
Securing a Sallie Mae student loan hinges significantly on your credit score. Understanding its impact is crucial for navigating the loan application process and securing favorable terms. This guide explores the intricate relationship between your creditworthiness and obtaining a Sallie Mae loan, offering insights into improving your score, managing your loan effectively, and planning for long-term financial success.
From understanding how your credit score influences interest rates and loan approval to strategies for improving your score before applying, we’ll cover all the essential aspects. We’ll also delve into managing your loan repayments, exploring options like refinancing to potentially lower your interest rates, and addressing the importance of maintaining a positive credit history.
Sallie Mae Loan Basics
Sallie Mae, a well-known private student loan provider, offers various loan options to help students finance their education. Understanding the different loan types, interest rates, and repayment plans is crucial for making informed borrowing decisions. This section provides a foundational overview of Sallie Mae student loans.
Sallie Mae Loan Types and Features
Sallie Mae offers several types of student loans, each with its own set of features and eligibility requirements. These loans generally fall under two main categories: federal and private. While Sallie Mae’s private loans are the focus here, it’s important to remember that federal student loans often offer more favorable terms and borrower protections.
Private Student Loans
Sallie Mae’s private student loans are designed to supplement federal loans or cover educational expenses not met by federal aid. These loans typically require a creditworthy co-signer, especially for undergraduate students. The interest rates are variable, meaning they can fluctuate over the life of the loan, and are generally higher than federal loan interest rates. Loan amounts vary depending on individual creditworthiness and the cost of attendance. Sallie Mae offers both undergraduate and graduate private student loans. Specific features may vary depending on the loan product.
Interest Rates and Repayment Options
Sallie Mae’s interest rates on private student loans are variable and depend on several factors, including the borrower’s creditworthiness, co-signer’s credit (if applicable), loan term, and the prevailing market interest rates. It is essential to review the loan terms carefully to understand the exact interest rate and fees associated with the loan. Repayment options typically include standard repayment plans (fixed monthly payments over a set period), graduated repayment plans (payments increase over time), and extended repayment plans (longer repayment terms, leading to lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid). Borrowers can often choose a repayment plan that best suits their financial situation. For example, a standard 10-year repayment plan will have higher monthly payments but less interest paid overall compared to a 20-year plan.
Applying for a Sallie Mae Loan
Applying for a Sallie Mae loan involves a straightforward process.
- Check Eligibility: Before applying, assess your eligibility based on Sallie Mae’s requirements. This typically includes factors such as credit history, income, and enrollment status.
- Gather Necessary Documents: Collect required documentation, including proof of enrollment, financial aid award letters, and personal identification.
- Complete the Application: Fill out the online application form accurately and completely. This will typically require providing personal information, educational details, and financial information.
- Submit Supporting Documents: Upload or submit the necessary supporting documents as requested by Sallie Mae.
- Review and Accept Loan Offer: Once your application is processed, review the loan offer carefully, including the interest rate, repayment terms, and fees. If you agree to the terms, accept the loan offer.
- Loan Disbursement: After acceptance, the loan proceeds will be disbursed according to the terms Artikeld in your loan agreement. This may be directly to the educational institution or to the borrower.
Credit Score Impact on Sallie Mae Loans
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining your eligibility for a Sallie Mae loan and the terms you’ll receive. A higher credit score generally translates to better loan options, while a lower score can limit your choices and increase the cost of borrowing. Understanding this relationship is crucial for securing the most favorable loan terms possible.
Sallie Mae, like most lenders, uses credit scores to assess the risk involved in lending you money. A strong credit history indicates a higher likelihood of repayment, making you a less risky borrower. Conversely, a weak credit history suggests a greater risk of default, leading to less favorable loan terms or even loan denial. This risk assessment directly impacts both your approval chances and the interest rate you’ll be offered.
