Navigating the world of student loans can feel overwhelming, especially when trying to understand the nuances of subsidized loans. This guide demystifies the application process, providing a clear path to securing the financial aid you need to pursue your educational goals. We’ll cover everything from eligibility requirements and completing the FAFSA form to understanding repayment plans and managing your debt effectively. Whether you’re a prospective student or a parent supporting a student’s education, this resource is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools for success.
Securing a subsidized student loan involves understanding your eligibility, diligently completing the FAFSA, and making informed decisions about loan types and repayment plans. This process requires careful planning and attention to detail, but the potential benefits—a smoother path to higher education—make the effort worthwhile. This guide breaks down each step, offering practical advice and resources to simplify the process and empower you to make the best choices for your financial future.
Completing the FAFSA Application
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the gateway to federal student financial aid, including subsidized loans. Completing it accurately and efficiently is crucial to securing the funding you need for your education. This section will guide you through the process, explaining each section and offering helpful tips.
The FAFSA is an online application requiring personal and financial information from both the student and their parents (if applicable). The information provided determines your eligibility for federal student aid, including grants, loans, and work-study programs. Accurate and complete information is essential for a successful application.
FAFSA Sections and Required Information
The FAFSA is organized into several sections, each requesting specific information. Providing accurate and complete information in each section is vital for a smooth application process. Inaccurate information can lead to delays or rejection of your application.
Key sections include student information (name, address, Social Security number, date of birth), parent information (if applicable, including their financial details), school information (the college or university you plan to attend), and financial information (income, assets, and tax information). You will need your tax returns (or access to the information contained within them) and other relevant financial documents to complete the application accurately.
Tips for Accurate and Efficient FAFSA Completion
Completing the FAFSA can seem daunting, but careful planning and attention to detail can make the process much smoother. Gathering all necessary documents beforehand is essential. This includes tax returns, W-2 forms, and bank statements. Double-checking all information before submitting the application is also crucial to prevent errors. Utilizing the IRS Data Retrieval Tool can significantly streamline the process by automatically transferring tax information from the IRS directly into your FAFSA.
It’s also wise to start the application early, as it often opens in October for the following academic year. This allows ample time to gather necessary information and address any potential issues. The FAFSA website offers helpful resources and FAQs to assist you throughout the process. Remember to keep a copy of your completed FAFSA for your records.
Step-by-Step FAFSA Completion Guide
The following table provides a visual step-by-step guide to completing the FAFSA application. Note that the specific screens and steps may vary slightly depending on updates to the FAFSA website. This guide is intended to illustrate the general process.
| Step | Action | Screenshot Description (Illustrative) | Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create an FSA ID | A screen showing a login page with fields for creating a username and password. A confirmation message would be shown after successful ID creation. | Choose a strong password and keep your FSA ID information secure. |
| 2 | Enter Student Information | A form with fields for student’s name, address, Social Security number, date of birth, and other personal details. | Double-check all information for accuracy. |
| 3 | Enter Parent Information (if applicable) | A similar form to step 2, but requesting information for the parents. This might include their tax information and income details. | If your parents are divorced or separated, specific instructions are available on the FAFSA website. |
| 4 | Enter School Information | A form with fields for the school’s name, address, and Federal School Code. | Use the school’s official name and Federal School Code. |
| 5 | Enter Financial Information | A section with questions regarding income, assets, and tax information. It might include fields for income, tax returns, and bank statements. | Use the IRS Data Retrieval Tool if possible to expedite the process and minimize errors. |
| 6 | Review and Submit | A summary page displaying all the entered information. A button to submit the application would be clearly visible. | Thoroughly review all information before submitting. Make any necessary corrections. |
Understanding Loan Types and Repayment Plans

Securing a subsidized federal student loan is a significant step towards financing your education. Understanding the different loan types and repayment options available is crucial for making informed decisions that minimize long-term debt. This section will clarify the key features of various subsidized federal student loans and the implications of selecting different repayment plans.
