Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment often leaves borrowers questioning the fluctuating nature of interest rates. Understanding how these rates are determined, their historical trends, and the impact on long-term repayment is crucial for effective financial planning. This exploration delves into the various factors influencing student loan interest rates, providing insights into both federal and private loan structures, and equipping borrowers with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
From fixed versus variable rates to the influence of market conditions and government policies, we’ll examine the multifaceted landscape of student loan interest. We’ll also explore practical strategies for managing loans amidst fluctuating rates, empowering borrowers to take control of their financial future.
Types of Student Loans and Interest Rates

Understanding the different types of student loans and their associated interest rates is crucial for effective financial planning during and after your education. The interest rate significantly impacts the total cost of your loan, affecting your monthly payments and overall debt burden. This section will clarify the key distinctions between federal and private loans and the factors influencing their interest rates.
Federal Student Loan Interest Rates
Federal student loans, offered by the U.S. government, generally have lower interest rates than private loans. These rates are set by the government and can vary depending on the loan type and the borrower’s credit history (though this is less of a factor than with private loans). The primary types of federal student loans include subsidized and unsubsidized loans, as well as PLUS loans (for parents and graduate students). Subsidized loans typically have lower interest rates because the government pays the interest while the student is in school at least half-time, during grace periods, and during deferment. Unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed, regardless of the borrower’s enrollment status. PLUS loans, while having a higher interest rate than subsidized and unsubsidized loans, offer a way for parents or graduate students to borrow additional funds to cover educational expenses. The interest rates for these loans are fixed for the life of the loan.
Private Student Loan Interest Rates
Private student loans, offered by banks and other financial institutions, are subject to more variable interest rates influenced by several factors. These factors include the borrower’s credit score, credit history, the loan amount, the loan term, and the type of loan. A higher credit score generally leads to a lower interest rate. Similarly, a longer loan term might result in a slightly lower interest rate but leads to a higher overall cost due to more accumulated interest. Private lenders also assess the borrower’s co-signer’s creditworthiness if one is involved. The interest rate on a private student loan can be either fixed or variable.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain constant throughout the loan’s repayment period, providing predictability and stability in monthly payments. Variable interest rates, on the other hand, fluctuate based on an underlying benchmark index, such as the prime rate or LIBOR. This means your monthly payment could increase or decrease over time depending on market conditions. While a variable rate might start lower than a fixed rate, it carries the risk of significant increases over the life of the loan. Choosing between fixed and variable rates depends on your risk tolerance and financial outlook. A fixed rate offers certainty, while a variable rate offers the potential for lower initial payments, but with increased uncertainty.
Comparison of Student Loan Interest Rates
| Loan Type | Interest Rate Type | Typical Interest Rate Range (as of October 26, 2023 – Note: Rates are subject to change) | Repayment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Subsidized Loan (Undergraduate) | Fixed | 4.99% – 7.54% | Standard, Income-Driven Repayment Plans |
| Federal Unsubsidized Loan (Undergraduate) | Fixed | 4.99% – 7.54% | Standard, Income-Driven Repayment Plans |
| Federal PLUS Loan (Graduate/Parent) | Fixed | 7.54% – 10.5% | Standard, Income-Driven Repayment Plans (for Parent PLUS Loans, some restrictions apply) |
| Private Student Loan | Fixed or Variable | 5% – 15% (Highly Variable) | Various options depending on the lender |
*Note: The interest rate ranges provided are estimates and can vary significantly based on individual circumstances and lender policies. Always check with the lender for the most up-to-date information.*
How Interest Rates are Determined
Understanding how student loan interest rates are determined is crucial for borrowers, as it directly impacts the total cost of their education. Several factors, both governmental and market-driven, play a significant role in shaping these rates.
The federal government plays a dominant role in setting interest rates for federal student loans. These rates are not arbitrarily chosen but are influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors and government policy. While the government doesn’t directly control the market, its actions significantly influence the overall interest rate environment.
The Federal Government’s Role in Setting Interest Rates
The U.S. Department of Education sets interest rates for federal student loans annually. These rates are often tied to the 10-year Treasury note, a benchmark for long-term borrowing costs. The government may also adjust rates based on broader economic conditions, aiming for a balance between affordability for students and responsible fiscal management. For example, during periods of low inflation and low Treasury yields, the government might set lower interest rates on federal student loans to encourage borrowing and support higher education access. Conversely, during periods of high inflation or increased government borrowing costs, the rates may be adjusted upward. This approach seeks to reflect prevailing market conditions while maintaining a degree of predictability for borrowers.
