
Securing financial aid for higher education is a crucial step for many students. The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the gateway to federal student loans and grants. This guide navigates the FAFSA application process, from creating an FSA ID to understanding different loan types and managing repayment. We’ll demystify the process, providing clear steps and helpful tips to ensure a smooth and successful application.
Understanding the FAFSA form, gathering necessary documents, and accurately inputting financial information are key components. We will also explore the various types of federal student loans available, their associated interest rates, and repayment plans to help you make informed decisions about your financial future. Successfully navigating the FAFSA process empowers you to access the financial resources needed to pursue your educational goals.
Understanding FAFSA

The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is a crucial gateway to accessing federal student financial aid in the United States. Completing this form accurately and thoroughly is essential for determining your eligibility for grants, loans, and work-study opportunities to help fund your education. Understanding the process and requirements will streamline your application and increase your chances of receiving financial assistance.
The FAFSA form serves as a central application for various federal student aid programs. It collects information about you, your family’s financial situation, and your educational plans to determine your financial need and eligibility for different types of aid. The information provided is used to calculate your Expected Family Contribution (EFC), a key factor in determining your eligibility for need-based aid.
FAFSA Eligibility Requirements
Eligibility for federal student aid hinges on several factors. Applicants must be a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen, have a valid Social Security number, and possess a high school degree or its equivalent. Furthermore, they must be enrolled or accepted for enrollment in an eligible educational program at a participating institution, maintain satisfactory academic progress, and agree to provide accurate information on the FAFSA form. Additional requirements may apply depending on the specific type of aid sought. For instance, some programs have age restrictions or require completion of a certain number of credit hours.
Creating an FSA ID
An FSA ID is a username and password combination that provides secure access to your FAFSA information. It’s essential for both the student and a parent (if required) to each have their own FSA ID. The process begins by visiting the official Federal Student Aid website. You’ll need to provide personal information, such as your Social Security number, date of birth, and email address. The system will then guide you through creating a strong password and verifying your identity. Once created, you’ll use this FSA ID to electronically sign your FAFSA and access your financial aid information. It’s crucial to keep your FSA ID secure, as it protects your personal and financial data.
Required Documents for FAFSA Completion
Before starting your FAFSA, gather the necessary documents to streamline the process. This typically includes your Social Security number, your federal income tax returns (IRS Form 1040), your W-2s, and other relevant records of income and untaxed income. You will also need your driver’s license or state identification and your alien registration number (if applicable). If you are a dependent student, your parents’ information will be required, including their Social Security numbers, tax returns, and W-2s. Having this information readily available will prevent delays and ensure a smoother FAFSA completion. Remember to keep accurate records of all submitted information for your records. Accurate information is vital to prevent delays or potential issues with your application.
Completing the FAFSA Form
Successfully navigating the FAFSA application requires careful preparation and accurate data entry. This section details the process of completing the form, ensuring a smooth and efficient application. Understanding the requirements and gathering necessary information beforehand is crucial for a successful submission.
Gathering Necessary Information
Before starting the FAFSA application, collect all the required financial documents. This includes your and your parents’ (if applicable) federal tax returns (IRS Form 1040), W-2s, and other relevant financial records. You’ll also need Social Security numbers for yourself and your parents, as well as information about your assets, such as bank accounts and investments. Keep this information readily accessible as you will be entering it directly into the FAFSA form. Accurate information is paramount; inaccuracies can delay processing or lead to eligibility issues.
Entering Financial Information
The FAFSA application will ask for detailed financial information. Be sure to enter your data precisely as it appears on your tax documents. For example, if your adjusted gross income (AGI) on your tax return is $50,000, enter exactly that amount. Do not round numbers or estimate. The system will perform the necessary calculations based on the information you provide. Similarly, accurately report the value of your assets, including savings accounts, investments, and other financial holdings. Remember, the FAFSA uses this information to determine your eligibility for financial aid.