Interest Rate Variations Based on Credit Score
Lenders typically categorize borrowers into different credit tiers based on their FICO scores (a widely used credit scoring model). Borrowers with excellent credit scores (generally 750 and above) often qualify for the lowest interest rates. Those with good credit (around 670-749) will likely receive higher rates, and borrowers with fair or poor credit (below 670) may face significantly higher interest rates or even be denied a loan altogether. The exact interest rate offered will depend on various factors beyond your credit score, including the loan amount, loan type, and prevailing market interest rates. However, a higher credit score consistently acts as a strong predictor of a lower interest rate.
Examples of Improved Loan Terms with Higher Credit Scores
Let’s consider two hypothetical borrowers applying for a $10,000 Sallie Mae loan. Borrower A has an excellent credit score of 780, while Borrower B has a fair credit score of 620. Borrower A might qualify for a fixed interest rate of 5%, resulting in significantly lower monthly payments and less interest paid over the life of the loan compared to Borrower B, who might receive a rate of 10% or even be denied the loan entirely. This substantial difference in interest rates highlights the significant financial advantage of maintaining a strong credit score before applying for a Sallie Mae loan. In this scenario, Borrower A could save thousands of dollars in interest payments over the loan’s duration. This difference underscores the importance of proactively managing your credit health.
Improving Credit Score Before Applying

A strong credit score can significantly impact your Sallie Mae loan application, potentially leading to better interest rates and loan terms. Improving your credit score before applying is a proactive step that can save you money in the long run. By strategically managing your debt and credit utilization, you can demonstrate financial responsibility and increase your chances of loan approval on favorable terms.
Improving your credit score takes time and consistent effort, but the rewards are substantial. The following strategies offer a structured approach to enhancing your creditworthiness before applying for a Sallie Mae student loan.
Debt Reduction Strategies
Effectively managing existing debt is crucial for improving your credit score. High levels of debt negatively impact your credit utilization ratio, a key factor in credit scoring models. Prioritizing high-interest debt, such as credit card balances, is often the most effective approach. Consider strategies like the debt snowball or debt avalanche methods to systematically pay down your debts. The debt snowball method involves paying off the smallest debt first for motivational purposes, while the debt avalanche method focuses on paying off the debt with the highest interest rate first to minimize overall interest paid. Both methods require discipline and commitment to consistent repayment. Creating a realistic budget and allocating funds specifically for debt repayment is essential for success.
Credit Utilization Improvement
Credit utilization refers to the percentage of your available credit that you’re currently using. Keeping your credit utilization low (ideally below 30%) is vital for a healthy credit score. This demonstrates responsible credit management. To lower your credit utilization, you can pay down existing balances on your credit cards and avoid maxing them out. Consider increasing your credit limits if you have a long history of responsible credit use. This will lower your credit utilization percentage without changing your debt levels. However, remember that increasing your credit limit doesn’t magically improve your score; responsible spending habits are still key.
Common Credit Score Damaging Mistakes
Several common mistakes can negatively affect your credit score. These include consistently late or missed payments on loans or credit cards. Even one missed payment can significantly impact your score. Applying for multiple lines of credit in a short period can also lower your score, as it suggests increased risk to lenders. Additionally, closing old credit accounts, especially those with a long history of responsible payments, can reduce your credit history length, which can negatively affect your score. Finally, inaccurate information on your credit report can also lead to a lower score. Regularly reviewing your credit report and disputing any errors is crucial to maintaining an accurate credit history.
