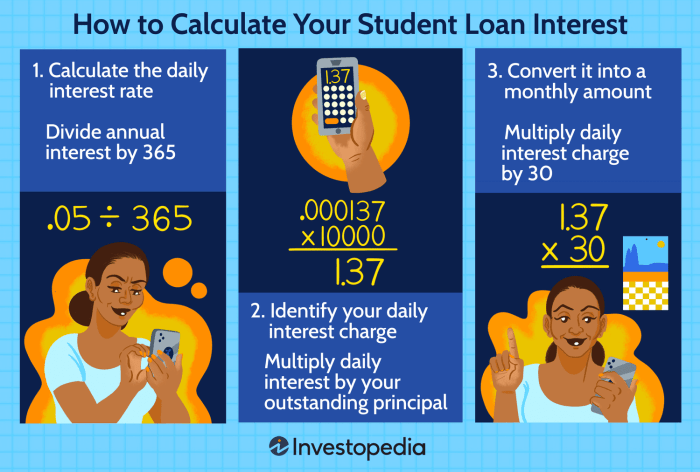
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment often feels like deciphering a financial code. Understanding interest rates is paramount to making informed decisions and avoiding potential pitfalls. This guide provides a clear and concise explanation of student loan interest rates, how to utilize interest rate calculators effectively, and strategies for minimizing your overall loan cost. We’ll explore fixed versus variable rates, the impact of different repayment plans, and factors influencing your interest rate.
From understanding the mechanics of interest capitalization to exploring various repayment strategies, we aim to empower you with the knowledge needed to manage your student loans confidently. We’ll demystify the often-confusing world of student loan finance, providing practical tools and insights to help you achieve your financial goals.
Understanding Student Loan Interest Rates
Understanding student loan interest rates is crucial for effectively managing your debt and minimizing long-term costs. The interest rate determines how much your loan balance grows over time, significantly impacting the total amount you’ll repay. This section will clarify the different types of rates and how they affect your repayment.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
Student loans typically come with either fixed or variable interest rates. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan’s life, providing predictable monthly payments. Conversely, a variable interest rate fluctuates based on an underlying benchmark index, such as the prime rate or LIBOR (although LIBOR is being phased out). This means your monthly payments could increase or decrease over time, depending on market conditions.
Interest Capitalization
Interest capitalization is the process of adding accumulated interest to the principal loan balance. This typically occurs when you have a grace period (a period after graduation before repayment begins) or during periods of deferment (temporary suspension of payments). Capitalization increases the principal amount, leading to higher total interest payments over the life of the loan. For example, if you have $10,000 in accumulated interest during a deferment period, that amount is added to your principal, increasing the total amount you owe and, consequently, the amount of interest that accrues on that larger amount going forward.
Illustrative Examples of Interest Rate Effects
Let’s consider two scenarios to illustrate the impact of different interest rates on total loan costs. Assume a $20,000 student loan with a 10-year repayment period.
Scenario 1: Fixed interest rate of 5%. Over 10 years, the total interest paid would be approximately $4,700, resulting in a total repayment of roughly $24,700.
Scenario 2: Variable interest rate starting at 4%, but increasing to 7% over the 10-year period. The total interest paid could be significantly higher, potentially exceeding $7,000, leading to a total repayment of over $27,000. This illustrates the risk associated with variable rates; while potentially lower initially, they can lead to substantially higher overall costs.
Comparison of Fixed and Variable Interest Rates
| Feature | Fixed Interest Rate | Variable Interest Rate | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rate | Stays the same throughout the loan term | Fluctuates based on a benchmark index | Predictable vs. unpredictable monthly payments |
| Monthly Payment | Consistent | Can increase or decrease | Budget planning certainty vs. uncertainty |
| Total Interest Paid | Generally predictable | Potentially higher or lower depending on market fluctuations | Lower risk of unexpectedly high total cost vs. higher risk |
| Risk | Low | High | Predictable repayment vs. potential for increased repayment burden |
Using an Interest Rate Calculator

Understanding how student loan interest works is crucial for effective financial planning. A student loan interest rate calculator is a valuable tool that simplifies this process, providing clear projections of your loan’s total cost and repayment schedule. By inputting key information, you can quickly compare different repayment options and make informed decisions.
