
Securing higher education shouldn’t be financially crippling. The pursuit of knowledge and career advancement is often hampered by the burden of student loan debt. This guide explores the landscape of interest-free student loans, examining various programs, eligibility criteria, and the long-term implications of such funding. We’ll delve into the nuances of grants, scholarships, and interest-free loans, helping you navigate the complexities of securing financial aid without the added pressure of accumulating interest.
Understanding the options available for interest-free student funding is crucial for responsible financial planning. We will compare different programs, highlight potential challenges, and offer alternatives for students who may not qualify for interest-free loans. This comprehensive overview will empower you to make informed decisions about your financial future and pursue your educational goals with confidence.
Impact of Interest-Free Student Loans on Students

Interest-free student loans represent a significant potential boon for students, offering a pathway to higher education without the crippling weight of accumulating debt. This can have profound effects on their academic performance, future career choices, and overall financial well-being, both during and after their studies. The absence of interest payments allows students to focus on their education rather than being constantly burdened by financial anxieties.
The availability of interest-free loans can significantly improve students’ academic performance. Reduced financial stress allows students to dedicate more time and energy to their studies, leading to improved grades and a higher likelihood of graduating on time. This, in turn, opens doors to better career opportunities and higher earning potential in the long run. Furthermore, the absence of looming debt allows students to explore extracurricular activities, internships, and volunteer work – experiences that enhance their resumes and prepare them for the job market. This can lead to a more fulfilling and successful career path, ultimately contributing to improved long-term financial stability.
Improved Financial Well-being During and After Education
Access to interest-free loans directly impacts students’ financial well-being throughout their educational journey and beyond. Without the pressure of interest payments, students can better manage their living expenses, reducing the need to take on part-time jobs that might detract from their studies. This improved financial stability reduces stress and anxiety, allowing them to focus on their academic pursuits. Post-graduation, the absence of student loan debt significantly enhances their financial flexibility. They have more freedom to save for a down payment on a house, invest in their future, or pursue further education without the burden of substantial loan repayments. This translates to greater financial security and improved overall quality of life. For example, a graduate with an interest-free loan might be able to save for a down payment on a house much faster than a peer burdened with high-interest student loan debt, allowing them to achieve a major financial milestone earlier in their lives.
Challenges in Accessing Interest-Free Loans
While interest-free loans offer substantial benefits, students might encounter several challenges in accessing them. The availability of such loans is often limited, with eligibility criteria potentially stringent and competitive. This can exclude students from disadvantaged backgrounds or those pursuing less popular fields of study. Furthermore, the application process itself can be complex and time-consuming, requiring extensive documentation and potentially involving lengthy waiting periods. The amount of funding available through interest-free loans might also be insufficient to cover all educational expenses, leaving students to seek additional funding sources, which may carry interest.
- Limited availability and stringent eligibility criteria.
- Complex and time-consuming application processes.
- Potential insufficiency of funds to cover all educational costs.
- Need for additional financial planning and budgeting.
Governmental and Institutional Roles in Providing Interest-Free Student Aid

The provision of interest-free student aid is a complex undertaking, requiring a collaborative effort between governmental agencies and educational institutions. Effective programs necessitate clear policies, robust management systems, and a commitment to equitable access. The roles played by each entity are crucial to the success of such initiatives.
The government plays a pivotal role in establishing the framework for interest-free student aid. This includes defining eligibility criteria, setting funding levels, and overseeing the disbursement of funds. Government agencies, such as education ministries or dedicated student loan bureaus, are responsible for designing and implementing these programs, often in collaboration with financial institutions. They also establish the regulatory environment, ensuring transparency, accountability, and the prevention of fraud. Effective monitoring and evaluation mechanisms are crucial to ensure the programs achieve their intended goals and are responsive to changing needs.
