
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment and its impact on your credit score can feel daunting. Understanding how long student loan information remains on your credit report is crucial for long-term financial planning. This guide delves into the intricacies of student loan reporting, exploring the factors that influence reporting duration and offering strategies for managing your credit health effectively.
From the initial reporting of your loans to the eventual removal after repayment, we’ll clarify the timeline for various loan types and repayment statuses. We’ll also address common misconceptions and provide practical advice to help you proactively manage your student loan debt and its impact on your creditworthiness.
The Basics of Student Loan Reporting to Credit Bureaus
Understanding how student loans impact your credit score is crucial for financial planning. Your student loan repayment history is a significant factor in determining your creditworthiness. This section details the process of student loan reporting to credit bureaus, covering different loan types and their reporting timelines.
Student Loan Reporting to Credit Bureaus: The Process
Lenders, both private and government-backed, report your student loan information to the three major credit bureaus: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. This reporting typically begins once your loan enters repayment, although some lenders may report earlier. The lender transmits data including your loan amount, payment history (on-time or late payments), loan status (current, delinquent, defaulted), and the loan’s original and current balance. This information is then incorporated into your credit report, influencing your credit score. The frequency of reporting varies depending on the lender, but it’s usually monthly or quarterly. Consistent on-time payments contribute positively to your credit score, while missed or late payments can negatively affect it.
Types of Student Loans and Their Reporting
Different types of student loans have varying reporting procedures. Federal student loans, such as Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans, are generally reported to the credit bureaus once they enter repayment. Private student loans, offered by banks and other financial institutions, also follow a similar reporting process. However, the specific timing and frequency of reporting may differ between lenders. Federal Family Education Loans (FFEL) programs, while largely phased out, may still be reported depending on the servicing agency. It’s important to note that the reporting of defaulted loans will significantly impact your credit score.
Student Loan Reporting Timeline
The following table provides a general timeline for the reporting of different student loan types. Keep in mind that these are estimates, and the actual reporting timeline may vary depending on the lender and servicing agency. Also, it’s crucial to note that consistently on-time payments are vital regardless of the loan type for maintaining a positive credit history.
| Loan Type | Reporting Agency | Initial Reporting Time | Reporting Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Direct Loans (Subsidized & Unsubsidized) | Equifax, Experian, TransUnion | Typically within 1-3 months of entering repayment | Until the loan is paid in full |
| Private Student Loans | Equifax, Experian, TransUnion | Typically within 1-3 months of disbursement or entering repayment (varies by lender) | Until the loan is paid in full |
| Federal Family Education Loans (FFEL) | Equifax, Experian, TransUnion | Varies depending on the lender and servicer; generally within 1-3 months of entering repayment | Until the loan is paid in full |
Factors Affecting How Long Student Loans Appear on Credit Reports
The length of time student loans remain on your credit report isn’t fixed; several factors influence how long this information is visible to potential lenders and creditors. Understanding these factors is crucial for managing your credit effectively and planning your financial future. The primary determinant is your repayment history, but other significant events can also impact the reporting timeline.
Loan Repayment Status and Credit Report Duration
Your repayment history is the most significant factor influencing how long student loan information appears on your credit report. Consistent on-time payments demonstrate responsible credit management, and while the information will remain visible for seven years from the date of the last payment (or the date of the account closure if it’s paid in full), it will generally have a positive impact on your credit score. Conversely, late payments or defaulting on your loan will extend the negative impact on your credit report for a longer period. A defaulted loan, in particular, can remain on your report for seven years from the date of the default, significantly impacting your creditworthiness during that time. Even after seven years, the negative impact might still be seen by some lenders who use more extensive credit scoring models.
The Effect of Loan Consolidation on Reporting Timelines
Consolidating your student loans into a single loan can affect how long the information appears on your credit report. While the original loans will remain on your report, the consolidated loan will be reported as a new account. This means that the negative history associated with past-due payments on individual loans might be less visible than it would be if the loans were not consolidated, however, any late payments made on the consolidated loan itself will be reported as such. The consolidated loan’s reporting period will start anew from the date of the consolidation. The original loans’ reporting timelines are unaffected.
Other Factors Affecting Student Loan Visibility on Credit Reports
Several other factors can influence the duration of student loan reporting. Bankruptcy, for instance, can significantly impact your credit report. While student loans are often difficult to discharge through bankruptcy, the bankruptcy filing itself will be reported on your credit report for 10 years. Death also affects reporting; after a borrower’s death, the information might remain on the report until the debt is settled or the account is closed, depending on the specifics of the loan and any co-signers. These events can significantly complicate credit reporting timelines.
Student Loan Repayment and Credit Report Removal
Paying off your student loans is a significant financial achievement, and understanding how this impacts your credit report is crucial. Once your loans are paid in full, the information will eventually be removed from your credit report, improving your credit score over time. However, the process isn’t instantaneous, and there are several factors that influence the timeline.
