Navigating the complex world of student loans can feel overwhelming, especially when the goal is to secure the lowest possible interest rate. The amount you pay in interest can significantly impact your overall loan repayment burden, potentially stretching your repayment timeline and increasing the total cost of your education. This guide delves into the strategies and considerations necessary to achieve the most favorable interest rates on your student loans, helping you make informed decisions and minimize your long-term financial obligations.
From understanding the factors influencing interest rates to exploring various federal and private loan options and refinancing strategies, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the loan landscape. We’ll cover everything from improving your credit score to negotiating with lenders and comparing loan offers, ensuring you have the tools to secure the best possible terms for your student loans.
Understanding Student Loan Interest Rates
Securing a student loan is a significant financial decision, and understanding the interest rates involved is crucial for responsible borrowing. Interest rates determine the total cost of your loan, impacting your monthly payments and overall repayment burden. This section will clarify the factors affecting these rates and provide a comparative overview of different loan types.
Factors Influencing Student Loan Interest Rates
Several key factors influence the interest rate you’ll receive on a student loan. These include your creditworthiness (for private loans), the type of loan (federal vs. private), the loan’s repayment term, and prevailing market interest rates. Federal student loan interest rates are typically set by the government and are often lower than private loan rates due to the reduced risk involved. In contrast, private lenders assess applicants’ credit scores and financial history to determine their risk profile, directly impacting the interest rate offered. The longer the repayment period, the lower the monthly payment, but the higher the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Finally, broader economic conditions and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy also play a role in shaping interest rate trends.
Types of Student Loans and Their Interest Rates
Student loans are broadly categorized into federal and private loans. Federal student loans are offered by the U.S. government and generally come with more favorable terms, including lower interest rates and income-driven repayment plans. Subsidized federal loans don’t accrue interest while the borrower is enrolled at least half-time, while unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed. Federal Direct PLUS loans are available to graduate students and parents of undergraduate students. Private student loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks and other financial institutions. Their interest rates are variable and are typically higher than federal loan rates, reflecting the lender’s assessment of the borrower’s credit risk. These rates can fluctuate based on market conditions and the borrower’s credit history.
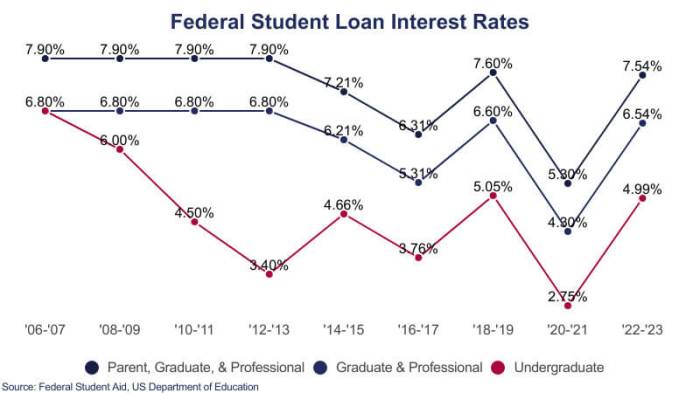
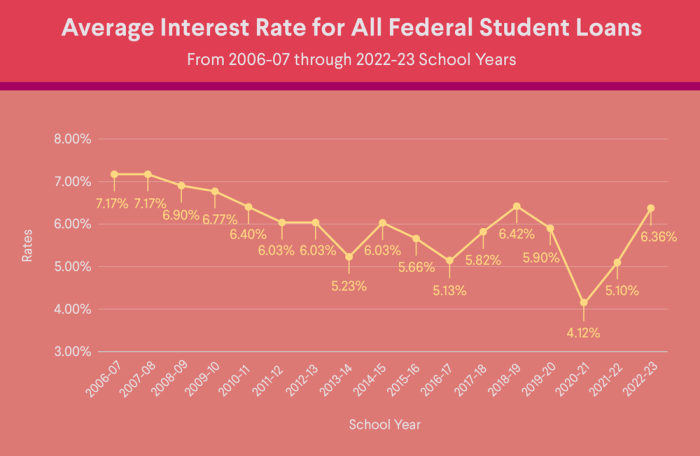
Historical Overview of Student Loan Interest Rate Trends
Student loan interest rates have fluctuated historically, influenced by broader economic factors. During periods of low inflation and economic stability, rates have tended to be lower. Conversely, times of high inflation and economic uncertainty have often led to higher rates. For example, rates were relatively low in the early 2010s, but increased in subsequent years before experiencing some fluctuation in recent years. Tracking these trends helps borrowers understand the potential range of rates they might encounter when applying for a loan.
