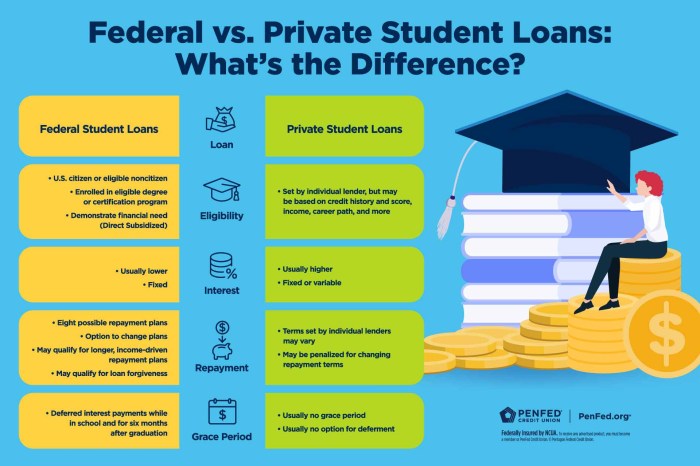
Navigating the world of student loans can feel overwhelming, a labyrinth of interest rates, repayment plans, and lender options. This guide aims to simplify the process, empowering you to make informed decisions about financing your education. From understanding your eligibility and exploring different loan types to avoiding potential scams and planning for repayment, we’ll cover all the essential steps to ensure a smooth and successful journey.
We’ll delve into the key differences between federal and private loans, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each. You’ll learn how to compare lenders, understand loan terms, and create a realistic repayment budget. Crucially, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to identify and avoid predatory lending practices, protecting your financial well-being.
Completing the Loan Application Process

Securing student loans can seem daunting, but understanding the application process and necessary steps can significantly simplify the experience. This section details the requirements and procedures involved in obtaining federal and private student loans, emphasizing efficient and accurate completion. We will cover the necessary documentation, the FAFSA application, and provide a checklist to guide you through the process.
The student loan application process generally involves several key steps, regardless of whether you are applying for federal or private loans. First, you’ll need to gather all the required documentation, which can vary depending on the lender. Then, you will complete the application itself, ensuring accuracy in every detail. Finally, you will submit the application and await processing and approval. This process can take several weeks, so starting early is crucial.
Required Documentation for Student Loan Applications
Gathering the necessary documents before beginning the application is vital to streamline the process. Lenders typically require proof of identity, such as a driver’s license or passport. You’ll also need your Social Security number and tax information (including your tax returns or W-2 forms, if applicable). For federal loans, your FAFSA data will be used to verify your financial information. Private lenders may require additional financial documentation, such as bank statements or proof of income from parents or guardians (if applicable). Accurate and complete documentation ensures a faster processing time.
Completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA)
The FAFSA is the gateway to federal student aid, including federal student loans. Completing it accurately and efficiently is crucial. Begin by creating an FSA ID, which is your unique username and password for accessing the FAFSA website. Then, gather the required information, including your Social Security number, tax information (yours and your parents’, if you are a dependent student), and information about your assets. Double-check all the information entered to avoid delays caused by errors. The FAFSA website provides detailed instructions and helpful resources to guide you through the process. Submitting the FAFSA early is highly recommended, as many aid programs are awarded on a first-come, first-served basis.
Step-by-Step Checklist for a Smooth Application Process
A well-organized approach significantly reduces stress and potential errors. This checklist provides a structured approach to the application process:
- Gather all required documentation (identification, Social Security number, tax information, bank statements, etc.).
- Complete the FAFSA (or equivalent application for private loans) accurately and thoroughly. Review and double-check all information before submitting.
- Submit your application and any supporting documents to the lender(s).
- Monitor your application status online or via phone, as needed.
- Once approved, review the loan terms and conditions carefully before accepting the loan.
- Understand your repayment options and plan accordingly.
Following this checklist will help ensure a smooth and efficient application process. Remember to allow ample time for each step, and don’t hesitate to seek assistance if needed. Contacting the financial aid office at your school or the lender directly can provide valuable support.
Planning for Repayment

Successfully navigating student loan repayment requires careful planning and proactive strategies. Understanding your repayment options and creating a realistic budget are crucial steps to minimize the long-term financial impact of your debt. This section will explore effective methods for budgeting, strategies for minimizing debt’s influence on your future, and illustrate the effects of different repayment plans.
Creating a Realistic Repayment Budget
Developing a realistic repayment budget involves assessing your income, expenses, and loan details. Start by calculating your monthly net income (income after taxes and deductions). Then, meticulously list all your monthly expenses, including housing, transportation, food, utilities, and entertainment. Subtract your total monthly expenses from your net income to determine your disposable income – the amount available for loan repayment. Allocate a portion of this disposable income to your student loan payments, ensuring the amount is manageable without compromising your essential living expenses. Consider using budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track your income and expenses effectively. Remember to factor in unexpected expenses, building a small buffer into your budget for emergencies.
Strategies for Minimizing the Impact of Student Loan Debt
Several strategies can help minimize the long-term effects of student loan debt. Prioritizing high-interest loans for early repayment can significantly reduce the overall interest paid. Exploring income-driven repayment plans can lower monthly payments, although it might extend the repayment period and increase total interest paid over time. Consolidating multiple loans into a single loan can simplify repayment and potentially lower the interest rate. Furthermore, actively seeking opportunities for professional development and higher-paying jobs can increase your earning potential, allowing for faster debt repayment. Finally, maintaining a strong credit score is crucial, as it can influence your access to future financial products and potentially better interest rates on loans.
Sample Repayment Schedule
The following table demonstrates the impact of different repayment plans on a hypothetical $30,000 student loan with a 6% interest rate. The examples illustrate the trade-offs between monthly payment amounts and total interest paid. These figures are for illustrative purposes only and actual repayment amounts will vary based on individual loan terms and repayment plans.
| Repayment Plan | Monthly Payment | Loan Term (Years) | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard 10-Year Plan | $330.38 | 10 | $9645.60 |
| Extended 15-Year Plan | $239.75 | 15 | $14355.00 |
| Income-Driven Plan (Example) | $150 (Assumed) | 20-25 (Variable) | $18000+ (Variable) |
Epilogue

Securing student loans shouldn’t be a daunting task. By carefully considering your needs, researching loan options, and understanding the application process, you can confidently navigate the complexities of financing your education. Remember to always read the fine print, compare offers meticulously, and prioritize responsible borrowing to pave the way for a brighter financial future. Taking the time to understand these crucial aspects will set you up for success, both academically and financially.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a subsidized and unsubsidized federal loan?
With subsidized loans, the government pays the interest while you’re in school (under certain conditions). Unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed, even while you’re studying.
Can I refinance my student loans?
Yes, refinancing can lower your interest rate and monthly payments, but it might involve switching from a federal to a private loan, potentially losing certain benefits like income-driven repayment plans.
What happens if I miss a student loan payment?
Missing payments can severely damage your credit score, lead to late fees, and potentially result in default, which has serious long-term consequences.
What is loan forgiveness?
Loan forgiveness programs, such as those for public service, can eliminate a portion or all of your student loan debt under specific circumstances and after meeting certain requirements.
How can I find a reputable student loan lender?
Check the lender’s licensing and accreditation, read online reviews, and compare interest rates and terms from multiple sources before committing to a loan.