Selecting Schools and Programs
The FAFSA allows you to list multiple schools and programs. You will need the Federal School Code for each institution you are applying to. These codes can be found on the schools’ websites or through the FAFSA website’s school search tool. When selecting your program, choose the program you intend to pursue. Providing accurate program information ensures your financial aid is appropriately allocated. It’s advisable to review each school’s requirements to avoid any discrepancies between your application and the institution’s needs.
FAFSA Submission Checklist
A thorough review before submission is essential. This checklist helps ensure accuracy and completeness:
- Verify all personal information, including names, Social Security numbers, and addresses.
- Double-check all financial data, comparing it to your tax documents and financial records.
- Confirm the accuracy of the school codes and program information.
- Review the entire application for any errors or omissions.
- Ensure you have electronically signed the application.
- Submit the application well before the deadlines set by your chosen institutions.
Following this checklist and taking your time to accurately complete the FAFSA application will significantly increase your chances of receiving the financial aid you need. Remember, accurate information is crucial for a successful application.
Submitting the FAFSA
Submitting your completed FAFSA is the final step in the application process. This crucial step initiates the process of determining your eligibility for federal student aid. There are several ways to submit your application, each offering varying levels of convenience and tracking capabilities. Understanding the submission process and how to manage any potential issues is essential for a smooth application experience.
FAFSA Submission Methods
The FAFSA can be submitted electronically online or via mail. Submitting online is the preferred and most efficient method. The online submission allows for immediate confirmation and provides access to online tracking tools. Submitting by mail, while still an option, is significantly slower and lacks the immediate feedback of online submission. The online submission process guides you through each step, and the system validates your information as you enter it, helping to minimize errors before submission. Mailing your FAFSA requires printing the form, completing it accurately, and mailing it to the designated address. This method introduces a significant delay in processing due to postal transit times.
Tracking FAFSA Application Status
Once you’ve submitted your FAFSA, you can easily track its progress online. The Federal Student Aid website provides a secure portal where you can log in using your FSA ID and monitor the status of your application. This portal provides updates on the processing of your application, including any requests for additional information. Regularly checking your status allows you to address any issues promptly and ensures a timely processing of your application. You’ll receive notifications about the status of your application via email, but checking the website directly offers a more comprehensive overview of your application’s progress.
Correcting Errors or Making Changes
Mistakes happen. If you discover errors after submitting your FAFSA, you can correct them online through your student aid report. The online system allows you to make changes to your application as needed, provided the FAFSA hasn’t already been processed. If your FAFSA has already been processed, you may need to contact the Federal Student Aid office directly to request corrections. Making corrections promptly is crucial to avoid delays in receiving your financial aid. The online correction process is generally straightforward, guiding you through the necessary steps to update your information. Detailed instructions are available on the Federal Student Aid website.
Avoiding Common FAFSA Mistakes
Several common mistakes can delay or hinder your FAFSA application. Accurate and complete information is paramount. Double-checking all information before submission is crucial. Common errors include incorrect Social Security numbers, inaccurate tax information, and inconsistent information across different sections of the application. Using the FAFSA online help resources and ensuring you understand the definitions of all terms can help prevent these errors. Furthermore, ensuring that your tax information is up-to-date and readily available will streamline the process. Reviewing your completed FAFSA carefully before submission can catch many errors that could otherwise cause delays. For example, a common mistake is entering incorrect parent information, especially if the student is independent. Another common error is failing to report all income sources accurately.
Understanding Student Loan Types
Navigating the world of student loans can feel overwhelming, especially with the various types available. Understanding the key differences between federal student loan options is crucial for making informed financial decisions that align with your individual circumstances and future goals. This section will clarify the distinctions between subsidized, unsubsidized, and PLUS loans, focusing on interest rates, repayment plans, and eligibility.