Student loan repayment and the subsequent removal from your credit report is a relatively straightforward process, but it requires understanding the reporting timelines and verification methods. The length of time a paid student loan remains on your report depends on several factors, including the lender and the reporting agencies. This section will clarify these aspects and provide practical steps for verification.
Student Loan Payoff Process and Credit Reporting
Paying off your student loans involves making consistent, timely payments until the full balance is zero. This can be achieved through various repayment plans, each with its own terms and conditions. Once the final payment is processed and confirmed by your lender, they will report the status of your loan to the credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion). The credit bureaus then update your credit report to reflect the “paid” status of the loan. It’s important to note that this update is not immediate and can take several weeks or even months. Many lenders utilize automated systems, but occasional manual intervention might cause delays. For example, a large national lender might take 45-60 days to update its records, whereas a smaller institution might be faster.
Verifying Student Loan Removal from Credit Reports
After paying your student loans in full, it’s essential to verify that the information has been accurately updated on your credit reports. This involves checking your credit report with each of the three major credit bureaus. You can obtain free credit reports annually from AnnualCreditReport.com. This website is the only authorized source for free credit reports from the three bureaus, avoiding potentially fraudulent sites. When reviewing your reports, look for the entry related to your student loan. It should indicate a “paid” or “closed” status and should not negatively impact your credit score. If the loan is still listed as outstanding or negatively affecting your score after a reasonable period (typically 60-90 days after payment confirmation), contact your lender and the credit bureaus to investigate the discrepancy and request a correction.
Typical Timeframe for Student Loan Removal
While there’s no universally set timeframe, most paid student loans are removed from credit reports within seven years of the loan’s closure. This is the standard period for most negative credit information, although some lenders may update their reports sooner. However, it’s crucial to remember that the “paid” status will remain visible on your report for seven years even though the account is closed. This “paid” status is positive credit history and should benefit your credit score. It’s not a negative mark; it simply reflects your past financial activity. For example, if you paid off your student loans in 2024, the “paid” status would typically remain on your report until at least 2031.
Student Loan Repayment and Credit Report Update Flowchart
The flowchart would visually represent the following steps:
1. Make consistent loan payments: This would be the starting point, represented by a rectangle.
2. Final payment processed: Another rectangle indicating the completion of payments.
3. Lender reports to credit bureaus: A diamond shape indicating a decision point or action.
4. Credit bureaus update reports: A rectangle showing the update process.
5. Verify report updates (AnnualCreditReport.com): A rectangle representing the verification step.
6. Loan removed after 7 years (Paid status remains): A terminal point, indicating the end of the process. The flow would move from one step to the next, with arrows indicating the direction. The flowchart would visually clarify the sequential steps and timelines involved.
The Impact of Negative Student Loan Information on Credit Scores

Student loan debt significantly impacts your credit score, and managing it responsibly is crucial for maintaining good financial health. Negative information related to your student loans, such as late payments or defaults, can severely damage your creditworthiness, making it harder to obtain loans, rent an apartment, or even secure certain jobs. Understanding how this negative information affects your credit and employing strategies to mitigate the damage is essential.
Late Payments, Defaults, and Collections Impact on Credit Scores
Late payments on your student loans are reported to the credit bureaus, negatively affecting your credit score. The severity of the impact depends on the frequency and duration of the late payments. A single late payment might cause a minor dip, but consistent late payments can significantly lower your score. Defaulting on your student loans, which occurs when you fail to make payments for an extended period, results in a much more severe drop in your score. Furthermore, if your debt is sent to collections, this negative mark remains on your credit report for seven years, considerably impacting your creditworthiness. The impact of these negative events is substantial and can affect your ability to obtain favorable interest rates on future loans. For example, a consistent pattern of 30-60 day late payments could drop your FICO score by 50-100 points or more. A default can result in a significantly larger drop, often exceeding 100 points.
Long-Term Consequences of Negative Student Loan Information
The long-term consequences of negative student loan information extend far beyond a temporary dip in your credit score. A damaged credit history can make it challenging to secure loans with favorable interest rates, resulting in higher borrowing costs in the future. This could affect major life decisions such as purchasing a home or a car. It may also affect your ability to rent an apartment, as many landlords conduct credit checks. In some cases, employers may also consider credit reports during the hiring process, potentially impacting your job prospects. For instance, someone with a history of student loan defaults may find themselves paying significantly higher interest rates on a mortgage, potentially adding tens of thousands of dollars to the overall cost of their home.
Strategies for Mitigating the Negative Impact of Delinquent Student Loans
Addressing delinquent student loans requires proactive steps to minimize the long-term damage. Contacting your loan servicer immediately to discuss repayment options is crucial. They may offer hardship programs, income-driven repayment plans, or forbearance, which can temporarily suspend or reduce payments. Negotiating a repayment plan that fits your budget can prevent further negative marks on your credit report. Keeping open communication with your lender and demonstrating a commitment to repayment is key. Furthermore, if your debt has already been sent to collections, contacting the collection agency to negotiate a settlement can potentially reduce the amount owed and remove the negative mark from your report more quickly.
