
The burden of student loan debt weighs heavily on millions, impacting financial futures and economic growth. Lowering interest rates on student loans presents a potential solution, offering immediate relief to borrowers and stimulating the economy. This exploration delves into the multifaceted implications of such a policy, examining its economic effects, government actions, and impact on borrowers, alongside alternative approaches to tackling the student loan crisis.
This analysis considers the potential benefits and drawbacks for various borrower groups, including undergraduates and graduates, while also assessing the feasibility and long-term sustainability of interest rate reductions from both governmental and private sector perspectives. A comparative analysis of alternative solutions, such as loan forgiveness programs, provides a comprehensive overview of the challenges and opportunities inherent in addressing the pervasive issue of student loan debt.
Government Policies and Lower Interest Rates

Lowering student loan interest rates is a complex issue with significant political and economic ramifications. Achieving this requires careful consideration of legislative and executive actions, potential compromises, and the overall budgetary impact on the government. Understanding the historical context of government interventions is crucial to predicting the effectiveness of future policies.
Government intervention in student loan interest rates typically occurs through legislative and executive actions. Legislative actions involve Congress passing bills that directly alter interest rates or authorize the executive branch to do so. Executive actions, often taken by the President or relevant agencies, might involve adjusting the rate within existing legal frameworks or implementing temporary interest rate relief programs. These actions often involve intricate negotiations and compromises between different political factions and stakeholders.
Legislative and Executive Actions Affecting Interest Rates
Several legislative and executive actions could lead to lower student loan interest rates. Congress could pass legislation mandating lower rates for all federal student loans or specific loan programs. Alternatively, legislation could authorize the Secretary of Education to adjust interest rates based on prevailing market conditions or economic indicators. Executive actions might include using existing authority to temporarily reduce interest rates during economic downturns or directing federal agencies to explore refinancing options for existing loans. The political landscape, however, often dictates the feasibility of such actions.
Political Challenges and Compromises
Implementing policies to lower student loan interest rates faces significant political challenges. Different political parties often hold opposing views on the appropriate level of government intervention in the student loan market. Some may advocate for substantial reductions, while others may prefer more modest changes or market-based solutions. Reaching a consensus often requires compromises, potentially involving phased reductions, targeted assistance for specific demographics, or linking interest rate reductions to other policy initiatives. For instance, a compromise might involve lowering interest rates for low-income borrowers in exchange for stricter repayment terms.
Examples of Past Government Interventions
Historically, the federal government has intervened in student loan interest rates multiple times. For example, the Obama administration implemented temporary interest rate reductions for federal student loans during the 2008 financial crisis, providing immediate relief to borrowers. However, these were temporary measures, and rates eventually reverted to previously established levels. The impact of such interventions varied, with some arguing that they provided necessary relief, while others questioned their long-term effectiveness and fiscal sustainability. The effects of these policies were often debated, with varying analyses on their success in achieving their stated goals and their broader economic consequences.
Budgetary Implications of Reduced Interest Rates
Reducing student loan interest rates has significant budgetary implications for the government. Lower rates directly reduce the revenue generated from student loan interest payments, increasing the federal deficit. The magnitude of this impact depends on the extent of the rate reduction, the number of borrowers affected, and the duration of the policy. This necessitates careful consideration of the trade-offs between providing relief to borrowers and managing the federal budget. The government may need to explore alternative revenue streams or spending cuts to offset the reduced revenue from student loan interest payments. Detailed cost-benefit analyses, including modeling different scenarios and considering potential long-term economic effects, are crucial in assessing the overall fiscal impact.
Impact on Student Loan Borrowers
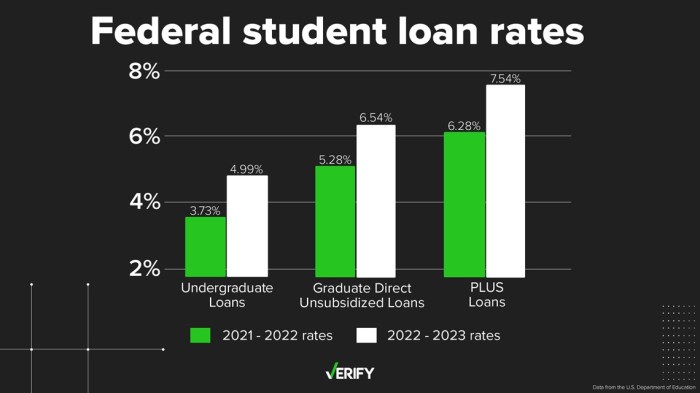
Lowering student loan interest rates has a significant and multifaceted impact on borrowers, affecting their repayment schedules, overall financial health, and long-term financial planning. The extent of this impact varies considerably depending on the type of loan, the loan amount, and the individual borrower’s financial circumstances.
