
Navigating the world of student loans can be daunting, especially when considering private options. This guide delves into the specifics of Navy Federal private student loans, providing a clear understanding of eligibility requirements, interest rates, repayment plans, and the application process. We’ll compare them to federal loans and other private lenders, highlighting potential benefits and risks to help you make informed decisions about your educational financing.
Understanding the nuances of Navy Federal’s offerings is crucial for prospective borrowers. This in-depth analysis aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to confidently assess whether a Navy Federal private student loan aligns with your financial situation and long-term goals. We’ll explore various scenarios, providing practical examples to illustrate the financial implications of different choices.
Loan Eligibility Requirements
Securing a Navy Federal private student loan involves meeting specific eligibility criteria. These requirements are designed to assess the applicant’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan. Understanding these requirements is crucial for a successful application.
Navy Federal’s private student loan eligibility hinges on several key factors. Applicants must meet minimum credit score thresholds, demonstrate a consistent income stream, and often require a creditworthy co-signer, especially for those with limited credit history. The specific requirements can vary based on the applicant’s financial profile and the loan amount sought.
Credit History Requirements
Navy Federal, like other private lenders, assesses the applicant’s credit history to gauge their repayment risk. A higher credit score generally improves the chances of approval and may lead to more favorable interest rates. While the exact minimum credit score isn’t publicly advertised, a strong credit history, demonstrating responsible borrowing and repayment, significantly enhances eligibility. Applicants with limited or poor credit history may need a co-signer to qualify.
Income Verification Methods
To verify income, Navy Federal may request documentation such as pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements. The purpose is to confirm the applicant’s ability to manage monthly loan repayments alongside their other financial obligations. Self-employment income may require additional documentation, such as business tax returns or profit and loss statements.
Co-Signer Qualifications
A co-signer is an individual who agrees to share responsibility for the loan repayment if the primary borrower defaults. Navy Federal requires co-signers to meet certain creditworthiness standards, similar to those for the primary borrower. A co-signer with a strong credit history can significantly increase the chances of loan approval, particularly for applicants with limited credit experience. The co-signer’s income will also be considered as part of the overall assessment of the applicant’s ability to repay the loan.
Comparison of Eligibility Requirements
The following table compares Navy Federal’s eligibility requirements with those of other major private student loan providers. Note that specific requirements can change, so it’s always advisable to check directly with the lender for the most up-to-date information. This table provides a general overview and should not be considered exhaustive.
| Lender | Minimum Credit Score (Approximate) | Income Verification | Co-signer Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Navy Federal | Not Publicly Disclosed, but generally requires good credit | Pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements | May be required for applicants with limited credit history |
| Sallie Mae | Generally requires good credit, but may consider applicants with lower scores with a co-signer | Pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements | Often required for applicants with limited or poor credit history |
| Discover | Generally requires good credit, but may consider applicants with lower scores with a co-signer | Pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements | May be required for applicants with limited or poor credit history |
| Wells Fargo | Generally requires good credit, but may consider applicants with lower scores with a co-signer | Pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements | Often required for applicants with limited or poor credit history |
Required Documentation
To apply for a Navy Federal private student loan, applicants will typically need to provide various documents to verify their identity, income, and creditworthiness. This usually includes government-issued identification, proof of enrollment, tax returns (or other income verification), and possibly bank statements. The specific documents requested may vary depending on individual circumstances. Providing complete and accurate documentation will streamline the application process and increase the likelihood of a timely approval.
Interest Rates and Fees

Understanding the interest rates and fees associated with a Navy Federal private student loan is crucial for responsible financial planning. This section details the cost components, allowing you to make informed decisions about your borrowing. We will examine rate variations, fee structures, and provide a sample loan cost calculation to illustrate the impact of these factors over time.