Federal Student Loan Types: Subsidized, Unsubsidized, and PLUS Loans
The federal government offers several student loan programs designed to help students finance their education. Three prominent types are subsidized, unsubsidized, and PLUS loans. Each carries different terms and conditions that significantly impact the borrower’s overall cost and repayment strategy.
Interest Rates and Repayment Plans
Interest rates for federal student loans fluctuate, determined annually by the government. Subsidized loans generally have lower interest rates than unsubsidized loans, reflecting the government’s interest subsidy during the in-school period. PLUS loans typically carry higher interest rates than both subsidized and unsubsidized loans. Repayment plans vary, offering options such as standard repayment (10 years), extended repayment, graduated repayment, and income-driven repayment (IDR) plans. IDR plans adjust monthly payments based on income and family size, making them potentially more manageable for borrowers with lower post-graduation earnings.
Implications of Choosing Different Loan Types
The choice of loan type has significant long-term financial implications. Subsidized loans are advantageous because the government pays the interest while the borrower is enrolled at least half-time and during certain grace periods. Unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed, increasing the total amount owed upon graduation. PLUS loans, while accessible to parents and graduate students, come with higher interest rates and potentially larger overall debt burdens. Careful consideration of the interest rates, repayment options, and long-term financial impact is crucial before selecting a loan type.
Comparison of Federal Student Loan Types
| Loan Type | Interest Rate | Repayment Period | Eligibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidized | Variable; generally lower than unsubsidized | Standard: 10 years; other options available | Undergraduate students demonstrating financial need |
| Unsubsidized | Variable; generally higher than subsidized | Standard: 10 years; other options available | Undergraduate, graduate, and professional students |
| PLUS | Variable; generally highest of the three | Standard: 10 years; other options available | Parents of dependent undergraduate students and graduate/professional students |
Managing Student Loans

Securing student loans is a significant step towards higher education, but responsible management is crucial for successful repayment. Understanding the process of accepting loan offers, exploring repayment options, and creating a robust budget are key to navigating your student loan journey effectively. This section will provide practical guidance on these essential aspects.
Accepting Your Student Loan Offer
After applying for federal student aid through FAFSA, you’ll receive a notification outlining the types and amounts of loans you’ve been offered. Carefully review this offer. This includes the loan amount, interest rate, repayment terms, and any associated fees. To accept the loan, you typically need to complete an electronic acceptance process through your student loan servicer’s online portal. This usually involves logging in, reviewing the loan details, and electronically signing an agreement. Failure to accept your loan offer within the specified timeframe may result in the loss of funding for that academic year. Contact your school’s financial aid office if you have questions or require assistance with the acceptance process.
Understanding Loan Repayment Options
Several repayment options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options allows you to choose a plan that best suits your financial situation. Standard repayment plans involve fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period. Graduated repayment plans start with lower payments that gradually increase over time. Income-driven repayment plans (IDR) tie your monthly payment to your income and family size, offering lower payments but potentially extending the repayment period. Extended repayment plans stretch the repayment period, lowering monthly payments but increasing the total interest paid. The federal government provides resources, including the Federal Student Aid website, to compare these options and choose the best fit. It’s advisable to explore the repayment calculators available on these websites to estimate your monthly payments under different plans.
Budgeting and Managing Student Loan Debt
Creating a realistic budget is paramount to managing student loan debt effectively. This involves tracking your income and expenses, identifying areas for potential savings, and allocating funds for your loan payments. Prioritize essential expenses like housing, food, and transportation before allocating funds for discretionary spending. Consider exploring ways to reduce expenses, such as cutting back on entertainment or finding more affordable options for groceries or transportation. Tracking your spending using budgeting apps or spreadsheets can help you gain a clearer understanding of your financial situation and make informed decisions.