Market Conditions and Their Influence on Student Loan Interest Rates
Market conditions significantly influence student loan interest rates, even for federal loans. The 10-year Treasury note rate, for instance, serves as a key indicator. When investors demand higher returns due to factors like inflation or economic uncertainty, Treasury yields rise, pushing up borrowing costs across the board, including student loans. Similarly, the overall health of the credit markets impacts the cost of borrowing. Periods of economic instability or decreased investor confidence can lead to higher interest rates across all types of loans, including student loans. The demand for student loans themselves also plays a role; if demand surges, rates might increase to reflect this increased pressure.
Key Economic Indicators Impacting Interest Rate Changes
Several key economic indicators significantly influence student loan interest rates. These include:
- Inflation: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, leading to higher interest rates to compensate lenders for the diminished value of future repayments.
- Treasury Yields: As mentioned, the yield on the 10-year Treasury note is a benchmark for long-term borrowing costs, directly influencing federal student loan rates.
- Federal Funds Rate: The target rate set by the Federal Reserve influences short-term interest rates, which can indirectly affect long-term rates like those on student loans.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can lead to lower interest rates, while weak growth may cause them to rise.
These indicators are interconnected, and changes in one can trigger ripple effects throughout the economy, impacting student loan rates.
Calculating Student Loan Interest Rates
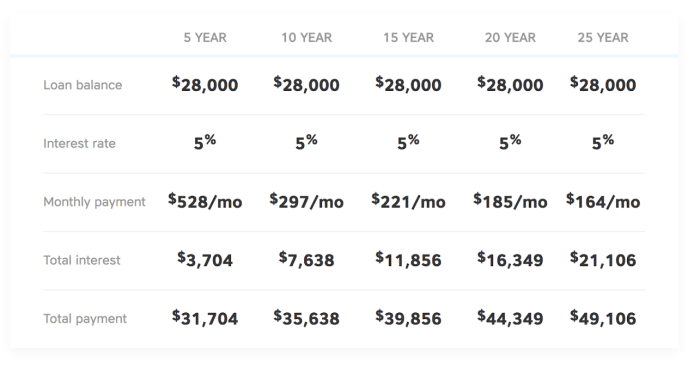
The calculation of student loan interest is generally straightforward, though the specifics depend on the loan type (fixed or variable) and the loan’s terms. For federal loans with fixed interest rates, the rate is set at the time the loan is disbursed and remains constant throughout the loan’s life. Interest accrues daily on the outstanding principal balance. The daily interest is calculated by dividing the annual interest rate by 365 and multiplying by the principal balance. This daily interest is then added to the principal, increasing the balance on which future interest is calculated. For example, if a student has a $10,000 loan with a 5% annual interest rate, the daily interest is approximately $0.14 ($10,000 * 0.05 / 365). Variable rate loans, on the other hand, adjust periodically based on a benchmark index, making the calculation more complex as the rate changes over time. The calculation method remains similar, but the interest rate used in the calculation changes with each adjustment period.
Interest Rate Changes Over Time
Student loan interest rates are not static; they fluctuate based on various economic factors. Understanding these changes is crucial for borrowers, as it directly impacts the overall cost of their education. This section will explore historical interest rate trends for federal student loans over the past decade, illustrating their impact on loan repayment.
Analyzing historical data reveals a dynamic landscape of student loan interest rates. While specific rates vary depending on the loan type (e.g., subsidized vs. unsubsidized, graduate vs. undergraduate), general trends can be observed. Over the past decade, rates have experienced both periods of relative stability and significant volatility, often mirroring broader economic conditions.
Historical Interest Rate Data and Graphical Representation
The following data represents a simplified overview of average federal student loan interest rates for undergraduate subsidized loans over the past ten years (2014-2023). Note that these are averages and actual rates may have varied slightly based on the specific loan program and disbursement date. Precise figures can be found on the official websites of the U.S. Department of Education or the relevant lending institution.
Imagine a line graph with “Year” on the x-axis (ranging from 2014 to 2023) and “Interest Rate (%)” on the y-axis. The line would show a general downward trend from 2014 to approximately 2017, followed by a period of relative stability, then a slight upward tick around 2020-2021, before settling to a moderately lower level by 2023. The graph would not be perfectly smooth; there would be minor fluctuations year to year, reflecting the complex interplay of economic indicators affecting interest rate determination.
