refinancing. Conversely, a high DTI might make it difficult to secure a loan or result in less attractive terms.
The Impact of Co-signers on Refinancing Eligibility
A co-signer can significantly improve your chances of approval, especially if your credit history is limited or less than ideal. A co-signer essentially agrees to share responsibility for the loan repayment. Their strong credit history can offset a weaker credit history of the primary borrower. However, it’s important to remember that co-signing involves significant risk for the co-signer, as they become legally responsible for the debt if the primary borrower defaults.
Comparing Loan Offers from Different Lenders
Before committing to a refinancing loan, it’s crucial to compare offers from multiple lenders. This allows you to identify the most favorable terms, including interest rates, fees, and repayment options. Factors to compare include the annual percentage rate (APR), which includes interest and fees; the loan term (length of repayment); and any prepayment penalties. Using online comparison tools can simplify this process, but it’s also essential to carefully review the terms and conditions of each offer before making a decision. For example, a lender might offer a lower interest rate but charge higher fees, resulting in a higher overall cost.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Refinancing
A flowchart visualizing the decision-making process might look like this:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a “Start” box, followed by a decision box asking “Do you have significant student loan debt?”. A “Yes” branch would lead to another decision box asking “Is your credit score good (e.g., above 700)?”. A “Yes” branch would lead to a box instructing “Compare loan offers from multiple lenders”. A “No” branch would lead to a box asking “Do you have a co-signer with good credit?”. A “Yes” branch would again lead to “Compare loan offers from multiple lenders”. A “No” branch would lead to a box saying “Consider alternative debt management strategies”. All paths eventually lead to an “End” box.]
Protecting Yourself During Refinancing

Refinancing your student loans can offer significant savings, but it’s crucial to approach the process cautiously to avoid potential pitfalls. Understanding how to choose a reputable lender, negotiate favorable terms, and avoid predatory practices is key to ensuring a positive outcome. This section provides guidance on protecting yourself throughout the refinancing journey.
Selecting a Reputable Lender
Choosing the right lender is paramount. Consider lenders’ accreditation, customer reviews, interest rates, and fees. Look for lenders with a history of fair lending practices and transparent terms and conditions. Checking with the Better Business Bureau (BBB) or similar organizations can help you assess a lender’s reputation. Compare offers from multiple lenders to ensure you’re getting the best possible terms. Avoid lenders who pressure you into making quick decisions or who have unclear or hidden fees. A reputable lender will provide clear and concise information about their loan products and the refinancing process.
Negotiating Favorable Terms
Once you’ve identified a few reputable lenders, you can begin negotiating. While interest rates are often fixed, you may have some leverage in negotiating fees or other loan terms. For example, you might be able to negotiate a lower origination fee or a shorter repayment term (though this will increase your monthly payments). Strong credit scores and a history of on-time payments significantly improve your negotiating power. Presenting multiple offers from competing lenders can also strengthen your position. Remember to clearly articulate your needs and financial goals during negotiations.
Reading the Fine Print of Loan Agreements
Before signing any loan agreement, meticulously review every detail. Pay close attention to the interest rate (both fixed and variable), fees (origination, late payment, prepayment), repayment terms, and any potential penalties. Understand the implications of different repayment plans and how they will affect your monthly payments and total interest paid. Don’t hesitate to ask questions if anything is unclear. A thorough understanding of the loan agreement protects you from unexpected costs or penalties.
Avoiding Predatory Lending Practices
Predatory lenders often target borrowers with poor credit or those who are financially vulnerable. Be wary of lenders who offer extremely low interest rates with hidden fees or high prepayment penalties. Avoid lenders who pressure you into making decisions quickly or who don’t clearly explain the terms of the loan. If a deal seems too good to be true, it probably is. Legitimate lenders will be transparent and upfront about all fees and charges. Researching and comparing multiple lenders are essential steps in avoiding predatory lending.
Refinancing Checklist
Before you begin: Check your credit score, gather your financial documents (tax returns, pay stubs), and research different lenders. During the process: Compare loan offers carefully, ask questions, and read all documents thoroughly. After refinancing: Confirm the new loan terms are accurately reflected in your account and monitor your payments regularly. A systematic approach ensures a smoother and safer refinancing experience.