Lower interest rates directly translate into lower monthly payments for borrowers. This reduction in monthly expenses can free up funds for other financial priorities, such as saving, investing, or paying down other debts. The overall cost of the loan is also reduced, meaning borrowers pay less in total interest over the life of the loan. Conversely, higher interest rates lead to increased monthly payments and a significantly higher total cost over the life of the loan.
Impact on Different Loan Types
The impact of lower interest rates differs across various student loan categories. Federal student loans, which comprise the majority of student loans, typically offer lower interest rates than private student loans. Undergraduate borrowers often benefit from even lower rates than graduate borrowers due to differing risk assessments. A reduction in interest rates would therefore provide more substantial relief to borrowers with federal loans and undergraduate loans, compared to those with private loans or graduate loans. The reduction in monthly payments would be most significant for borrowers with larger loan balances, irrespective of the loan type.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Lower Interest Rates for Borrowers
Lower interest rates present several advantages for borrowers. The most immediate benefit is reduced monthly payments, improving cash flow and reducing financial stress. Borrowers also pay less interest overall, resulting in significant long-term savings. This can accelerate debt repayment and improve credit scores, unlocking access to better financial products in the future. However, there are potential drawbacks. For example, some borrowers might be tempted to borrow more due to lower interest rates, potentially increasing their overall debt burden. Furthermore, the benefits are not uniform across all borrowers; those with smaller loan amounts might see less significant savings compared to those with substantial debt.
- Benefit: Reduced monthly payments, freeing up disposable income.
- Benefit: Lower total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Benefit: Faster debt repayment and improved credit scores.
- Drawback: Potential for increased borrowing due to lower rates.
- Drawback: Uneven distribution of benefits across borrowers.
Scenario: Long-Term Financial Impact
Consider two borrowers: Borrower A has a $50,000 federal student loan at a 5% interest rate, while Borrower B has the same loan amount but at a reduced 3% rate. Over a 10-year repayment period, Borrower A would pay approximately $6,200 more in interest than Borrower B. This difference becomes even more pronounced with larger loan amounts or longer repayment periods. Now, imagine a scenario where Borrower C has a $100,000 loan at 5%, and Borrower D has a $100,000 loan at 3%. The interest differential between Borrower C and Borrower D will be significantly higher. This illustrates how lower interest rates can lead to substantial long-term savings.
Impact on Repayment and Financial Well-being
Lower interest rates can significantly improve borrowers’ ability to repay their loans. Reduced monthly payments make it easier to manage expenses and avoid delinquency. This, in turn, positively affects their credit scores, enabling them to access better financial products like mortgages or auto loans in the future. Improved financial well-being is a direct consequence of lower financial stress associated with manageable student loan repayments. The increased disposable income can be used for investments, savings, or other financial goals, contributing to overall financial security. Conversely, higher interest rates can lead to financial strain, impacting credit scores and hindering long-term financial planning.
Epilogue

Ultimately, the pursuit of lower interest rates for student loans necessitates a careful balancing act. While offering immediate financial relief to borrowers and potentially boosting economic activity, it requires a comprehensive understanding of its broader economic and budgetary consequences. A holistic approach, incorporating alternative solutions and considering the roles of both government and private sectors, is crucial to create a sustainable and equitable system that addresses the student loan debt crisis effectively and fairly.
Helpful Answers
What types of student loans are eligible for lower interest rates?
Eligibility depends on the specific policy implemented. It could include federal student loans, certain private loans, or both. Details would be Artikeld in the legislation or government program.
How would lower interest rates affect my credit score?
On-time payments, regardless of interest rate, are key to maintaining a good credit score. Lower interest rates can indirectly help by reducing the overall debt burden, making timely payments more manageable.
Are there any hidden fees associated with lower interest rates?
It’s unlikely that lower interest rates themselves would introduce new fees. However, always review loan documents carefully for any associated costs.
How long would it take to see the effects of lower interest rates on my monthly payments?
The changes would be reflected in your next billing cycle after the interest rate reduction is implemented. The exact timing depends on your loan servicer’s processes.
