
Navigating the world of student loans can feel overwhelming, especially with the sheer number of lenders and loan options available. Choosing the right lender is crucial, as it directly impacts your repayment terms, overall cost, and overall borrowing experience. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to make an informed decision, ensuring you find a student loan that aligns perfectly with your financial needs and future goals.
We’ll explore the key differences between federal and private loans, delve into interest rates and fees, and examine various repayment options. We’ll also guide you through the process of researching lenders, verifying their legitimacy, and understanding the often-overlooked fine print. Ultimately, our aim is to empower you to become a savvy borrower, capable of making smart financial choices that set you up for success.
Repayment Options and Plans
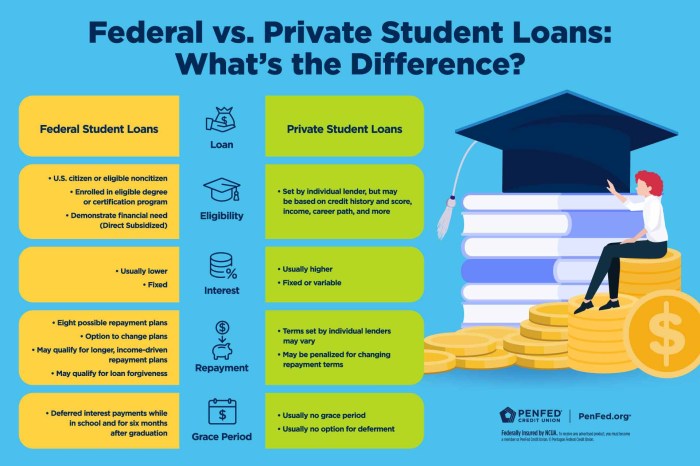
Choosing a student loan lender involves understanding the repayment options available. The repayment terms significantly impact your overall loan cost and your monthly budget. Federal and private loans offer different repayment structures, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Careful consideration of these options is crucial for responsible borrowing.
Federal Student Loan Repayment Plans
Federal student loans offer several repayment plans designed to accommodate various financial situations. The standard repayment plan is the most common, while others, such as graduated and extended plans, provide more flexibility. Understanding these options is vital for managing your debt effectively. The specific terms and conditions can vary slightly depending on the loan type (e.g., subsidized vs. unsubsidized).
Private Student Loan Repayment Options
Private student loan repayment plans typically offer less flexibility than federal loan options. Private lenders often provide a standard repayment plan with a fixed monthly payment and loan term. While some may offer graduated repayment, the terms and conditions are usually less favorable than those available through federal programs. Borrowers should carefully review the terms and conditions of any private loan before signing. Factors such as prepayment penalties and variable interest rates can significantly affect the total cost of the loan.
Comparison of Repayment Plans
The following table compares typical repayment plans for federal and private student loans. Note that these are examples and actual terms may vary depending on the lender and individual loan agreement. It is crucial to obtain detailed information directly from your lender.
| Repayment Plan | Monthly Payment | Loan Term (Years) | Total Interest Paid (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Standard Repayment | Fixed; Calculated based on loan amount and interest rate | 10 | Varies significantly based on loan amount and interest rate; generally lower than other plans due to shorter repayment period. Example: A $20,000 loan at 5% interest could result in approximately $4,000 in total interest. |
| Federal Graduated Repayment | Starts low and increases over time | 10 | Generally higher than standard repayment due to longer periods of lower payments and accumulating interest. Example: A $20,000 loan at 5% interest could result in approximately $5,000 to $6,000 in total interest. |
| Federal Extended Repayment | Lower monthly payments than standard repayment | Up to 25 | Significantly higher than standard repayment due to the extended repayment period and accumulating interest. Example: A $20,000 loan at 5% interest could result in approximately $8,000 to $10,000 in total interest. |
| Private Standard Repayment | Fixed; Determined by loan amount, interest rate, and loan term | Typically 5-15 | Varies based on loan amount, interest rate, and loan term. Example: A $20,000 loan at 7% interest over 10 years could result in approximately $6,000 in total interest. |
Customer Service and Support
Choosing a student loan lender involves more than just interest rates and repayment plans; the quality of customer service is paramount throughout the loan lifecycle. Navigating the complexities of student loans can be stressful, and having reliable support readily available can significantly ease the burden. A lender’s commitment to excellent customer service is a crucial factor to consider when making your decision.
The availability and responsiveness of a lender’s customer support channels are key indicators of their commitment to borrowers. Prompt and helpful responses to inquiries, efficient resolution of issues, and a generally positive and supportive interaction are hallmarks of excellent customer service in this context. Easy access to support through multiple channels allows borrowers to choose the method most convenient for them, fostering a positive and efficient experience.
Customer Support Channels
Effective communication is crucial for a positive borrowing experience. Borrowers need multiple avenues to reach their lender with questions, concerns, or issues. A lender should provide readily accessible support through phone, email, and online chat. Phone support offers immediate assistance and allows for more complex issues to be addressed efficiently. Email allows for detailed inquiries and provides a record of communication. Online chat offers a convenient, quick way to address less complex questions. The availability of 24/7 support, or at least extended hours, is also a significant advantage, especially for borrowers in different time zones or those with busy schedules.
Examples of Positive and Negative Customer Service Experiences
Positive experiences often involve prompt responses to inquiries, empathetic and helpful representatives who clearly explain complex information, and efficient resolution of problems. For example, a borrower might describe a positive experience where a representative quickly resolved an issue with their payment, proactively alerted them to potential problems, or provided clear and understandable explanations regarding their loan terms. Conversely, negative experiences might involve long wait times on hold, unhelpful or rude representatives, difficulty reaching someone by phone or email, or slow responses to critical issues. A borrower might recall a negative experience where they spent hours on hold only to receive unhelpful or dismissive responses, or where their requests for clarification went unanswered for extended periods. These experiences highlight the importance of researching a lender’s reputation for customer service before committing to a loan.