Federal Subsidized Stafford Loans
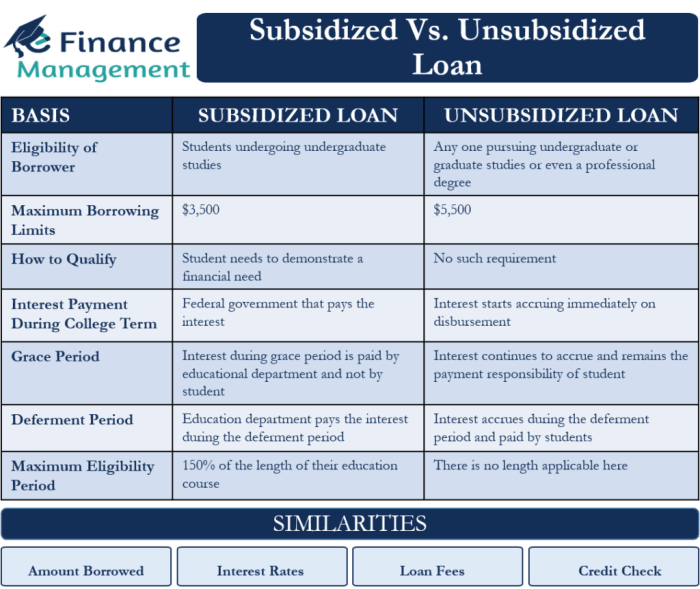
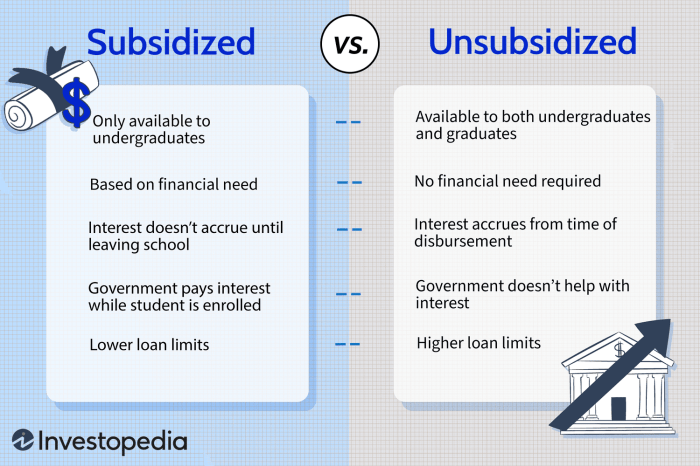
Federal Subsidized Stafford Loans are awarded based on financial need, as determined by the FAFSA. A key feature is that the government pays the interest on the loan while you’re in school at least half-time, during grace periods, and during periods of deferment. This means your loan balance doesn’t grow during these periods. The maximum loan amount varies depending on your year in school and your dependency status. These loans are generally the most favorable option for students with demonstrated financial need.
Federal Unsubsidized Stafford Loans
Unlike subsidized loans, unsubsidized Stafford Loans are not based on financial need. Interest accrues on the loan from the time it’s disbursed, regardless of your enrollment status. Borrowers are responsible for paying this accumulated interest, which can significantly increase the total amount owed if not addressed promptly. While these loans are available to all students regardless of financial need, they are generally less favorable than subsidized loans due to the accruing interest.
Repayment Plan Options
Choosing the right repayment plan significantly impacts the total cost and length of your loan repayment. Several plans exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Comparison of Repayment Plans
Understanding the long-term implications of different repayment plans requires careful consideration of your financial situation and future income projections. Choosing a shorter repayment term will lead to higher monthly payments but will result in less interest paid over the life of the loan. Conversely, a longer repayment term will result in lower monthly payments but will lead to a higher total interest paid. For example, a 10-year repayment plan for a $20,000 loan will have significantly higher monthly payments than a 20-year plan, but the total interest paid will be substantially lower.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate (Example – Rates Vary) | Repayment Options | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidized Stafford Loan | 3.73% (Example – Variable) | Standard, Extended, Graduated, Income-Driven | Interest subsidized during certain periods; need-based |
| Unsubsidized Stafford Loan | 5.28% (Example – Variable) | Standard, Extended, Graduated, Income-Driven | Interest accrues from disbursement; not need-based |
Managing Student Loan Debt
Successfully navigating student loan debt requires proactive planning and consistent effort. Understanding your loan terms, creating a realistic budget, and exploring available resources are crucial steps towards responsible repayment and financial well-being. Failing to manage debt effectively can have significant long-term consequences.