Sample Budget Incorporating Student Loan Payments
Let’s assume a monthly income of $2500 and monthly student loan payments of $300.
| Category | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Housing | 800 |
| Food | 400 |
| Transportation | 200 |
| Student Loan Payment | 300 |
| Utilities | 150 |
| Other Expenses (Entertainment, etc.) | 250 |
| Savings | 400 |
| Total | 2500 |
This is a sample budget; adjust the amounts based on your individual circumstances. Remember that this budget prioritizes loan repayment and savings, highlighting the importance of responsible financial planning when managing student loan debt. It’s crucial to regularly review and adjust your budget as your income or expenses change.
Additional Resources and Support
Securing financial aid for higher education can be a complex process. Beyond completing the FAFSA, numerous resources are available to guide students and families through the financial aid landscape and provide support throughout the process. Understanding these resources can significantly improve your chances of accessing the funding you need.
Navigating the world of financial aid often requires more than just filling out the FAFSA. Supplementing your knowledge with information from trusted sources and utilizing available support services can greatly enhance your understanding and increase your chances of success. This section will Artikel several valuable resources and support systems to help you on your journey.
Reputable Websites Offering Financial Aid Information
Several reputable websites provide comprehensive and up-to-date information on financial aid. These sites offer valuable resources beyond the official government websites, including guides, articles, and tools to help you understand and navigate the financial aid process effectively. They often provide comparative analyses of different loan options and offer tips for managing student loan debt.
- Federal Student Aid (FSA): This is the official website of the U.S. Department of Education’s office of Federal Student Aid. It offers a wealth of information on all aspects of federal student aid, including eligibility requirements, application procedures, and loan repayment options. This should be your primary source for official information.
- The College Board: The College Board offers extensive resources on college planning, including financial aid information. Their website provides tools and guidance on understanding financial aid awards, exploring scholarships, and managing student loan debt.
- Sallie Mae: While a private lender, Sallie Mae provides valuable information and resources on student loans and financial aid. Their website offers educational materials and tools that can help students and families make informed decisions about financing their education.
Contact Information for Federal Student Aid Offices
Direct contact with the Federal Student Aid (FSA) office can be crucial for resolving issues or obtaining clarification on specific aspects of your financial aid application. Their contact information is readily available on their website and allows for various methods of communication.
The Federal Student Aid website (studentaid.gov) provides multiple contact options, including a phone number, email address, and a live chat feature. The specific contact method that best suits your needs will depend on the nature of your inquiry and your preference for communication.
Financial Aid Counseling Services
Many colleges and universities offer free financial aid counseling services to their students. These services provide personalized guidance on navigating the financial aid process, understanding financial aid offers, and creating a budget for college. Additionally, many independent organizations provide similar services, often specializing in specific areas such as budgeting or debt management.
These services can be invaluable in helping students understand their options, make informed decisions, and avoid potential pitfalls. They can assist with creating a comprehensive financial plan that considers tuition, fees, living expenses, and other educational costs. These services are often available in person, over the phone, or online.
Appealing a Financial Aid Decision
If you disagree with a financial aid decision, you have the right to appeal. The appeal process typically involves submitting a formal request to the financial aid office, providing additional documentation to support your case, and clearly explaining why you believe the initial decision was incorrect. The specific requirements for appealing a financial aid decision vary depending on the institution.
It is essential to understand the institution’s specific appeal process and deadlines. Gathering all necessary documentation, including supporting evidence for your appeal, is crucial for a successful outcome. It’s advisable to carefully review the institution’s financial aid policies and appeal procedures before initiating the process.
Illustrative Examples
Understanding the FAFSA process is best done through real-world examples. These scenarios illustrate both successful applications and potential challenges, highlighting the importance of careful planning and proactive problem-solving. We will also explore how different loan types impact long-term financial health.
Successful FAFSA Application
Sarah, a high school senior, diligently gathered all the necessary documents – her social security number, tax returns for herself and her parents, and her driver’s license. She carefully reviewed the FAFSA instructions and completed the online form accurately. She double-checked all the information for errors before submitting it. Within a few weeks, she received her Student Aid Report (SAR), confirming her eligibility for federal student aid. This allowed her to confidently plan for college, knowing she had access to financial assistance. Sarah’s proactive approach and attention to detail ensured a smooth application process.