Managing Loans After Approval
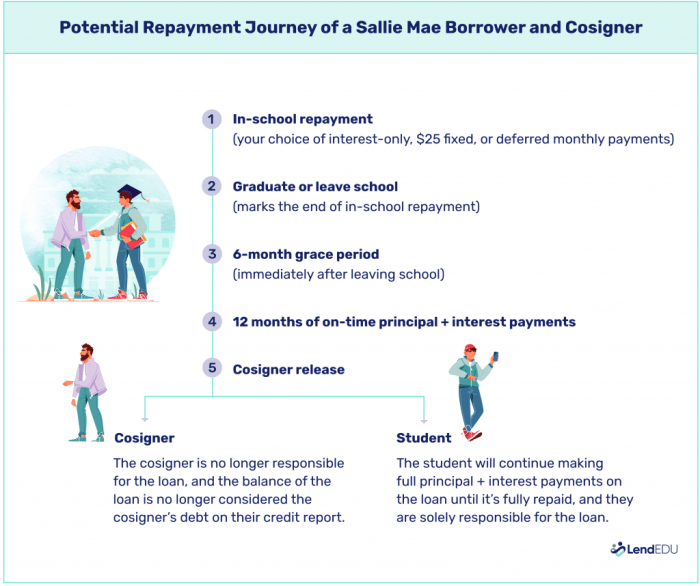
Successfully securing a Sallie Mae student loan marks a significant step towards your educational goals. However, responsible loan management is crucial for maintaining a positive credit history and avoiding financial difficulties. This section Artikels key strategies for effectively managing your Sallie Mae loan repayment and exploring options for potential future savings.
Effective loan management begins with a comprehensive understanding of your financial obligations and the development of a robust repayment plan. This plan should consider not only your loan payments but also other essential expenses to ensure you can comfortably meet all your financial commitments.
Creating a Budget for Sallie Mae Loan Repayments
Developing a detailed budget is paramount to successful loan repayment. This involves carefully tracking all income and expenses to identify areas for potential savings and ensure sufficient funds are allocated for your Sallie Mae loan payments. Consider using budgeting apps or spreadsheets to categorize expenses, track progress, and visualize your financial situation. A realistic budget prevents missed payments, which can negatively impact your credit score. For example, if your monthly income is $2,500 and your essential expenses (rent, utilities, groceries) total $1,500, you can allocate a portion of the remaining $1,000 towards your Sallie Mae loan payment, ensuring timely repayment and building positive credit history.
Making On-Time Payments to Maintain a Good Credit History
Consistent and timely loan payments are critical for building and maintaining a strong credit history. Late payments can significantly damage your credit score, making it more difficult to secure loans or credit cards in the future, and potentially increasing interest rates on future borrowing. Set up automatic payments through your bank or Sallie Mae’s online portal to ensure payments are made on time each month. Consider setting reminders on your phone or calendar to stay organized and avoid missing deadlines. Maintaining a consistent record of on-time payments demonstrates financial responsibility to lenders and contributes to a healthy credit profile. For instance, consistently making on-time payments for 12 months demonstrates reliability and responsibility, positively impacting your credit score.
Refinancing Sallie Mae Loans to Potentially Lower Interest Rates
Refinancing your Sallie Mae loan might offer the opportunity to lower your interest rate and potentially save money over the life of the loan. However, this option depends on several factors, most notably your credit score. Lenders typically offer lower interest rates to borrowers with higher credit scores, reflecting a lower perceived risk. Before refinancing, thoroughly research different lenders, compare interest rates and terms, and carefully evaluate the total cost of the loan, including any fees. A higher credit score, for example, above 700, significantly increases your chances of securing a more favorable interest rate during the refinancing process, potentially saving you thousands of dollars over the loan’s duration. It is crucial to understand that refinancing involves applying for a new loan, and a credit check will be conducted.
Credit Score Reporting and Disputes
Understanding your credit report is crucial for managing your finances, especially when dealing with student loans like those from Sallie Mae. Your credit report is a detailed record of your credit history, and its accuracy directly impacts your credit score, which in turn affects your loan terms and interest rates. This section explains how to obtain, understand, and correct inaccuracies on your credit report.
Your credit report contains information from various sources about your credit history. This includes payment history on loans and credit cards, amounts owed, length of credit history, new credit accounts opened, and types of credit used. Each piece of information contributes to your overall credit score, which is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. The three major credit reporting agencies – Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion – maintain separate credit reports for each individual.