Interest Rates for Private Student Loans
Navy Federal’s interest rates for private student loans are variable and depend on several factors, including your creditworthiness, the loan term, and the prevailing market interest rates. These rates are not fixed and can fluctuate throughout the loan’s life. It’s important to note that the rates presented here are examples and may not reflect current rates. Always check the Navy Federal website for the most up-to-date information.
| Loan Term (Years) | Interest Rate Type | Example Interest Rate Range (APR) | Repayment Option |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Variable | 6.00% – 10.00% | Standard Monthly Payments |
| 10 | Variable | 7.00% – 11.00% | Standard Monthly Payments |
| 15 | Variable | 8.00% – 12.00% | Standard Monthly Payments |
| 10 | Variable | 7.50% – 11.50% | Graduated Monthly Payments |
Fees Associated with Navy Federal Private Student Loans
Several fees can be associated with Navy Federal private student loans. Understanding these fees is vital to accurately calculating the total cost of borrowing.
| Fee Type | Description | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Origination Fee | A fee charged by the lender to process your loan application. | Variable, typically a percentage of the loan amount. Check with Navy Federal for current rates. |
| Late Payment Penalty | A penalty assessed if you make a payment after the due date. | Variable, typically a percentage of the missed payment. Check with Navy Federal for current rates. |
| Prepayment Penalty | A fee charged if you pay off your loan early. | Generally, Navy Federal does not charge prepayment penalties. However, it’s always best to verify this directly with them. |
Example Loan Cost Calculation
Let’s illustrate the total cost of a loan with varying interest rates and fees. Consider a $20,000 loan.
Scenario 1: 5-year loan with a 7% APR and a 1% origination fee ($200). The total interest paid would be approximately $2,642. Adding the origination fee, the total cost would be approximately $22,842.
Scenario 2: 10-year loan with a 9% APR and a 1% origination fee ($200). The total interest paid would be significantly higher, approximately $6,346. Including the origination fee, the total cost would be approximately $26,546. This highlights the impact of a longer repayment period and higher interest rate.
Note: These are simplified examples. Actual interest paid will depend on the specific interest rate, repayment schedule, and any additional fees. Always refer to your loan documents for the precise figures.
Repayment Options and Plans
Choosing the right repayment plan for your Navy Federal private student loan is crucial for managing your finances effectively. Understanding the available options and their implications will help you make informed decisions and avoid potential financial strain. This section details the various repayment plans offered by Navy Federal and provides a guide to help you navigate the application process.
Navy Federal offers several repayment options to suit different financial situations and preferences. These options generally fall into two categories: the type of interest rate (fixed or variable) and the repayment schedule (standard or graduated).
Fixed-Rate vs. Variable-Rate Loans
A key decision when choosing a private student loan is selecting between a fixed or variable interest rate. A fixed-rate loan maintains the same interest rate throughout the loan’s term, providing predictability in your monthly payments. A variable-rate loan, on the other hand, has an interest rate that fluctuates based on market conditions. While a variable rate might start lower, it could increase over time, leading to higher monthly payments and potentially a higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. The stability of a fixed rate offers greater financial planning certainty.
Standard vs. Graduated Repayment Plans
Navy Federal also offers different repayment schedules. A standard repayment plan involves equal monthly payments over the loan’s term. This approach simplifies budgeting but may result in higher initial payments. A graduated repayment plan features lower initial payments that gradually increase over time. This option can be beneficial for recent graduates entering the workforce with potentially lower initial incomes. However, it’s important to note that the total interest paid may be higher compared to a standard repayment plan due to the longer period of lower payments.
Applying for Different Repayment Plans
The process of applying for a different repayment plan with Navy Federal typically involves these steps:
- Log in to your Navy Federal online account.
- Navigate to your student loan account overview.
- Locate the section related to repayment options or plan changes.
- Review the available repayment plans and their terms.
- Select the desired repayment plan and submit your request.
- Navy Federal will review your application and notify you of the outcome.
It’s important to contact Navy Federal directly if you have any questions or need assistance with the application process. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Example: Repayment Plan Comparison
Let’s consider a hypothetical example to illustrate the impact of different repayment plans on the total interest paid. Suppose you have a $30,000 private student loan with a 7% interest rate.
| Repayment Plan | Monthly Payment (approx.) | Loan Term (years) | Total Interest Paid (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (Fixed Rate) | $376 | 10 | $15,000 |
| Graduated (Fixed Rate) | $250 (initially, increasing over time) | 15 | $22,000 |
This example demonstrates that while the graduated repayment plan initially offers lower monthly payments, it ultimately leads to a significantly higher total interest paid due to the longer repayment period. This highlights the importance of carefully considering your financial situation and long-term goals when selecting a repayment plan.