Student loan interest rate calculators require several key inputs to generate accurate estimations. These inputs allow the calculator to model your unique loan situation and provide personalized results. The primary inputs are the loan amount, the annual interest rate, and the loan repayment period (term).
Key Inputs for Student Loan Interest Rate Calculators
The accuracy of the calculator’s projections depends heavily on the precision of these inputs. Incorrect or incomplete data will lead to inaccurate results, potentially affecting your financial planning. Let’s examine each input in detail.
- Loan Amount: This is the total principal amount borrowed for your student loans. It’s crucial to include all federal and private student loans in your calculation for a comprehensive overview.
- Interest Rate: This is the annual percentage rate (APR) charged on your loan. It’s essential to use the precise interest rate provided by your lender, not an estimated rate. Note that interest rates can vary depending on the type of loan and your creditworthiness.
- Repayment Period (Loan Term): This refers to the total time you have to repay the loan, typically expressed in months or years. Different repayment plans will offer varying loan terms.
Using a Typical Student Loan Interest Rate Calculator
Most calculators follow a similar process. While the specific layout might vary slightly, the underlying principles remain consistent. Below is a step-by-step guide illustrating a typical usage scenario.
- Find a Reliable Calculator: Numerous online calculators are available; ensure you select a reputable source to guarantee accuracy.
- Input Loan Details: Enter the loan amount, interest rate (as a percentage), and the loan term (in years or months), as specified by your lender.
- Select Repayment Plan: Choose the repayment plan that best suits your financial situation. Most calculators offer options like standard, extended, and income-driven repayment plans (detailed below).
- Review Results: The calculator will display the estimated total interest paid, the monthly payment amount, and the total repayment cost (principal plus interest).
Repayment Plan Options
Understanding the different repayment plan options is crucial for making informed decisions about your student loan repayment strategy. Each plan has its advantages and disadvantages, and the best option will depend on your individual circumstances.
- Standard Repayment Plan: This is typically a fixed monthly payment plan over a 10-year period. It results in the lowest total interest paid but requires higher monthly payments.
- Extended Repayment Plan: This plan extends the repayment period, usually to 25 years, resulting in lower monthly payments. However, it leads to a significantly higher total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plan: These plans (such as ICR, PAYE, REPAYE) base your monthly payments on your income and family size. Monthly payments are typically lower, but the repayment period is often longer, resulting in higher total interest payments.
Sample User Interface for a Student Loan Interest Rate Calculator
A well-designed calculator interface should be intuitive and easy to use. Below is a description of a sample user interface.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Loan Amount | Input field for the total loan amount (e.g., $20,000) |
| Annual Interest Rate | Input field for the annual interest rate (e.g., 6%) |
| Loan Term (Years) | Input field for the loan term in years (e.g., 10) |
| Repayment Plan | Dropdown menu with options: Standard, Extended, Income-Driven (ICR, PAYE, REPAYE – if applicable) |
| Calculate | Button to initiate the calculation |
| Monthly Payment | Output field displaying the calculated monthly payment |
| Total Interest Paid | Output field displaying the total interest paid over the loan term |
| Total Repayment Cost | Output field displaying the total repayment cost (principal + interest) |
Impact of Interest Rates on Repayment

Understanding how interest rates affect your student loan repayment is crucial for effective financial planning. Even small differences in interest rates can significantly impact the total amount you pay over the life of your loan. This section will explore the relationship between interest rates and repayment, demonstrating the importance of considering this factor when choosing a loan and managing repayment.
The total cost of a student loan is directly influenced by the interest rate. A higher interest rate means you’ll pay more in interest charges over the loan’s term, leading to a higher overall repayment amount. Conversely, a lower interest rate will reduce the total interest paid and the overall cost. This impact becomes even more pronounced over longer loan terms. For instance, a small difference of even 1% in the interest rate on a large loan can translate to thousands of dollars in extra interest paid over the life of the loan. This highlights the significance of securing the most favorable interest rate possible.