Problem Encountered and Resolved During FAFSA Application
John, also a high school senior, encountered a problem when attempting to access his tax information online. The IRS website was experiencing technical difficulties, preventing him from retrieving the necessary data. Instead of panicking, John contacted the IRS help desk, who provided him with alternative methods to access his tax information. He also contacted the FAFSA helpline, explaining his situation. The FAFSA representatives were able to provide guidance and reassured him that he could submit the application even with a temporary delay in providing the tax information. He was given an extension and ultimately successfully completed his application. This illustrates the importance of seeking help when encountering difficulties.
Impact of Different Loan Types on Long-Term Financial Planning
Choosing between subsidized and unsubsidized federal loans significantly impacts a student’s long-term financial plan. Subsidized loans, for example, don’t accrue interest while the student is enrolled at least half-time. This can lead to lower overall interest payments and a smaller loan balance upon graduation. Unsubsidized loans, however, accrue interest throughout the entire loan period, potentially resulting in a larger overall debt. A student choosing unsubsidized loans might need to make more significant monthly payments after graduation or face a longer repayment period. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about financing higher education. For instance, a student prioritizing minimizing long-term debt would likely favor subsidized loans whenever possible.
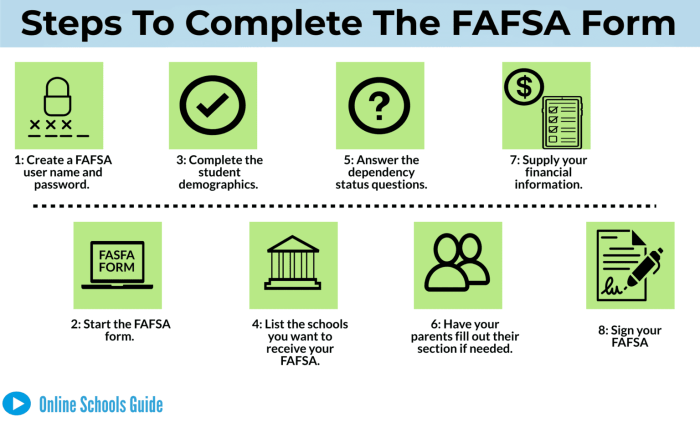
Visual Representation of the FAFSA Application Process
Imagine a flowchart. The first box would be “Gather Required Documents,” leading to “Complete the FAFSA Online Form.” This box branches into two: “Submit the FAFSA” and “Correct Errors/Seek Assistance.” “Submit the FAFSA” leads to “Receive SAR (Student Aid Report).” The “Correct Errors/Seek Assistance” box loops back to “Complete the FAFSA Online Form.” The final box is “Plan for College Funding.” This visual representation simplifies the steps involved, emphasizing the iterative nature of the process and the importance of error correction.
Concluding Remarks
Successfully completing the FAFSA application is a significant achievement in your educational journey. By understanding the process, from initial application to loan management, you’ve taken a proactive step towards securing your financial future. Remember to utilize the available resources and seek assistance when needed. Careful planning and informed decisions will ensure you can focus on your studies without undue financial stress. Your commitment to planning will pay off in the long run.
Answers to Common Questions
What happens if I make a mistake on my FAFSA application?
You can correct errors online through your FAFSA account. The system allows for updates and revisions until the deadlines.
What if I don’t qualify for federal student loans?
Explore alternative options like private student loans, scholarships, grants, and work-study programs. Your school’s financial aid office can provide guidance.
How long does it take to process my FAFSA application?
Processing times vary, but you can generally expect a response within several weeks. Check your FAFSA status online regularly.
Can I apply for FAFSA after the deadline?
There are deadlines for each academic year. Late applications may impact your eligibility for certain funds. Check the official FAFSA website for deadlines.