Obtaining and Understanding Credit Reports
You are entitled to a free credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus annually through AnnualCreditReport.com. This website is the only authorized source for free credit reports; be wary of other sites that may charge a fee. Your report will detail all your credit accounts, including open and closed accounts, showing the account type, creditor, date opened, high credit limit (if applicable), current balance, payment history, and any public records (like bankruptcies or judgments). Reviewing your report carefully allows you to identify potential errors or inconsistencies that could negatively affect your credit score. Understanding the components of your credit report enables you to proactively manage your credit and improve your financial standing.
Disputing Credit Report Inaccuracies
If you find any inaccuracies on your credit report, you have the right to dispute them. Each credit bureau has a process for filing a dispute. Generally, you’ll need to submit a dispute form, either online or by mail, providing detailed evidence supporting your claim. This evidence could include canceled checks, receipts, or correspondence with the creditor. The credit bureau is obligated to investigate your dispute and contact the creditor to verify the information. If the inaccuracy is confirmed, the bureau must correct the report. Failure to resolve the dispute satisfactorily can lead to further action, such as contacting the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB).
Examples of Credit Score Disputes
The following table illustrates situations where a credit score dispute might be necessary:
| Error Type | Example | Impact on Score | Steps to Dispute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Account Information | A loan account listed that you never opened. | Significant negative impact, potentially lowering your score substantially. | File a dispute with each credit bureau providing proof you did not open the account (e.g., bank statements, loan applications). |
| Late Payment Reporting Error | A late payment reported when payments were made on time. | Negative impact, depending on the severity and frequency of reported late payments. | Provide proof of timely payments (e.g., bank statements, payment confirmations). |
| Incorrect Account Balance | A significantly higher balance reported than the actual amount owed. | Potentially negative impact, affecting your credit utilization ratio. | Submit documentation showing the correct balance (e.g., credit card statements, loan agreements). |
| Identity Theft | Accounts opened in your name without your knowledge or consent. | Severe negative impact, potentially devastating your credit score. | File a police report, contact the credit bureaus to place a fraud alert or security freeze on your accounts, and follow the instructions provided by the credit bureaus. |
Alternative Loan Options
Choosing the right student loan is crucial, as it significantly impacts your financial future. While Sallie Mae offers private student loans, understanding the broader landscape of available options is essential for making an informed decision. This section compares and contrasts Sallie Mae loans with other types of student loans, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each.
The student loan market offers a diverse range of options, broadly categorized into federal and private loans. Federal loans, offered by the U.S. government, typically come with more borrower protections and flexible repayment plans compared to private loans, which are offered by banks and other private lenders like Sallie Mae. However, private loans might offer more competitive interest rates depending on your creditworthiness.
Federal Student Loans versus Private Student Loans
Federal student loans are generally preferred due to their borrower-friendly features. These include income-driven repayment plans, deferment options during periods of unemployment or financial hardship, and loan forgiveness programs for certain professions. Private loans, on the other hand, often have stricter eligibility requirements, potentially higher interest rates, and fewer repayment options. The interest rates on private loans are usually variable and based on your credit score, making them potentially more expensive for borrowers with lower credit scores. Conversely, federal loans offer fixed interest rates for certain loan types, providing predictability and stability in repayment costs. For example, a Direct Subsidized Loan might offer a fixed rate of 4.99% for a specific period, whereas a private loan from Sallie Mae could fluctuate, potentially exceeding 7% depending on market conditions and the borrower’s credit profile.
Impact of Different Loan Types on Credit Scores
Both federal and private student loans can impact your credit score, but the effects differ. On-time payments on any loan, including student loans, positively affect your credit score, demonstrating responsible borrowing behavior to credit bureaus. Conversely, late or missed payments on either type of loan will negatively impact your credit score, potentially resulting in a lower credit rating and higher interest rates on future loans. The impact of a negative mark on your credit report is more severe with private loans because they often report to credit bureaus more frequently than federal loans. A significant difference is that defaulting on a federal student loan can have serious consequences, including wage garnishment and tax refund offset, while the consequences of defaulting on a private student loan may vary depending on the lender and state laws. Careful management of both types of loans is crucial for maintaining a healthy credit score.