For example, a hypothetical data set might look like this: 2014 (4.69%), 2015 (4.29%), 2016 (3.76%), 2017 (3.49%), 2018 (4.45%), 2019 (4.53%), 2020 (4.78%), 2021 (4.99%), 2022 (4.21%), 2023 (4.05%). This data is illustrative and should not be taken as precise historical figures. Refer to official government sources for accurate historical rates.
Timeline of Significant Interest Rate Changes and Associated Events
Significant shifts in student loan interest rates are often linked to broader economic factors. For instance, periods of economic uncertainty or changes in the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy can impact borrowing costs.
A simplified timeline might include:
- 2014-2017: Gradual decline in rates, potentially reflecting a period of economic recovery following the 2008 financial crisis.
- 2018-2019: Relatively stable rates, possibly indicating a period of economic growth and low inflation.
- 2020-2021: Slight increase in rates, potentially influenced by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and associated economic uncertainty.
- 2022-2023: A return to lower rates, which could be attributed to a combination of factors including post-pandemic economic recovery and central bank policies.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Total Loan Cost
Even seemingly small changes in interest rates can significantly affect the total cost of a student loan over its repayment period, especially for larger loan amounts and longer repayment terms. This is due to the compounding effect of interest.
For example, consider two scenarios: a $30,000 loan with a 4% interest rate versus the same loan with a 6% interest rate, both repaid over 10 years. The higher interest rate would result in a considerably larger total amount repaid, due to the accumulation of interest over the repayment period. A simple calculation using a loan amortization calculator would demonstrate the substantial difference in total cost. The exact difference will depend on the specific repayment plan used.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Borrowers
Fluctuations in student loan interest rates directly impact borrowers’ monthly payments and overall repayment burden. Understanding these effects is crucial for effective financial planning and minimizing long-term debt. This section will explore how interest rate increases affect monthly payments, strategies for managing loans during rate hikes, the comparison between fixed and variable rate loans, and illustrate the long-term implications of interest rate changes on loan repayment.
Interest Rate Increases and Monthly Payments
An increase in interest rates translates directly into higher monthly payments. This is because a larger portion of each payment goes towards covering the interest accrued, leaving less to reduce the principal loan amount. For example, a borrower with a $50,000 loan at a 5% interest rate might have a monthly payment of approximately $268. If the interest rate rises to 7%, that same loan could result in a monthly payment closer to $337 – a significant increase of almost $70 per month. This difference becomes even more pronounced over the life of the loan.
Strategies for Managing Loans When Interest Rates Rise
Several strategies can help borrowers manage their loans when interest rates increase. One approach is to explore refinancing options. If rates on new loans are lower than the current rate on the existing loan, refinancing can lower monthly payments. Another strategy involves making extra payments whenever possible. Even small additional payments can significantly reduce the total interest paid over the life of the loan and shorten the repayment period. Finally, borrowers should actively monitor their loan terms and communicate with their lender about potential hardship programs or payment plans if facing financial difficulties.
Fixed Versus Variable Interest Rate Loans: A Comparison
Choosing between a fixed and variable interest rate loan is a critical decision. A fixed-rate loan offers predictable monthly payments throughout the loan term, regardless of market interest rate fluctuations. A variable-rate loan, on the other hand, has an interest rate that adjusts periodically based on market conditions. While a variable-rate loan might initially offer a lower interest rate, it carries the risk of significantly higher payments if interest rates rise. For example, a borrower with a variable-rate loan might initially enjoy lower monthly payments but could face a substantial increase if the benchmark interest rate increases unexpectedly, leading to a potentially unaffordable monthly payment. A fixed-rate loan, while potentially starting with a higher monthly payment, offers the stability of knowing exactly what the payment will be for the loan’s duration.
Long-Term Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Loan Repayment
The long-term impact of interest rate changes on loan repayment can be substantial. Even a seemingly small increase in the interest rate can result in thousands of dollars more paid in interest over the life of the loan. Consider a $30,000 loan repaid over 10 years. At a 6% interest rate, the total interest paid would be approximately $9,700. However, at an 8% interest rate, the total interest paid would climb to nearly $13,000 – a difference of over $3,300. This example underscores the importance of carefully considering interest rates when choosing a student loan and proactively managing the loan throughout the repayment period.
