
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, especially when juggling multiple loans with varying interest rates and repayment terms. A multiple student loan calculator emerges as an invaluable tool, offering clarity and control in this often-daunting financial landscape. This guide delves into the functionality, benefits, and nuances of these calculators, empowering you to make informed decisions about your repayment strategy and achieve financial freedom.
Understanding how these calculators work is crucial for effectively managing your student loan debt. We will explore different calculator types, data input requirements, result interpretation, and advanced features to provide a holistic understanding of this essential financial planning tool. By the end, you’ll be equipped to confidently utilize a multiple student loan calculator to optimize your repayment journey.
Understanding Multiple Student Loan Calculators
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be daunting, especially when dealing with multiple loans. Multiple student loan calculators offer a crucial tool to simplify this process, providing users with a comprehensive overview of their repayment options and potential long-term costs. Understanding the features and capabilities of these calculators is essential for making informed financial decisions.
Different Types of Multiple Student Loan Calculators
Multiple student loan calculators vary in their features and complexity. Some are simple, focusing primarily on calculating total monthly payments and overall interest paid. Others offer more sophisticated features, including the ability to simulate different repayment plans, explore the impact of extra payments, and visualize repayment timelines. The most advanced calculators may incorporate factors like interest rate changes and potential loan forgiveness programs.
Key Features and Functionalities of a Robust Multiple Student Loan Calculator
A robust multiple student loan calculator should possess several key features to be truly effective. These include the ability to input multiple loans with varying interest rates, loan amounts, and repayment terms. The calculator should accurately calculate the total monthly payment, the total interest paid over the life of the loans, and the total amount repaid. Furthermore, it should allow users to explore “what-if” scenarios by adjusting variables such as extra payments, different repayment plans (e.g., standard, extended, income-driven), and potential interest rate changes. A strong visualization tool, such as a repayment schedule or amortization chart, is also beneficial. Finally, a robust calculator should handle various loan types effectively.
Handling Various Loan Types
Different calculators handle various loan types (federal, private, subsidized, unsubsidized) with varying degrees of sophistication. For example, a basic calculator might simply aggregate all loan payments without differentiating between loan types. More advanced calculators might incorporate the unique features of each loan type, such as the interest capitalization for unsubsidized loans or the income-based repayment options available for federal loans. Some may even allow for the input of specific loan details, like loan servicer information or unique loan identifiers. For example, a calculator might model the impact of Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) on a portfolio of federal student loans, factoring in the required 120 qualifying payments.
Comparison of Multiple Student Loan Calculators
| Calculator Name | Pros | Cons | Loan Type Handling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calculator A (Example) | Easy to use interface, comprehensive features, visual repayment schedule | Limited loan type options, no income-driven repayment plan simulation | Federal (Subsidized/Unsubsidized), Private |
| Calculator B (Example) | Handles various loan types, includes income-driven repayment simulations | Steeper learning curve, may require a subscription | Federal (Subsidized/Unsubsidized, various income-driven plans), Private |
| Calculator C (Example) | Free to use, simple interface | Limited features, does not handle complex scenarios | Federal, Private (basic aggregation) |
| Calculator D (Example) | Accurate calculations, detailed reports | May require manual data entry for some loan types, less user-friendly | Federal (Subsidized/Unsubsidized), Private (with detailed input fields) |
Inputting Data into a Multiple Student Loan Calculator

Accurately using a multiple student loan calculator hinges on correctly inputting your loan details. This ensures the calculator provides reliable projections of your repayment options and total costs. Failing to provide accurate information will result in inaccurate and potentially misleading results.
Understanding the data required and employing best practices for organization will significantly improve the accuracy and usefulness of your calculations. This section will guide you through the process, clarifying the necessary information and providing a step-by-step approach.
Required Data Inputs
Accurate calculations depend on complete and precise data. The typical inputs required by most multiple student loan calculators include loan amount, interest rate, repayment period, and loan type. Additional inputs may include origination fees, deferment periods, and forbearance periods, depending on the complexity of the calculator. For example, a calculator might require the principal balance for each loan, the annual interest rate (expressed as a percentage), the loan term in months or years, and whether the loan is subsidized or unsubsidized. Incorrectly inputting even one of these values can significantly alter the calculated results.
