Navigating the world of private student loans can feel like traversing a complex maze, particularly when understanding the often-confusing landscape of interest rates. These rates, the price of borrowing for your education, significantly impact the total cost of your loan and your long-term financial well-being. This guide aims to demystify the process, providing a clear understanding of the factors that influence these rates, different loan types, and strategies for managing your debt effectively.
From the impact of your credit score to the differences between fixed and variable rates, we will explore the various nuances of private student loan interest. We’ll also compare private loans to federal options, helping you make informed decisions about financing your education. Ultimately, our goal is to empower you with the knowledge necessary to make responsible borrowing choices and navigate the repayment process successfully.
Understanding Private Student Loan Interest Rates
Private student loans can be a crucial funding source for higher education, but understanding their interest rates is vital for responsible borrowing. Interest rates determine the total cost of your loan, significantly impacting your repayment burden. This section will clarify the factors influencing these rates and provide insights into navigating the complexities of private student loan financing.
Factors Influencing Private Student Loan Interest Rates
Several key factors interact to determine the interest rate you’ll receive on a private student loan. These factors are assessed by lenders to gauge the risk associated with lending to you. A higher perceived risk translates to a higher interest rate.
Credit Score’s Impact on Interest Rates
Your credit score is a paramount factor in determining your interest rate. Lenders use your credit history to assess your creditworthiness. A higher credit score indicates a lower risk of default, resulting in a lower interest rate. Conversely, a lower credit score suggests a higher risk, leading to a higher interest rate, potentially significantly impacting the overall cost of the loan. For example, a borrower with an excellent credit score (750 or above) might qualify for an interest rate of 6%, while a borrower with a fair credit score (660-679) might receive an interest rate of 10% or higher.
Interest Rate Comparison Across Lenders
Interest rates vary considerably across different private student loan lenders. Each lender has its own lending criteria and risk assessment models, resulting in a range of interest rates. It’s crucial to shop around and compare offers from multiple lenders before selecting a loan. Factors such as the lender’s size, market position, and specific loan products can influence the interest rates they offer. Comparing offers from at least three different lenders is recommended to ensure you secure the most favorable terms.
Loan Terms and Total Interest Paid
The loan term, or repayment period, significantly affects the total interest paid over the life of the loan. A longer loan term means lower monthly payments, but you’ll end up paying significantly more interest over time. Conversely, a shorter loan term leads to higher monthly payments but less total interest paid. For instance, a $20,000 loan with a 7% interest rate over 10 years will accrue significantly less interest than the same loan over 15 years. The difference in total interest paid can amount to thousands of dollars.
Average Interest Rates for Various Loan Amounts and Credit Scores
The following table provides estimated average interest rates. Remember that these are averages, and your actual rate will depend on your specific circumstances and the lender.
| Loan Amount | Excellent Credit (750+) | Good Credit (700-749) | Fair Credit (660-699) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | 6.0% – 7.0% | 7.0% – 8.5% | 9.0% – 11.0% |
| $20,000 | 6.5% – 7.5% | 7.5% – 9.0% | 9.5% – 11.5% |
| $30,000 | 7.0% – 8.0% | 8.0% – 9.5% | 10.0% – 12.0% |
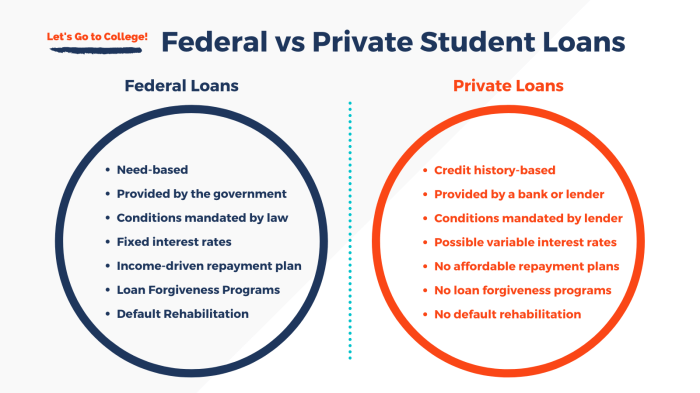
Comparing Private Student Loans to Federal Student Loans
Choosing between private and federal student loans is a crucial decision impacting your financial future. Understanding the key differences, particularly concerning interest rates and repayment options, is vital for making an informed choice. This section compares both loan types, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages to help you navigate this important process.