Resources and Further Information
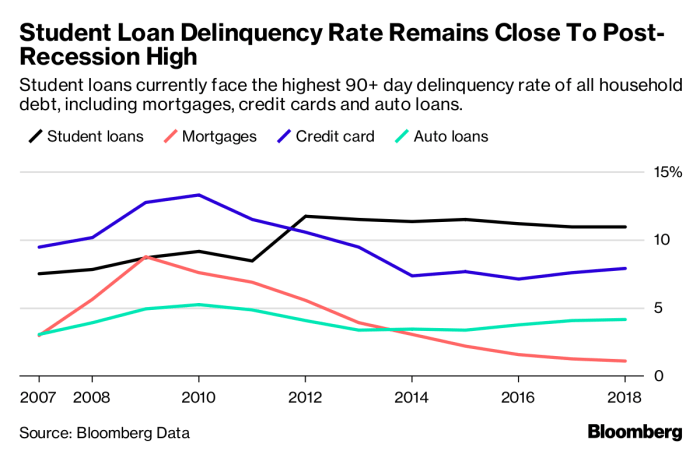
Navigating the complexities of student loan interest rates can be challenging. Fortunately, several resources are available to help borrowers understand their loans and manage their finances effectively. This section provides a list of reputable websites and organizations, along with steps to check your current interest rate.
Understanding your student loan interest rate is crucial for effective financial planning. Knowing this rate allows you to accurately budget for repayments, explore refinancing options, and make informed decisions about your long-term financial health. The following resources and steps will empower you to take control of your student loan situation.
Reputable Websites and Organizations
Finding reliable information about student loans is essential. The following list includes websites and organizations that provide accurate and up-to-date information on student loan interest rates and related topics. These resources are known for their credibility and commitment to helping borrowers.
- Federal Student Aid (FSA): This website, managed by the U.S. Department of Education, is the primary source for information on federal student loans. It provides details on interest rates, repayment plans, and other important aspects of loan management. The site is user-friendly and offers a wealth of resources for borrowers at all stages of repayment.
- National Student Loan Data System (NSLDS): NSLDS is a central database that allows you to access information about your federal student loans. It provides a consolidated view of your loan details, including the interest rate for each loan. Access to NSLDS is secure and requires proper authentication.
- Your Loan Servicer: Your loan servicer is the company responsible for managing your student loans. They will provide detailed information specific to your loans, including your interest rates, payment amounts, and repayment schedules. Contact information for your servicer can typically be found on your loan documents or through the NSLDS website.
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): The CFPB is an independent agency that works to protect consumers’ financial interests. Their website offers resources and guidance on various financial topics, including student loans. They provide valuable information about your rights and responsibilities as a borrower.
Checking Your Current Student Loan Interest Rate
Accessing your current student loan interest rate is a straightforward process. The exact steps may vary slightly depending on your loan type and servicer, but the general process is consistent across most lenders.
- Log in to your student loan account: Access your online account through your loan servicer’s website. You will need your login credentials to proceed.
- Locate your loan details: Once logged in, navigate to the section displaying your loan information. This section typically includes details such as your loan balance, payment history, and interest rate.
- Review your interest rate: Your interest rate will be clearly displayed, usually as a percentage. Note that you may have different interest rates for different loans, especially if you have both subsidized and unsubsidized loans.
- Contact your loan servicer (if necessary): If you cannot locate your interest rate online, contact your loan servicer directly. They will be able to provide you with the information you need.
Last Word
In conclusion, the ever-changing landscape of student loan interest rates necessitates a proactive approach to financial management. By understanding the factors that influence these rates, borrowers can make informed decisions about loan selection and repayment strategies, ultimately minimizing long-term costs and securing financial stability. Staying informed and utilizing available resources is key to navigating this complex financial terrain successfully.
Top FAQs
What factors affect private student loan interest rates?
Private student loan interest rates are influenced by several factors, including your credit score, credit history, the loan amount, the repayment term, and the prevailing market interest rates. Lenders also consider your co-signer’s creditworthiness (if applicable).
Can my student loan interest rate change after I’ve signed the loan agreement?
This depends on the type of loan. Fixed-rate loans maintain the same interest rate throughout the repayment period. Variable-rate loans, however, can fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially leading to changes in your monthly payments.
How often are federal student loan interest rates adjusted?
Interest rates for federal student loans are typically set annually and may vary depending on the loan type and the prevailing economic conditions. The rates are announced before the start of each academic year.
Where can I find my current student loan interest rate?
Your current student loan interest rate is typically found on your loan servicer’s website or on your monthly statement. You can also contact your loan servicer directly for this information.