Importance of Accurate Data Entry
The accuracy of a multiple student loan calculator’s projections directly correlates with the accuracy of the inputted data. Even small errors in interest rates or loan amounts can lead to substantial discrepancies in the calculated total interest paid, monthly payments, and overall repayment timeline. For instance, a seemingly insignificant error of 0.1% in the interest rate on a $50,000 loan could translate to hundreds or even thousands of dollars in additional interest paid over the life of the loan. Therefore, meticulously verifying the accuracy of each data point is crucial for informed decision-making.
Best Practices for Organizing Student Loan Data
Before inputting data into a calculator, organize your information systematically. This will streamline the process and minimize the risk of errors. A recommended approach is to create a spreadsheet listing each loan with its corresponding details (loan amount, interest rate, monthly payment, loan servicer, and remaining balance). You can gather this information from your loan documents or your loan servicer’s website. This organized approach helps ensure that no loan is overlooked and that all necessary information is readily available for input into the calculator.
Step-by-Step Guide to Data Input
A step-by-step guide, while dependent on the specific calculator’s interface, typically follows a similar pattern. Imagine a calculator with fields for each loan, requiring you to input the loan amount, interest rate, and repayment period for each.
- Step 1: Loan Information Entry: Begin by entering the details for your first student loan. This usually involves specifying the loan amount in the designated field, then inputting the annual interest rate (as a percentage), and finally, entering the loan term in months or years. For example, if you have a $10,000 loan with a 5% interest rate and a 10-year repayment term, you would enter those values into the respective fields. Repeat this process for each of your student loans.
- Step 2: Additional Loan Details (if applicable): Some calculators may ask for additional information, such as loan type (e.g., federal subsidized, federal unsubsidized, private), any existing deferment or forbearance periods, and origination fees. Carefully review the calculator’s instructions and fill in these fields as accurately as possible. For instance, indicating whether a loan is subsidized will influence the calculator’s calculations of interest accrual during periods of deferment.
- Step 3: Review and Verification: Before initiating the calculation, thoroughly review all entered data to ensure accuracy. Double-check each entry against your loan documents to prevent errors. This final verification step is crucial to ensuring the reliability of the calculator’s projections.
- Step 4: Initiate Calculation: Once you have verified the accuracy of all entered data, click the “Calculate” or equivalent button to initiate the calculation process. The calculator will then process the inputted data and generate a report summarizing your repayment options and overall loan costs.
Interpreting Calculator Results
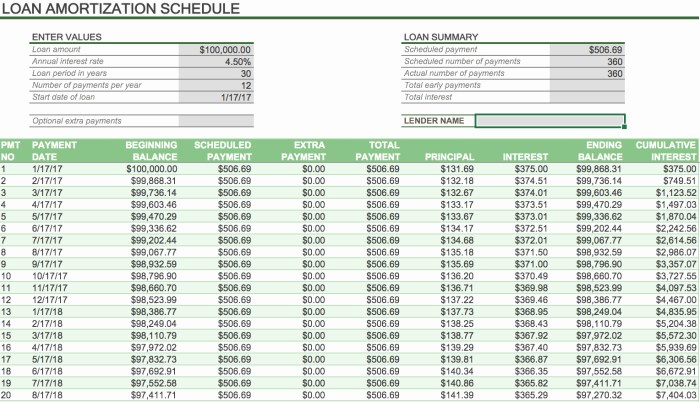
Understanding the output of a multiple student loan calculator is crucial for effective financial planning. These calculators provide a comprehensive overview of your loan repayment, allowing you to compare different strategies and make informed decisions. The key is to understand the different metrics presented and how they interact to impact your overall financial picture.
Key Output Metrics
Multiple student loan calculators typically provide several key metrics to help you understand your repayment options. These include your total interest paid, monthly payments, and the overall loan payoff timeline. Understanding these metrics allows you to effectively compare different repayment strategies and choose the one that best suits your financial circumstances. Let’s examine these metrics in more detail.