Strategies for Effective Student Loan Debt Management
Effective student loan debt management involves a multifaceted approach. Prioritizing repayment, exploring repayment plans, and consistently monitoring your progress are key elements. Budgeting is essential to ensure loan payments are integrated into your overall financial plan without compromising other necessities.
Budgeting and Prioritizing Loan Repayments
Creating a detailed budget is paramount to successful loan repayment. This involves tracking income and expenses to identify areas where spending can be reduced to allocate more funds towards loan payments. Prioritizing high-interest loans for repayment can significantly reduce the overall interest paid over the life of the loans, saving money in the long run. Consider using budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track your spending and progress towards your repayment goals. For example, a person earning $3000 per month might allocate $500 towards loan repayments, $1000 towards rent, $500 for groceries, and the remainder for other expenses. This illustrates a clear allocation of funds towards loan repayments within a realistic budget.
Consequences of Defaulting on Student Loans
Defaulting on student loans has severe repercussions. These consequences include damage to your credit score, wage garnishment, and difficulty obtaining future loans or credit. The government may also take legal action to recover the debt. In some cases, default can lead to the loss of professional licenses or eligibility for certain government benefits. For instance, a defaulted loan can significantly impact your ability to purchase a home or secure a car loan due to the negative impact on your credit history. This underscores the importance of consistent and timely repayment.
Resources for Students Facing Financial Hardship
Several resources exist to assist students facing financial difficulties related to loan repayment. These include income-driven repayment plans, which adjust monthly payments based on income and family size. Deferment or forbearance options may also be available, temporarily suspending or reducing payments during periods of financial hardship. Contacting your loan servicer to discuss your options and exploring government programs like the National Foundation for Credit Counseling can provide valuable support and guidance. For example, the Department of Education offers various repayment plans, such as the Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) plan, which caps monthly payments at 10% of discretionary income.
Seeking Financial Aid Advice
Navigating the world of student financial aid can be complex, and seeking expert guidance is often invaluable. A financial aid advisor can significantly simplify the process and help students make informed decisions about their funding options. Understanding the resources available and the benefits of professional advice is crucial for securing the best possible financial support for your education.
The Role of a Financial Aid Advisor in the Student Loan Application Process
Financial aid advisors act as navigators through the often-complicated landscape of student financial aid. They provide personalized guidance, helping students understand eligibility requirements, complete applications accurately, and explore various funding options. This includes assisting with the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) completion, understanding different loan types (subsidized, unsubsidized, private), and exploring grant and scholarship opportunities. They also help students understand repayment plans and manage their student loan debt effectively after graduation. Essentially, they act as a personalized resource, answering questions and providing support throughout the entire financial aid process.
Available Resources for Financial Aid Guidance
Many resources exist to assist students in securing financial aid. These resources vary in scope and accessibility, but all aim to provide support and information to help students make informed decisions. Utilizing these resources can significantly improve a student’s chances of securing sufficient funding for their education.
- Educational Institution Financial Aid Offices: Most colleges and universities have dedicated financial aid offices staffed with professionals who can provide personalized advice and assistance. They are often the first point of contact for students seeking financial aid. They offer expertise specific to the institution’s policies and available funding options.
- Federal Student Aid Website (studentaid.gov): This website is a comprehensive resource managed by the U.S. Department of Education. It offers information on federal student loans, grants, and other financial aid programs. The site provides detailed explanations of application processes, eligibility criteria, and repayment options.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Numerous nonprofit organizations provide financial aid counseling and resources. These organizations often specialize in assisting students from specific backgrounds or with particular financial needs. They can offer guidance on scholarship searches and application strategies, as well as broader financial literacy education.
- Private Financial Aid Consultants: While often requiring a fee, private financial aid consultants can provide highly personalized guidance and support. They can help students navigate complex financial aid applications and explore a wider range of funding opportunities, including scholarships and grants that might be overlooked.
Benefits of Seeking Professional Financial Aid Advice
Seeking professional advice offers several significant benefits in the student loan application process. A well-informed decision regarding student loans can save a student significant amounts of money and stress over the long term.
- Increased Access to Funding: Advisors can help students identify and apply for all available funding opportunities, including scholarships and grants that they might not have been aware of. This can lead to significantly reduced loan burdens.
- Reduced Loan Debt: By helping students understand different loan types and repayment plans, advisors can guide them towards the most cost-effective options, minimizing the total amount of debt accumulated.