Interest Rate Differences
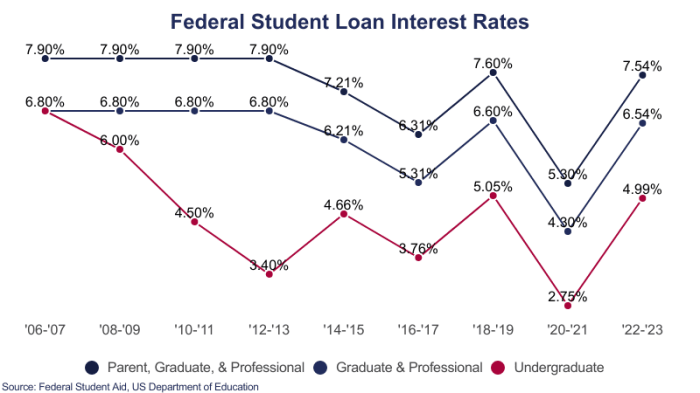
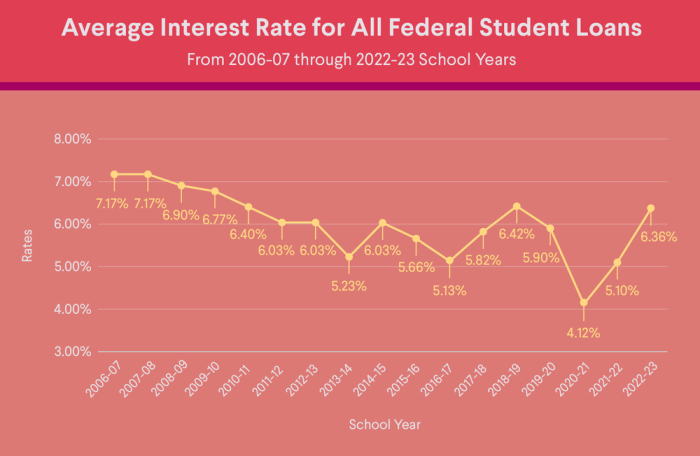
Federal student loans generally offer lower interest rates than private student loans. This is because the federal government subsidizes these loans, minimizing the lender’s risk and allowing for more competitive rates. Private lenders, on the other hand, assess risk based on individual creditworthiness, resulting in higher rates for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit or limited credit history. The specific interest rate for both federal and private loans varies depending on several factors including the loan type, the borrower’s credit history, and the prevailing market interest rates. For example, a federal unsubsidized loan might have a fixed interest rate of around 5%, while a private loan for a similar borrower might carry a variable interest rate ranging from 7% to 12% or even higher, depending on creditworthiness.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Loan Type Regarding Interest Rates
Federal student loans typically offer the advantage of lower, often fixed, interest rates, making them more affordable in the long run. However, the amount you can borrow through federal loans is limited. Private loans, while potentially carrying higher interest rates, can provide access to larger loan amounts, especially when federal loan limits are insufficient to cover educational expenses.
Conversely, a disadvantage of private student loans is their higher interest rates, potentially leading to a significantly larger overall debt burden. Furthermore, private loan interest rates can fluctuate, making it harder to budget for repayment. The advantages of federal loans lie in their fixed interest rates, government protections, and various repayment options. However, they might not offer the flexibility or loan amounts available through private lenders.
Situations Where Private or Federal Loans Are Preferable
Private student loans might be preferable when the cost of education exceeds the maximum federal loan limits. For instance, students attending expensive private universities might need to supplement their federal loans with private loans to cover tuition, fees, and living expenses. Conversely, federal student loans are generally the better option for students who qualify, due to their lower interest rates and government protections, such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs. This is particularly true for students with limited or poor credit histories, who would likely face significantly higher interest rates with private loans.
Repayment Options and Forgiveness Programs
Federal student loans offer a wider range of repayment options, including income-driven repayment plans, which adjust monthly payments based on income and family size. Some federal loans even qualify for loan forgiveness programs after a certain number of years of qualifying payments in public service or certain other professions. Private student loans typically offer fewer repayment options, usually only standard repayment plans. Forgiveness programs are generally not available for private student loans. The differences in repayment flexibility and forgiveness programs can significantly impact the long-term affordability and manageability of student loan debt.
Key Differences Summarized
The following points summarize the key differences between federal and private student loans:
| Feature | Federal Student Loans | Private Student Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Generally lower, often fixed | Generally higher, can be fixed or variable |
| Loan Limits | Set by the government | Set by the lender, often higher |
| Repayment Options | More flexible, including income-driven plans | Fewer options, typically standard repayment |
| Loan Forgiveness | Potential for forgiveness programs | Generally no forgiveness programs |
| Credit Check | Generally no credit check required for subsidized loans | Credit check required, impacting interest rates |
Last Word

Securing a private student loan requires careful consideration of interest rates and repayment terms. Understanding the factors that influence these rates, such as credit score and loan type, is crucial for making informed decisions. By comparing offers from different lenders, exploring strategies for reducing interest payments, and carefully planning your repayment strategy, you can minimize the long-term financial burden of student loan debt. Remember, responsible borrowing and proactive management are key to successfully navigating the complexities of private student loan financing.
FAQ Summary
What is the average interest rate on a private student loan?
The average interest rate varies greatly depending on factors like credit score, loan amount, and lender. However, it’s generally higher than federal student loan rates and can range from 6% to 15% or more.
Can I negotiate my interest rate on a private student loan?
Negotiating interest rates on private student loans is less common than with other types of loans. However, having a strong credit score and a co-signer can improve your chances of securing a more favorable rate. It’s always worth asking the lender about potential discounts or special offers.
What happens if I default on my private student loan?
Defaulting on a private student loan can have severe consequences, including damage to your credit score, wage garnishment, and legal action from the lender. It can also make it difficult to obtain future loans or credit.
How long does it take to get approved for a private student loan?
The approval process varies depending on the lender but typically takes a few days to a few weeks. Faster processing times may be available if you provide all necessary documentation promptly.