Total Interest Paid
This metric represents the total amount of interest you will pay over the life of your loans. A lower total interest paid indicates a more cost-effective repayment strategy. For example, a standard repayment plan might result in a total interest paid of $30,000, while an accelerated repayment plan might reduce this to $20,000, saving you $10,000. This significant difference highlights the importance of exploring different repayment options.
Monthly Payments
This metric shows your estimated monthly payment amount under each repayment plan. Lower monthly payments are easier on your budget but often result in a longer repayment period and higher total interest paid. Conversely, higher monthly payments shorten the repayment timeline and reduce the total interest paid. For instance, a standard repayment plan might have a monthly payment of $500, while an aggressive repayment plan could be $750, leading to quicker debt elimination. Consider your current budget and financial goals when evaluating this metric.
Payoff Timelines
This metric displays the total time it will take to repay your loans under different repayment plans. Shorter payoff timelines are generally preferred, as they minimize the total interest paid. However, shorter timelines often require higher monthly payments. For example, a standard 10-year repayment plan might be compared to a 15-year extended plan, showing the significant difference in time to payoff and total interest.
Repayment Plan Comparisons
The following table illustrates how different repayment plans can affect the overall cost of your student loans. These are illustrative examples and actual results will vary based on individual loan terms and interest rates.
| Repayment Plan | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid | Payoff Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | $500 | $30,000 | 10 years |
| Extended | $350 | $45,000 | 15 years |
| Income-Driven | $300 (variable) | $40,000 (estimated) | 20-25 years (variable) |
| Accelerated | $750 | $20,000 | 5 years |
Advanced Features and Considerations
Multiple student loan calculators offer a range of features beyond basic repayment calculations. Understanding these advanced features and their potential limitations is crucial for making informed decisions about your student loan debt management strategy. This section explores the benefits and drawbacks of advanced features, potential calculator limitations, and the impact of external factors on long-term repayment.
Loan Consolidation and Refinancing Options
Many calculators incorporate options for simulating loan consolidation or refinancing. Consolidation combines multiple loans into a single loan, potentially simplifying repayment. Refinancing involves replacing existing loans with a new loan, often at a lower interest rate. A multiple loan calculator can help compare the potential savings from these strategies by modeling different scenarios, including varying interest rates and repayment terms. However, it’s important to note that while calculators provide estimates, the actual savings will depend on individual lender offers and creditworthiness. For example, a calculator might show a potential monthly payment reduction of $100 after refinancing, but the actual amount could vary based on the specific terms offered by the lender. Similarly, fees associated with consolidation or refinancing should be considered; these costs might offset some of the projected savings.
Limitations of Multiple Student Loan Calculators and Mitigation Strategies
Multiple student loan calculators, while useful tools, have inherent limitations. One significant limitation is the reliance on user-provided data. Inaccurate input, such as missing a small loan or entering an incorrect interest rate, can lead to inaccurate projections. To mitigate this, users should carefully review and verify all input data. Another limitation lies in the calculators’ inability to predict future interest rate fluctuations or changes in personal financial circumstances. These unpredictable variables can significantly affect long-term repayment plans. Therefore, users should consider running multiple scenarios with varying interest rates and income projections to assess the potential impact of these uncertainties. For example, a calculator might project a 10-year repayment plan under current interest rates, but a scenario with a 1% interest rate increase could extend the repayment period significantly.
Comparison of Results from Different Calculators
Different multiple student loan calculators may produce slightly varying results even with identical input data. This discrepancy can stem from differences in calculation methodologies, rounding practices, or the inclusion/exclusion of certain fees. To gain a more comprehensive understanding, it’s advisable to use several different calculators and compare their outputs. Significant discrepancies should prompt further investigation to ensure the accuracy of the input data and understand the underlying calculation differences. For example, one calculator might use a slightly different amortization method, leading to a minor variation in the total interest paid compared to another calculator.
Impact of Inflation and Interest Rate Changes on Long-Term Repayment Plans
Inflation and interest rate changes significantly impact long-term student loan repayment. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, meaning that the real cost of a loan repayment may be lower in the future than it appears today. Conversely, rising interest rates can increase the total interest paid over the loan’s lifetime. Multiple student loan calculators often don’t fully account for these dynamic factors. To address this limitation, users should consider adjusting their input data to reflect potential future inflation and interest rate scenarios. For instance, one could input a higher interest rate to account for potential increases or use an inflation adjustment factor to estimate the future value of loan payments. This proactive approach allows for a more realistic assessment of the long-term financial implications.