Loan Application Process
Applying for a Navy Federal private student loan involves a straightforward process designed to guide you through each step efficiently. The application itself is primarily completed online, offering convenience and accessibility. Understanding the process beforehand will help ensure a smooth and timely application.
The application process is designed to be user-friendly and transparent. Applicants will need to gather necessary documentation and carefully review the terms and conditions before submitting their application. Successful completion leads to a loan disbursement, enabling you to finance your education.
Step-by-Step Application Process
The following steps Artikel the typical application process for a Navy Federal private student loan. While specific steps may vary slightly, this provides a general overview.
- Pre-qualification: Before a formal application, you may choose to pre-qualify to get an estimate of your potential loan amount and interest rate. This is a soft inquiry and doesn’t impact your credit score.
- Complete the Online Application: This involves providing personal information, educational details (school, program, expected costs), and financial information. The application will guide you through each required field.
- Submit Supporting Documentation: Upload the necessary documents as specified in the application. This usually requires electronic copies of the documents.
- Review and Sign the Loan Documents: Once your application is reviewed and approved, you’ll receive loan documents electronically. Carefully review all terms and conditions before signing and submitting them electronically.
- Loan Disbursement: After you’ve signed the documents, the funds will be disbursed according to the terms of your loan agreement, typically directly to your educational institution.
Required Documentation
Having the necessary documentation ready will expedite the application process. Ensure all documents are accurate and legible.
- Government-issued photo ID: Such as a driver’s license or passport.
- Social Security number: Needed for verification purposes.
- Proof of enrollment: Acceptance letter or enrollment verification from your educational institution.
- Financial information: This may include tax returns, pay stubs, or bank statements, depending on the loan amount and your financial situation.
- Co-signer information (if applicable): If required, you’ll need to provide information for your co-signer, including their identification and financial documents.
Pre-Application, Application, and Post-Application Checklist
This checklist helps ensure a smooth and efficient application process. Completing these steps will help minimize potential delays or complications.
- Before Applying:
- Research different loan options and compare interest rates and terms.
- Understand your financial obligations and repayment capabilities.
- Gather all required documentation.
- During Application:
- Complete the application accurately and thoroughly.
- Upload all required documents in the correct format.
- Review the loan terms and conditions carefully before signing.
- After Application:
- Monitor the status of your application.
- Confirm loan disbursement to your educational institution.
- Understand your repayment schedule and plan accordingly.
Customer Service and Support
Navy Federal Credit Union prioritizes providing comprehensive customer service to its private student loan borrowers. Understanding the complexities of student loan management, they offer multiple avenues for support, aiming to resolve issues efficiently and effectively. Access to timely and helpful assistance is crucial for borrowers navigating repayment and potential challenges.
Accessing assistance is straightforward through various channels. Borrowers can expect a consistent and helpful experience regardless of their chosen method of contact.
Contact Methods
Several methods are available for contacting Navy Federal’s customer service regarding private student loans. These options cater to different preferences and levels of urgency.
- Phone Support: A dedicated phone number provides direct access to representatives who can address inquiries and resolve issues in real-time. This is often the preferred method for immediate assistance or complex situations.
- Email Support: For non-urgent matters, borrowers can submit inquiries via email. While response times may be slightly longer than phone support, email allows for detailed explanations and the inclusion of supporting documentation.
- Online Chat: A live chat feature on the Navy Federal website offers a convenient way to receive immediate assistance for less complex questions. This method is ideal for quick answers or clarification on account information.
- Mobile App: The Navy Federal mobile app provides access to account information, payment options, and secure messaging with customer service representatives.
Common Issues and Resolutions
Borrowers frequently encounter issues such as understanding repayment options, navigating deferment or forbearance processes, or resolving billing discrepancies. Navy Federal addresses these concerns through personalized support. For example, if a borrower is struggling with payments, representatives can help explore options like income-driven repayment plans or temporary deferments. Billing discrepancies are usually resolved through account verification and adjustments. In cases of identity theft or fraud, dedicated fraud departments are available to assist.
Customer Service Rating
Based on available online reviews and testimonials, Navy Federal’s customer service for private student loans receives a generally positive rating. While individual experiences may vary, many borrowers praise the helpfulness and responsiveness of the representatives. However, some reviews mention occasional long wait times, particularly during peak periods. Overall, the majority of feedback suggests a satisfactory level of support, reflecting Navy Federal’s commitment to assisting its members. Specific numerical ratings vary across review platforms but generally fall within the 4-star range out of 5.