Alternatives to Refinancing

Refinancing your student loans isn’t always the best option. Several alternatives exist, offering different approaches to managing your debt and potentially leading to lower overall costs depending on your individual circumstances. These alternatives often involve government programs designed to make repayment more manageable. Understanding these options allows for a more informed decision about your student loan strategy.
Before considering refinancing, exploring government-backed repayment plans and potential loan forgiveness programs is crucial. These programs offer varying levels of assistance based on income, employment, and loan type. Direct comparison between refinancing and these alternatives requires careful consideration of long-term costs, eligibility, and potential benefits.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-driven repayment (IDR) plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. Several plans exist, including the Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR), and Pay As You Earn (PAYE) plans. These plans typically extend the repayment period, reducing monthly payments but potentially increasing the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Eligibility generally requires federal student loans and involves completing an application process through the federal student aid website. For example, a borrower earning $40,000 annually with $50,000 in federal student loans might see their monthly payments significantly reduced under an IDR plan compared to a standard repayment schedule, although they’ll pay more interest over time.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
Several loan forgiveness programs exist, primarily targeting borrowers in public service or specific professions. These programs may forgive a portion or all of your remaining loan balance after meeting specific requirements, such as working for a qualifying employer for a set number of years. Eligibility criteria vary widely depending on the program. For instance, the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program forgives the remaining balance of federal student loans after 120 qualifying monthly payments while working full-time for a qualifying government or non-profit organization. However, strict adherence to program guidelines is crucial; any deviation could jeopardize forgiveness.
Comparison of Refinancing and Alternatives
Refinancing offers lower monthly payments and potentially a shorter repayment term, but it often comes with a higher interest rate and the loss of federal protections. IDR plans and loan forgiveness programs maintain federal protections but may result in higher total interest paid over a longer repayment period. The best option depends on your individual financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals.
Scenarios Where Refinancing Might Not Be Ideal
Refinancing might not be beneficial if you have federal student loans and qualify for an IDR plan or loan forgiveness program. The potential benefits of lower monthly payments from refinancing may be outweighed by the loss of federal protections and the increased total cost due to higher interest rates. For example, a borrower with substantial federal student loan debt and a plan to pursue public service employment might find loan forgiveness more advantageous than refinancing.
Calculating Total Repayment Costs
Calculating the total cost under different scenarios requires careful consideration of interest rates, loan amounts, repayment periods, and any additional fees. A simple calculation involves determining the total interest paid over the life of the loan under each scenario. For example:
Scenario 1 (Refinancing): $50,000 loan at 6% interest over 10 years. Total interest paid: approximately $12,000. Total cost: $62,000.
Scenario 2 (IDR Plan): $50,000 loan at 4% interest over 25 years. Total interest paid: approximately $20,000. Total cost: $70,000.
This simplified example illustrates how a lower interest rate from refinancing can be offset by a longer repayment period under an IDR plan, leading to a higher total cost despite lower monthly payments. More complex calculations may be needed to account for varying interest rates, fees, and income-based adjustments. Online loan calculators can assist in this process.
Concluding Remarks
Refinancing citizen student loans presents a significant financial decision requiring careful consideration. By weighing the potential benefits of lower interest rates and simplified repayment against the risks of losing federal protections and the impact of fluctuating interest rates, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your individual circumstances. Remember to thoroughly research lenders, compare offers, and understand the terms of any loan agreement before proceeding. Empowering yourself with knowledge is the key to navigating this process successfully and achieving your long-term financial goals.
FAQ Resource
What is the impact of a late payment on my refinance application?
Late payments negatively affect your credit score, potentially lowering your chances of approval or resulting in higher interest rates.
Can I refinance private and federal loans together?
Some lenders allow refinancing of both federal and private loans, but others only refinance private loans. Check lender specifics.
What happens if interest rates rise after I refinance?
Your interest rate will be fixed, protecting you from increases. However, if you had chosen a variable rate loan, your payments could increase.
How long does the refinance process typically take?
The process usually takes several weeks, depending on lender processing times and the complexity of your application.