Governmental Policies and Regulations Governing Interest-Free Student Aid
Governmental policies and regulations surrounding interest-free student aid vary significantly across countries. However, common themes include establishing clear eligibility requirements (such as income thresholds, academic merit, or specific fields of study), outlining the application process, and defining the terms and conditions of the aid. These regulations often aim to ensure that the aid reaches the students who need it most, while also preventing misuse or abuse of the system. For instance, many governments implement rigorous verification processes to confirm student identity and academic progress. Furthermore, regulations may include provisions for loan forgiveness or repayment plans based on post-graduation income levels. These mechanisms aim to mitigate the burden of student debt and improve overall access to higher education.
Examples of Successful Government Initiatives
Several countries have implemented successful initiatives aimed at increasing access to interest-free student loans. For example, some Scandinavian countries have long-standing, robust systems where tuition is largely covered by the government, effectively providing a form of interest-free aid. These programs often integrate with broader social welfare systems, ensuring accessibility for a wider range of students. Other countries have focused on targeted initiatives, such as providing interest-free loans specifically for students pursuing studies in high-demand fields like STEM or healthcare. These targeted programs aim to address specific workforce needs and promote national economic growth. Successful initiatives typically combine generous funding with streamlined application processes and robust support services for students, fostering greater participation and reducing the administrative burden.
Institutional Roles in Managing Interest-Free Student Aid
Educational institutions, such as universities and colleges, play a critical role in administering interest-free student aid programs. They are often responsible for processing applications, verifying eligibility, and distributing funds to eligible students. Institutions may also offer their own internal scholarship or grant programs that supplement government-provided aid. Strong collaboration between the institution and the relevant government agency is essential to ensure the smooth and efficient operation of these programs. Transparency and clear communication with students regarding eligibility criteria, application procedures, and repayment terms are key elements of effective institutional management. Institutions may also provide financial literacy workshops and counseling services to support students in managing their finances and understanding the implications of accepting interest-free loans.
Last Recap
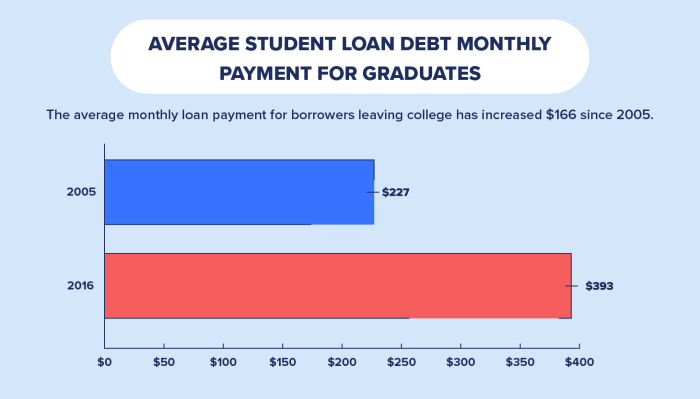
Accessing interest-free student loans can significantly impact a student’s academic journey and future financial well-being. By understanding the various programs, eligibility requirements, and potential challenges, students can navigate the process effectively and make informed choices that align with their financial goals. Remember, responsible financial planning is key to maximizing the benefits of interest-free loans and avoiding future debt. This guide serves as a starting point for your research; further investigation into specific programs and your individual circumstances is essential for a successful application.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a grant and a scholarship?
Grants are typically need-based, awarded based on financial circumstances. Scholarships are often merit-based, awarded for academic achievement or other talents.
Can I get interest-free loans for postgraduate studies?
The availability of interest-free loans for postgraduate studies varies significantly depending on the country and institution. Some programs may exist, but they are less common than undergraduate options.
What happens if I don’t repay a government-backed interest-free loan?
Consequences for non-repayment vary depending on the program and country but can include damage to credit score and potential legal action.
Are there any hidden fees associated with interest-free loans?
While the loan itself is interest-free, some programs may have administrative fees or other associated costs. Always review the terms and conditions carefully.