Comparison of Student Loan Interest Rates
The following table provides a comparison of typical interest rates for different types of student loans. Note that these are examples and actual rates may vary depending on the lender, borrower’s creditworthiness, and prevailing market conditions.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate Type | Typical Interest Rate Range (%) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Subsidized Loan | Fixed | 4-7 | Rates set annually by the government. |
| Federal Unsubsidized Loan | Fixed | 4-7 | Rates set annually by the government. |
| Federal Direct PLUS Loan | Fixed | 7-10 | Higher rates than subsidized and unsubsidized loans. |
| Private Student Loan | Variable or Fixed | 5-15+ | Rates vary significantly based on creditworthiness and market conditions. |
Finding the Lowest Rates

Securing the lowest possible interest rate on your student loans is crucial, as it directly impacts the total amount you’ll repay over the life of the loan. A lower interest rate translates to significant savings, allowing you to pay off your debt faster and reduce the overall cost of your education. Understanding the various avenues for finding and negotiating favorable rates is therefore paramount.
Finding the best student loan interest rates involves a multi-pronged approach, combining proactive research with strategic negotiation. Several key factors influence the interest rate you’ll receive, and understanding these factors is the first step towards securing a favorable deal.
Key Sources for Finding the Lowest Rates
Several avenues exist for discovering the most competitive student loan interest rates. Directly comparing offers from various lenders is essential. This includes federal loan programs, private lenders, and credit unions. Each lender has its own criteria and interest rate structures. Additionally, online comparison tools can streamline this process by aggregating information from multiple lenders simultaneously. Finally, seeking advice from a financial advisor can provide personalized guidance based on your unique financial circumstances.
Strategies for Negotiating Lower Interest Rates
While not always guaranteed, negotiating a lower interest rate is a possibility. Strong credit history is a significant factor here, as is demonstrating a commitment to responsible repayment. Providing a co-signer with excellent credit can also improve your chances. Furthermore, shopping around and presenting competing offers to your preferred lender can incentivize them to offer a more competitive rate. Finally, inquire about any available discounts or promotions the lender might offer.
The Importance of Credit Score in Securing Favorable Interest Rates
Your credit score significantly influences the interest rate you’ll receive on private student loans. Lenders assess your creditworthiness based on your credit history, and a higher credit score typically translates to a lower interest rate. A strong credit score demonstrates your ability to manage debt responsibly, making you a less risky borrower. Conversely, a poor credit score may lead to higher interest rates or even loan denial. Therefore, building and maintaining a good credit score before applying for student loans is highly advisable.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Comparing Loan Offers
Comparing loan offers from different lenders requires a systematic approach. First, gather offers from various sources – federal programs, private lenders, and credit unions. Second, meticulously analyze each offer, paying close attention to the interest rate, loan fees, repayment terms, and any associated penalties. Third, create a comparative table to easily visualize the key features of each loan. Fourth, consider the total cost of each loan over its lifetime, which includes the principal, interest, and fees. Finally, choose the loan with the lowest total cost that aligns with your repayment capabilities. Using a spreadsheet or dedicated loan comparison tool can significantly aid this process.
Wrap-Up

Securing the lowest student loan interest rate requires proactive planning and a thorough understanding of the available options. By carefully considering the factors influencing interest rates, comparing different loan types and lenders, and exploring strategies like refinancing, you can significantly reduce the overall cost of your education. Remember, a lower interest rate translates to substantial long-term savings, allowing you to manage your debt more effectively and achieve your financial goals sooner. This guide serves as a starting point; further research and consultation with financial professionals can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Popular Questions
What is the difference between subsidized and unsubsidized federal student loans?
Subsidized loans don’t accrue interest while you’re in school, grace periods, and during certain deferment periods. Unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed.
How can I improve my credit score to qualify for lower interest rates?
Pay all bills on time, keep credit utilization low, maintain a diverse credit history, and avoid opening numerous new accounts within a short period.
What are the risks associated with refinancing student loans?
Risks include losing access to federal loan benefits like income-driven repayment plans, potentially increasing your monthly payments, and locking in a higher rate if interest rates rise.
Is it always better to refinance my student loans?
Not necessarily. Refinancing is beneficial only if you can secure a significantly lower interest rate that outweighs the potential risks and loss of federal benefits.