Visualizing Repayment Scenarios
Understanding how different factors influence your student loan repayment is crucial for effective financial planning. Multiple student loan calculators offer powerful visualization tools to help you grasp these complexities and make informed decisions. These visuals transform complex data into easily digestible formats, allowing you to compare repayment options and understand the long-term financial implications of your choices.
Amortization Schedule Visualization
A typical amortization schedule, as displayed by a multiple student loan calculator, is usually presented as a table. Each row represents a payment period (typically monthly), showing the payment amount, the portion allocated to principal, the portion allocated to interest, and the remaining loan balance. The table visually tracks the gradual reduction of the principal balance over the loan term. For multiple loans, the calculator might present a separate table for each loan or a consolidated table summarizing all loans. A visual graph could accompany the table, showing the loan balance decreasing over time. This graph would clearly illustrate the balance reduction’s non-linear nature, with steeper declines occurring later in the repayment period as more of the payment goes towards the principal.
Visualization of Different Repayment Strategies
The calculator can visually compare different repayment strategies, such as standard repayment, extended repayment, graduated repayment, and income-driven repayment. This comparison might be shown using a combination of tables and graphs. For example, a bar chart could compare the total interest paid under each plan, while a line graph could display the monthly payment amounts over time for each strategy. This allows borrowers to quickly assess the trade-offs between shorter repayment periods (higher monthly payments, lower total interest) and longer periods (lower monthly payments, higher total interest). A clear legend would distinguish each repayment plan.
Impact of Interest Rates on Total Loan Cost
A visual representation of the impact of different interest rates on the total cost of loans over time could be presented as a line graph. The x-axis would represent the loan term (in years), and the y-axis would represent the total cost (principal plus interest). Multiple lines on the graph would represent different interest rates. For example, a line might show the total cost with a 5% interest rate, another with a 7% rate, and another with a 10% rate. This visualization dramatically illustrates how even small differences in interest rates can significantly impact the total amount paid over the life of the loan. The steeper the line, the higher the total cost due to higher interest. This helps borrowers understand the importance of securing the lowest possible interest rate.
Using Visual Representations for Informed Decisions
Visualizations from a multiple student loan calculator can empower borrowers to make informed decisions in several ways. For instance, by comparing the amortization schedules of different repayment plans, a borrower can determine which plan best aligns with their budget and long-term financial goals. The visual representation of the impact of interest rates helps borrowers prioritize strategies to reduce their interest rates, such as refinancing or loan consolidation. Analyzing the graphs showing the total interest paid under different scenarios allows borrowers to assess the true cost of borrowing and make a choice that minimizes this cost. For example, a borrower could see that choosing a shorter repayment plan, despite higher monthly payments, might save thousands of dollars in interest over the life of the loan.
Wrap-Up

Effectively managing multiple student loans requires a strategic approach, and a multiple student loan calculator serves as a cornerstone of this strategy. By leveraging the insights gained from these tools – understanding repayment options, visualizing long-term costs, and exploring advanced features like consolidation – you can confidently navigate the complexities of loan repayment and build a brighter financial future. Remember, accurate data input is paramount for reliable results, empowering you to make informed decisions and achieve your financial goals.
Q&A
What happens if I enter incorrect information into the calculator?
Incorrect data will lead to inaccurate projections of your monthly payments, total interest paid, and repayment timeline. Always double-check your input for accuracy.
Can these calculators help with income-driven repayment plans?
Many advanced calculators can incorporate income-driven repayment plans, allowing you to see how your monthly payments might change based on your income and family size. Check the calculator’s features to confirm this capability.
Are there any limitations to using these calculators?
Calculators provide estimations based on the data you input. They don’t account for unexpected life events or changes in interest rates that might occur during your repayment period.
How often should I use a student loan calculator?
It’s beneficial to use a calculator regularly, especially when considering refinancing, consolidation, or making significant changes to your repayment plan. Reviewing your projections periodically helps maintain financial awareness.