Effect of Extra Payments on Reducing Interest
Making extra payments on your student loans can substantially reduce the total interest paid and shorten the loan repayment period. Each extra payment reduces the principal balance, meaning less principal accrues interest in subsequent months. This snowball effect accelerates your repayment and saves you considerable money in the long run. For example, even an extra $50 per month can lead to significant savings over several years.
Strategies to Minimize Interest Payments
Careful planning and proactive strategies can help minimize the amount of interest you pay on your student loans. The following points Artikel effective approaches:
These strategies work in tandem to lower your overall interest costs and help you become debt-free sooner.
- Secure a low interest rate: Shop around for the best interest rates from various lenders before accepting a loan. Consider federal loan options, which often offer lower rates than private lenders.
- Make extra payments: As discussed previously, even small extra payments significantly impact interest paid.
- Refinance your loans: If interest rates fall after you’ve taken out your loans, refinancing to a lower rate can save you substantial amounts.
- Consider income-driven repayment plans: These plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income, making them more manageable and potentially reducing the total interest paid over time, though it may extend the loan’s term.
- Prioritize high-interest loans: If you have multiple loans with varying interest rates, focus on making extra payments toward the loan with the highest interest rate first.
Example of 1% Interest Rate Increase Impact
Let’s consider a $20,000 student loan with a 5% interest rate and a 10-year repayment period. Using a standard amortization calculator (easily found online), the total interest paid would be approximately $4,325, and the total repayment amount would be around $24,325.
Now, let’s increase the interest rate by just 1%, to 6%. With the same loan amount and repayment period, the total interest paid jumps to approximately $5,615, and the total repayment amount increases to roughly $25,615.
This seemingly small 1% increase results in an extra $1,290 in interest paid over the life of the loan. This clearly illustrates the significant impact even a minor interest rate fluctuation can have on your overall repayment costs. The larger the loan amount and the longer the repayment period, the more pronounced this effect will be.
Factors Affecting Student Loan Interest Rates
Several key factors interact to determine the interest rate you’ll receive on your student loans. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions and potentially secure a more favorable interest rate. This section will explore the primary influences on your student loan interest rate, highlighting both controllable and uncontrollable elements.
Credit Score’s Influence on Interest Rates
Your credit score is a significant factor influencing the interest rate offered on your student loan. Lenders use credit scores to assess your creditworthiness – essentially, your likelihood of repaying the loan. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate, reflecting the lender’s reduced perceived risk. Conversely, a lower credit score can result in a higher interest rate, as lenders compensate for the increased risk of default. For example, a borrower with an excellent credit score (750 or above) might qualify for a significantly lower interest rate compared to a borrower with a poor credit score (below 600). This difference can translate into substantial savings over the life of the loan.
Loan Type and Interest Rates
The type of student loan you choose directly impacts the interest rate. Federal student loans, backed by the government, often have lower interest rates than private student loans. Federal loans also typically offer more favorable repayment options and protections for borrowers. Within federal loans, there are further distinctions. For example, subsidized loans, where the government pays the interest while you’re in school, often have lower rates than unsubsidized loans. Private student loans, offered by banks and other financial institutions, have rates that vary considerably depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Lender’s Role in Determining Interest Rates
Different lenders have different lending criteria and risk assessments, resulting in variations in interest rates. Some lenders may prioritize certain factors more heavily than others when determining interest rates. For instance, one lender might place more emphasis on credit history, while another might give more weight to income stability. Shopping around and comparing offers from multiple lenders is crucial to securing the most favorable interest rate.
Economic Climate and Interest Rates
The overall economic climate significantly impacts student loan interest rates. Interest rates generally rise during periods of economic expansion and fall during recessions. This is because the Federal Reserve (the central bank of the U.S.) adjusts interest rates to manage inflation and economic growth. These adjustments influence the rates offered by lenders, impacting the cost of borrowing for students. For example, during periods of high inflation, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates, leading to higher student loan interest rates.
Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies play a critical role in shaping student loan interest rates, particularly for federal student loans. Changes in government policy, such as adjustments to interest rate subsidies or changes in eligibility criteria, can directly affect the cost of borrowing. For example, government intervention might cap interest rates on certain types of federal loans or offer temporary interest rate reductions to stimulate borrowing.
Controllable and Uncontrollable Factors
Understanding which aspects you can influence is vital for securing a favorable interest rate.
- Controllable Factors: Credit score improvement through responsible financial behavior, careful selection of loan type, and comparison shopping among lenders.
- Uncontrollable Factors: The prevailing economic climate, government regulations and policies, and the lender’s specific lending criteria.
Visualizing Interest Rate Calculations
Understanding the impact of interest rates on student loan repayment can be challenging. Visual aids, such as charts and tables, offer a clear and concise way to grasp the financial implications of different interest rates and repayment strategies. This section will present several visualizations to help illustrate these concepts.
Growth of Student Loan Debt Over Time with Varying Interest Rates
Imagine a line graph charting the growth of a $20,000 student loan balance over ten years. Multiple lines represent different interest rates: a low rate (e.g., 3%), a moderate rate (e.g., 6%), and a high rate (e.g., 9%). The x-axis represents the time elapsed (in years), and the y-axis represents the total loan balance. You would see that the line representing the 9% interest rate climbs much more steeply than the 3% line, demonstrating the significant impact of higher interest rates on the total amount owed. The 6% line would fall between the two, showing a moderate increase in the loan balance over time. This visual clearly demonstrates how even small differences in interest rates can lead to substantial differences in the total amount paid over the life of the loan.
Monthly Payment Amounts for Different Loan Amounts and Interest Rates
The following table shows the estimated monthly payments for various loan amounts and interest rates, assuming a standard 10-year repayment plan. Note that these are simplified calculations and do not include fees or other potential charges.
| Loan Amount | 3% Interest | 6% Interest | 9% Interest |
|---|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | $84.99 | $102.86 | $121.34 |
| $20,000 | $169.98 | $205.72 | $242.68 |
| $30,000 | $254.97 | $308.58 | $364.02 |
Visual Representation of the Impact of Prepayment on Total Interest Paid
Consider a bar chart. One bar represents the total interest paid over the life of a loan with no prepayments. A second, shorter bar represents the total interest paid if extra payments are made each month. The difference between the heights of the two bars visually illustrates the substantial savings achieved through prepayment. The longer bar represents a significantly larger amount of interest paid compared to the shorter bar representing the loan with prepayments. This difference emphasizes the substantial cost savings associated with prepaying your student loans. For example, prepaying even a small amount each month can significantly reduce the total interest paid over the life of the loan, saving thousands of dollars.
Last Recap

Mastering student loan repayment hinges on a thorough understanding of interest rates and the effective use of available resources. By utilizing interest rate calculators, exploring various repayment options, and proactively implementing strategies to minimize interest payments, you can significantly reduce your overall loan burden. Remember, informed decision-making is key to successfully navigating the student loan repayment journey. Take control of your financial future, and confidently chart a course towards debt-free living.
FAQ Compilation
What is interest capitalization?
Interest capitalization is when accrued interest is added to your principal loan balance, increasing the total amount you owe. This increases the overall interest paid over the life of the loan.
How does my credit score affect my interest rate?
A higher credit score typically qualifies you for lower interest rates. Lenders perceive borrowers with good credit as less risky.
What are income-driven repayment plans?
Income-driven repayment plans base your monthly payments on your income and family size, potentially lowering your monthly payments but extending the repayment period.
Can I refinance my student loans?
Yes, refinancing can potentially lower your interest rate, but it depends on your creditworthiness and market conditions. Carefully compare offers before refinancing.
What is the difference between a fixed and variable interest rate?
A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term, while a variable interest rate fluctuates based on market conditions. Fixed rates offer predictability, while variable rates might offer lower initial rates but carry more risk.