- Improved Understanding of Financial Aid Processes: Navigating the complexities of financial aid can be daunting. Professional guidance simplifies the process, reducing stress and increasing confidence in the application and decision-making processes.
- Strategic Planning for Repayment: Advisors can help students develop a comprehensive repayment plan to manage their student loan debt effectively after graduation, minimizing potential financial hardship.
Illustrative Example of the Application Process
This example follows Sarah, a diligent student aiming for a degree in nursing, as she navigates the subsidized student loan application process. Her journey highlights the common steps and potential challenges faced by many students seeking financial aid.
Sarah, a bright and ambitious 18-year-old, recently graduated high school with excellent grades. She’s accepted into the nursing program at State University, a highly competitive and demanding course of study. However, the tuition fees are significantly higher than her family can afford. Her parents, while supportive, work modest jobs and have limited savings. Sarah understands that a subsidized student loan is her best option to pursue her dream career.
Initial Research and Application Preparation
Sarah begins by thoroughly researching different types of financial aid available. She visits the State University’s financial aid website, explores government resources like the Federal Student Aid website (studentaid.gov), and even attends a financial aid workshop offered by the university. This research helps her understand the nuances of subsidized loans versus unsubsidized loans, and the importance of completing the FAFSA accurately and on time. She learns about the required documentation, including tax returns, and begins gathering these essential documents.
Completing the FAFSA
Sarah meticulously completes the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) online. She carefully reviews each section, ensuring accuracy and providing all necessary information. She understands that any errors or omissions could delay the processing of her application. She uses the IRS Data Retrieval Tool to seamlessly transfer her tax information, minimizing the risk of errors. She also ensures that her parents’ information is correctly entered, as their financial details are crucial to determining her eligibility. After careful review, she electronically submits her FAFSA application.
Notification and Award Letter
Several weeks later, Sarah receives her Student Aid Report (SAR) from the FAFSA processor. She reviews it carefully, checking for any discrepancies. She then receives her financial aid award letter from State University, which Artikels the amount of subsidized loan she’s been awarded, along with any other grants or scholarships she qualified for. The award letter details the terms and conditions of the loan, including the interest rate, repayment schedule, and deferment options. She is relieved to see that the subsidized loan will significantly reduce her out-of-pocket expenses.
Loan Acceptance and Disbursement
Sarah accepts the offered subsidized loan by signing the master promissory note. This legally binds her to the terms of the loan agreement. The university then processes the loan, and the funds are disbursed directly to her account in installments, usually aligned with the academic terms. The funds cover her tuition fees, housing costs, and other educational expenses. This financial assistance allows Sarah to focus on her studies without the added stress of constant financial worries.
Managing Loan Repayment
Sarah understands the importance of managing her loan repayment effectively after graduation. She plans to start making payments as soon as possible after completing her studies. She explores different repayment plans to find one that best suits her future income and financial situation. She also researches loan forgiveness programs for nurses, as this may reduce her overall loan burden. This proactive approach helps ensure that she can manage her loan debt responsibly without jeopardizing her future financial well-being.
Ending Remarks

Applying for a subsidized student loan is a significant step toward achieving your educational aspirations. By carefully considering your eligibility, accurately completing the FAFSA, and understanding the various loan options and repayment plans, you can secure the financial support you need while minimizing long-term financial burdens. Remember to utilize available resources and seek guidance when necessary to navigate this process effectively and confidently. With careful planning and informed decision-making, you can successfully manage your student loan debt and pave the way for a brighter future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a subsidized and unsubsidized student loan?
With a subsidized loan, the government pays the interest while you’re in school (and sometimes during grace periods). Unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed.
What happens if I don’t complete the FAFSA?
You won’t be eligible for most federal student aid, including subsidized loans. This significantly limits your financial aid options.
Can I refinance my subsidized student loan?
Yes, but refinancing might lose you federal protections and could result in higher interest rates depending on your creditworthiness.
What if I can’t afford my student loan payments?
Contact your loan servicer immediately. They can discuss options like income-driven repayment plans or deferment/forbearance.
Where can I find more information about student loan forgiveness programs?
The Federal Student Aid website (studentaid.gov) is a great resource. You can also consult with a financial aid advisor.