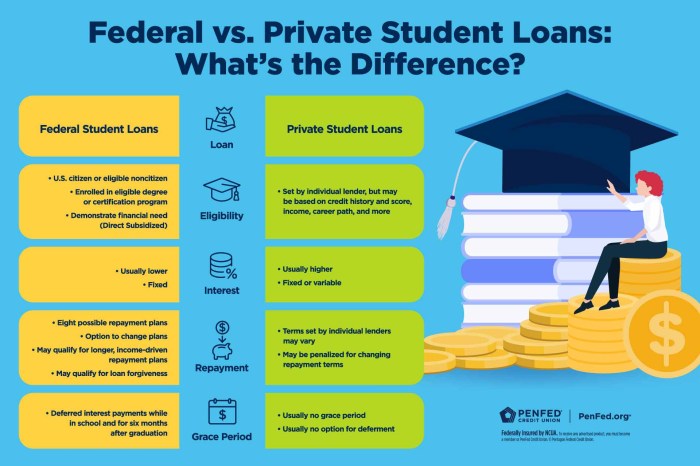
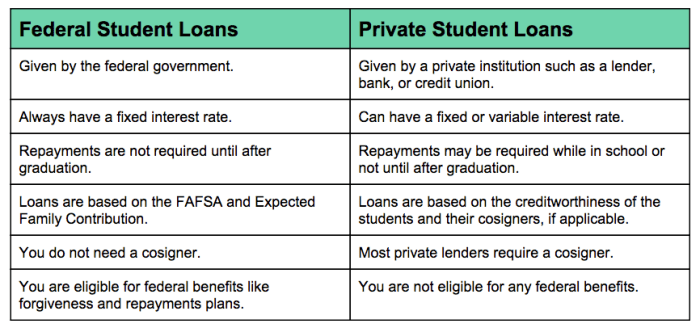
Comparison with Federal Student Loans
Choosing between a Navy Federal private student loan and a federal student loan is a significant decision impacting your financial future. Both offer funding for higher education, but they differ significantly in terms of eligibility, interest rates, repayment options, and long-term implications. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed choice.
This section compares and contrasts Navy Federal private student loans with federal student loans, highlighting scenarios where one might be preferable over the other, and discussing the long-term financial planning implications of each choice.
Interest Rates and Fees
Interest rates and fees are key differentiators between private and federal student loans. Federal student loans typically offer lower, fixed interest rates, especially subsidized loans which don’t accrue interest while the student is enrolled at least half-time. Private loan interest rates, including those from Navy Federal, are variable and generally higher, often reflecting the borrower’s creditworthiness. Furthermore, private loans frequently involve origination fees and other charges, adding to the overall cost of borrowing. For example, a federal subsidized loan might have a fixed rate of 5%, while a comparable Navy Federal private loan could have a variable rate starting at 7%, potentially increasing over the life of the loan. This difference can significantly impact the total amount repaid.
Repayment Options and Plans
Federal student loans offer various income-driven repayment plans, designed to make monthly payments more manageable based on income and family size. These plans can be crucial for borrowers facing financial hardship. Private loans, like those from Navy Federal, generally offer fewer repayment options, often limited to standard repayment plans with fixed monthly payments. While Navy Federal might provide options such as deferment or forbearance in certain circumstances, these are not as comprehensive or flexible as the income-driven repayment plans available with federal loans.
Eligibility Requirements
Eligibility for federal student loans is generally broader than for private loans. Federal loans are available to students who meet specific criteria, primarily enrollment in a degree program at an eligible institution. Private loans, including those from Navy Federal, typically require a creditworthy co-signer, especially for students with limited or no credit history. This can be a significant barrier for some borrowers. A strong credit history is usually required for independent applicants for private loans.