Hidden Costs and Fine Print

Securing a student loan is a significant financial commitment, and understanding the complete cost picture is crucial. While the advertised interest rate is a key factor, overlooking the fine print can lead to unexpected expenses and a higher overall debt burden. Carefully reviewing your loan agreement before signing is paramount to avoid unpleasant surprises down the line.
Before you sign on the dotted line, thoroughly examine the loan agreement for any hidden fees or terms that could impact your repayment. Many lenders include costs beyond the principal and interest, and these can significantly increase your total borrowing costs. Understanding these fees and how they are calculated will empower you to make an informed decision and choose the most financially responsible loan option.
Common Hidden Costs
Several fees are often buried within the loan agreement’s fine print. These can include origination fees (a percentage of the loan amount charged upfront), late payment fees, and prepayment penalties (fees charged for paying off the loan early). Some lenders also charge for things like electronic payments or for accessing your account information online. These seemingly small charges can accumulate over time, adding considerably to the total cost of your loan. For example, a 1% origination fee on a $10,000 loan adds $100 to your initial debt, while a $25 late payment fee, incurred several times, can quickly mount up.
Interpreting Key Terms and Conditions
Let’s consider a hypothetical example of a student loan agreement excerpt. Imagine a clause stating: “A late payment fee of $25 will be assessed for any payment received more than 15 days past the due date. A prepayment penalty of 1% of the outstanding principal balance will apply if the loan is repaid in full within the first two years.” This clearly indicates that any payment delayed beyond the 15-day grace period will result in a $25 fee, and repaying the loan early might incur a 1% penalty of the remaining loan amount.
Another common clause to watch for involves interest capitalization. This is when accrued interest is added to the principal balance, increasing the total amount you owe. For instance, if your loan agreement states that interest capitalizes annually, the interest accrued during the first year will be added to the principal, and subsequent interest calculations will be based on this higher amount. Understanding this can significantly impact the overall cost of your loan over its lifetime. Consider the effect of interest capitalization on a $20,000 loan with a 5% annual interest rate. If the interest capitalizes annually, the effective interest rate over the loan’s term could be higher than 5%, making a significant difference in the total amount repaid.
Financial Literacy and Budgeting

Managing student loan debt effectively requires a strong understanding of personal finance and a well-structured budget. Ignoring these crucial aspects can lead to significant financial stress and potential default. This section provides guidance on creating a realistic budget that incorporates loan repayments and strategies for managing your debt responsibly.
Creating a realistic budget is the cornerstone of responsible financial management, especially when dealing with student loan repayments. It involves carefully tracking your income and expenses to understand where your money is going and identifying areas where you can save. This process allows you to allocate funds for essential needs, loan repayments, and even some discretionary spending, preventing financial hardship.
Budget Creation and Loan Repayment Incorporation
Begin by listing all sources of income, including part-time jobs, scholarships, grants, and any financial support from family. Then, meticulously track your expenses. Categorize them into necessities (rent, utilities, groceries), transportation, education-related costs (textbooks, supplies), and discretionary spending (entertainment, dining out). Use budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or even a simple notebook to maintain a clear record. Once you have a comprehensive picture of your income and expenses, allocate a specific amount each month towards your student loan repayment. This amount should be realistic and manageable, considering your other financial commitments. Remember to factor in any potential increases in expenses or decreases in income.
Strategies for Effective Student Loan Debt Management
Several strategies can help you manage student loan debt effectively and avoid financial hardship. Prioritizing high-interest loans for repayment can save you money in the long run. Exploring options like income-driven repayment plans can adjust your monthly payments based on your income, making them more manageable during periods of lower earnings. Furthermore, consistent and timely payments demonstrate financial responsibility and help maintain a good credit score. Regularly reviewing your budget and adjusting it as needed is essential to adapt to changing circumstances.
Resources and Tools for Improving Financial Literacy
Numerous resources are available to enhance your financial literacy and improve your ability to manage student loan debt. Many universities offer free workshops and seminars on personal finance. Online resources such as the National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC) and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) provide valuable information and tools for budgeting, debt management, and credit counseling. These resources can offer personalized guidance and support to navigate the complexities of student loan repayment and improve your overall financial well-being. Utilizing these resources empowers you to make informed financial decisions and build a strong financial future.
Closing Summary
Securing a student loan is a significant financial commitment, and understanding the intricacies of the process is paramount. By carefully considering your individual needs, researching lenders thoroughly, and critically evaluating loan terms, you can confidently choose a lender that best supports your educational aspirations. Remember, responsible borrowing habits and financial literacy are key to managing your student loan debt effectively and achieving long-term financial well-being. Take your time, ask questions, and choose wisely.
Q&A
What is the difference between a co-signer and an endorser?
A co-signer shares responsibility for loan repayment, while an endorser typically only guarantees repayment if the borrower defaults.
Can I refinance my student loans?
Yes, refinancing can lower your interest rate and monthly payments, but it often involves switching from federal to private loans, potentially losing federal protections.
What happens if I miss a student loan payment?
Late payments can result in late fees, damage your credit score, and potentially lead to loan default, impacting your financial future significantly.
What is loan forgiveness?
Loan forgiveness programs, typically offered for federal loans, can eliminate your debt under specific circumstances, such as working in public service.
How do I check my credit score?
You can access your credit score through various credit reporting agencies (like Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion) or through some financial institutions.