Strategies to Improve Credit Score After Negative Student Loan History
Improving your credit score after experiencing negative student loan history takes time and consistent effort. The following strategies can help:
- Consistent On-Time Payments: Make all future payments on time, every time. This demonstrates responsible financial behavior and helps rebuild your credit history.
- Lower Credit Utilization: Keep your credit card balances low, ideally below 30% of your available credit. High utilization negatively impacts your credit score.
- Maintain Diverse Credit Accounts: Having a mix of credit accounts, such as credit cards and installment loans, can demonstrate responsible credit management.
- Monitor Your Credit Reports: Regularly check your credit reports from all three major bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) to identify and address any errors.
- Consider Credit Counseling: A reputable credit counseling agency can help you create a budget and develop a plan to manage your debt effectively.
Resources and Further Information
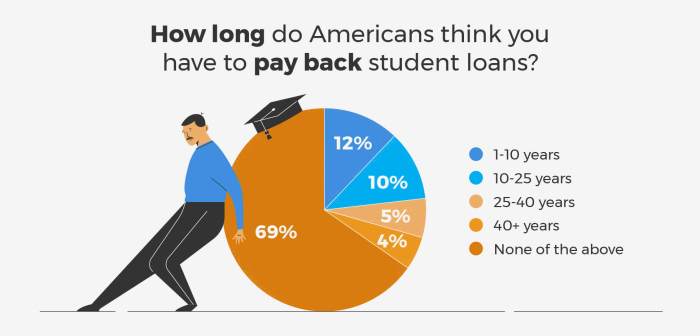
Navigating the complexities of student loans and their impact on your credit report can be challenging. Fortunately, numerous resources are available to help you understand your rights, manage your debt effectively, and ensure the accuracy of your credit information. This section provides details on accessing reliable information, disputing inaccuracies, and obtaining your credit report.
Understanding your options and utilizing available resources is crucial for maintaining a healthy credit profile. Proactive management of your student loan information can significantly impact your financial future.
Accessing Reliable Information on Student Loan Management and Credit Reports
Several reputable organizations offer comprehensive and reliable information on student loan management and credit reports. These resources provide guidance on repayment options, credit repair strategies, and understanding your credit score. They often include educational materials, tools, and calculators to assist you in making informed decisions.
Disputing Inaccurate Student Loan Information with Credit Bureaus
If you discover inaccurate information regarding your student loans on your credit report, you have the right to dispute it. Each credit bureau (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) has a process for submitting a dispute. This typically involves submitting a written request detailing the inaccuracies and providing supporting documentation. It’s important to keep records of all communication and responses from the credit bureaus. Failure to resolve the dispute may necessitate seeking legal counsel.
Obtaining and Reviewing Your Free Credit Report
Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), you are entitled to a free copy of your credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus annually. You can obtain these reports through AnnualCreditReport.com, the only authorized website for free credit reports. Carefully review your report for any inaccuracies, including student loan information. Discrepancies should be promptly disputed following the process Artikeld by the respective credit bureau.
Relevant Government Websites and Consumer Credit Agencies
| Resource Name | Website URL | Description | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| AnnualCreditReport.com | www.annualcreditreport.com | Obtain your free annual credit reports from all three major credit bureaus. | (Not applicable; website provides contact information as needed) |
| Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) | www.consumerfinance.gov | Provides resources and information on consumer financial protection, including student loans and credit reports. | (Contact information available on their website) |
| Federal Student Aid (FSA) | studentaid.gov | The U.S. Department of Education’s website for managing federal student loans. | (Contact information available on their website) |
| Equifax | www.equifax.com | One of the three major consumer credit reporting agencies. | (Contact information available on their website) |
| Experian | www.experian.com | One of the three major consumer credit reporting agencies. | (Contact information available on their website) |
| TransUnion | www.transunion.com | One of the three major consumer credit reporting agencies. | (Contact information available on their website) |
Ultimate Conclusion

Successfully managing student loan debt is a significant step towards building a strong financial future. By understanding the intricacies of how student loans affect your credit report and employing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can navigate this process confidently. Remember to regularly monitor your credit report for accuracy and proactively address any issues that may arise. Proactive management and a clear understanding of the process will contribute significantly to your long-term financial well-being.
Clarifying Questions
What happens if I miss a student loan payment?
Missing payments will negatively impact your credit score and extend the time the loan appears on your report. It may also lead to collection actions.
Can I dispute inaccurate information on my credit report regarding student loans?
Yes, you can contact the credit bureaus directly to dispute any inaccuracies. Provide documentation to support your claim.
Does bankruptcy affect how long student loans stay on my credit report?
Bankruptcy can significantly impact the reporting timeline, often extending the duration. The specifics depend on the type of bankruptcy filed.
How long does it take for a paid student loan to be removed from my credit report after repayment?
Generally, it takes seven years from the date of repayment for a paid student loan to be removed. However, this can vary slightly depending on the reporting agency and other factors.

convert vhs tapes