Scenarios Favoring Private or Federal Loans
| Scenario | Federal Loan Preference | Private Loan (Navy Federal) Preference | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student with limited credit history and no co-signer | Yes | No | Federal loans generally don’t require a co-signer. |
| Student needing lower interest rates and flexible repayment options | Yes | No | Federal loans often have lower interest rates and more repayment options. |
| Student with excellent credit and seeking a potentially lower interest rate than federal loans | No | Potentially Yes | In some cases, borrowers with excellent credit might secure a lower rate with a private loan. |
| Student needing a loan amount exceeding federal loan limits | No | Potentially Yes | Private loans can supplement federal loans when funding needs exceed federal limits. |
Long-Term Financial Planning Implications
Choosing a private loan over a federal loan can have significant long-term financial implications. The higher interest rates and fewer repayment options associated with private loans can lead to substantially higher overall borrowing costs and potentially prolonged debt repayment periods. Careful consideration of the total cost of borrowing and the potential impact on long-term financial goals, such as homeownership or retirement savings, is essential. For example, a $20,000 loan with a 7% interest rate over 10 years will cost significantly more than the same loan at 5%. This difference compounds over time, significantly impacting long-term financial stability.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Private student loans, while offering access to crucial funds for education, come with inherent risks that borrowers must carefully consider. Understanding these potential pitfalls is vital to making informed decisions and avoiding future financial hardship. Failing to fully grasp the implications of a private loan can lead to significant challenges down the line.
High interest rates, the possibility of default, and the impact on credit scores are key areas of concern. These factors can significantly influence a borrower’s long-term financial well-being. A thorough understanding of the loan agreement and responsible borrowing habits are essential for mitigating these risks.
High Interest Rates and Loan Costs
Private student loans often carry higher interest rates than federal student loans. This means that the total cost of the loan, including interest, will be significantly greater over the life of the loan. For example, a $20,000 loan with a 7% interest rate will accumulate substantially more interest than a similar loan with a 4% interest rate. This difference can amount to thousands of dollars over the repayment period. It is crucial to compare interest rates from multiple lenders before selecting a loan.
The Risk of Default
Defaulting on a private student loan can have severe consequences. Default occurs when a borrower fails to make payments for an extended period. This can lead to damage to credit scores, wage garnishment, and even legal action. The negative impact on credit history can make it difficult to obtain future loans, credit cards, or even rent an apartment. Responsible budgeting and proactive communication with the lender are essential to prevent default.
Impact on Credit Scores
Private student loans are reported to credit bureaus. Missed or late payments can negatively affect a borrower’s credit score, making it harder to secure favorable terms on future loans or credit cards. A lower credit score can also impact other aspects of financial life, such as insurance rates and even employment opportunities. Maintaining a good payment history is crucial for protecting one’s creditworthiness.
Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions
Before signing any loan agreement, it’s imperative to thoroughly review and understand all terms and conditions. This includes the interest rate, fees, repayment schedule, and any potential penalties for late or missed payments. Don’t hesitate to seek clarification from the lender if anything is unclear. Failing to understand the terms could lead to unforeseen financial burdens.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Private Student Loans
Borrowers can take several steps to mitigate the risks associated with private student loans. These include: carefully comparing loan offers from multiple lenders to secure the most favorable terms; creating a realistic budget to ensure loan repayments are manageable; establishing an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses that could impact repayment ability; and maintaining open communication with the lender to address any difficulties promptly. Proactive planning and responsible financial management are key to successful loan repayment.
Final Review
Securing funding for higher education is a significant step, and choosing the right loan is paramount. This exploration of Navy Federal private student loans offers a detailed overview, empowering you to compare options and make a well-informed decision. Remember to carefully review all terms and conditions, consider your financial circumstances, and explore all available options before committing to a loan. Proactive planning and understanding the potential risks associated with private student loans are key to successful repayment.
Q&A
What credit score is needed for a Navy Federal private student loan?
Navy Federal doesn’t publicly state a minimum credit score, but a good to excellent credit score significantly improves your chances of approval and securing favorable interest rates. A co-signer with good credit can also help.
Can I refinance my existing student loans with Navy Federal?
Yes, Navy Federal offers student loan refinancing options. The eligibility requirements and interest rates will depend on your creditworthiness and the terms of your existing loans.
What happens if I miss a payment on my Navy Federal student loan?
Missing payments will result in late fees and negatively impact your credit score. Contact Navy Federal immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment to explore options like forbearance or deferment.
Does Navy Federal offer any hardship programs for student loan borrowers?
Yes, Navy Federal may offer forbearance or deferment options in cases of financial hardship. Contact their customer service to discuss your specific situation and explore available programs.