Long-Term Financial Planning

Successfully navigating student loan debt requires a comprehensive long-term financial plan. This plan should integrate loan repayment strategies with broader goals for saving, investing, and achieving financial security. Failing to consider the long-term implications of student loan debt can significantly hinder your ability to reach your financial aspirations.
Integrating student loan repayment into your long-term financial plan is crucial for building a strong financial future. A well-structured plan allows you to proactively manage your debt while simultaneously working towards other financial objectives, such as purchasing a home, investing for retirement, or starting a family. Ignoring your student loans can lead to accumulating interest and negatively impact your credit score, making it harder to achieve these goals.
Student Loan Repayment Strategies and Financial Goals
Effective student loan repayment requires a strategic approach. Consider income-driven repayment plans which adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. Explore options like refinancing to potentially lower your interest rate. Prioritize high-interest loans to minimize overall interest paid. Creating a realistic budget that allocates funds for loan payments alongside essential living expenses and savings is vital. Consistent and timely payments are key to maintaining a healthy credit score, unlocking better financial opportunities in the future. For example, someone with a consistent repayment history might qualify for a lower interest rate on a mortgage or car loan compared to someone with a history of missed payments.
Saving and Investing After Graduation
Once you have a manageable student loan repayment plan in place, focus on building savings and investments. Start with an emergency fund, ideally covering 3-6 months of living expenses. This provides a financial cushion for unexpected events, preventing you from falling behind on loan payments or depleting your savings. After establishing your emergency fund, explore investment options like retirement accounts (401(k)s or IRAs) and taxable brokerage accounts. Consider your risk tolerance and investment timeline when making investment decisions. For example, a young graduate with a long investment horizon might allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to stocks, while someone closer to retirement might prefer a more conservative approach with bonds. Consistent contributions, even small ones, will compound over time, leading to significant growth.
Visual Representation of Loan Repayment, Credit Score, and Financial Goals
Imagine a three-layered pyramid. The base represents consistent loan repayment and responsible financial habits. This base is wide and sturdy, symbolizing the foundation for a strong credit score. The middle layer, slightly narrower than the base, depicts your improving credit score. This layer shows how responsible loan management directly translates to a better credit rating, opening doors to better financial opportunities like lower interest rates on future loans or higher approval chances for credit cards. The top layer, the smallest and most pointed, represents the achievement of your long-term financial goals – owning a home, comfortable retirement, or starting a business. The size difference illustrates that a solid foundation of responsible debt management and a good credit score are essential to reach your ambitious financial goals. The pyramid visually demonstrates the interconnectedness of these three elements: consistent repayment leads to a good credit score, which in turn enables the attainment of long-term financial objectives.
Final Review
Successfully navigating the Sallie Mae student loan process requires a proactive approach to credit management. By understanding the impact of your credit score, implementing strategies for improvement, and diligently managing your loan repayments, you can secure favorable loan terms and build a strong financial foundation for the future. Remember, a higher credit score can translate to lower interest rates, potentially saving you thousands of dollars over the life of your loan. Prioritize responsible financial habits to achieve long-term financial well-being.
Helpful Answers
What happens if I have a low credit score?
A low credit score may result in higher interest rates, a smaller loan amount, or even loan denial. It’s crucial to work on improving your credit score before applying.
Can I check my credit score for free?
Yes, several websites offer free credit score checks, though the information may be limited. AnnualCreditReport.com provides a free credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus annually.
How long does it take to improve my credit score?
Improving your credit score takes time and consistent effort. Significant improvements can be seen within six months to a year, depending on the strategies employed and the severity of any negative marks.
What if there’s an error on my credit report?
Immediately dispute any inaccuracies with the credit bureau. Provide documentation to support your claim. A corrected credit report can positively impact your score.
