
Navigating the complexities of higher education financing can be daunting, but understanding the landscape of non-interest student loans offers a potential pathway to alleviate financial burdens. This guide delves into the various types of non-interest loans available, outlining eligibility criteria, application processes, and repayment options. We’ll explore both the advantages and disadvantages, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your financial future.
From government-backed programs to private initiatives, we’ll dissect the nuances of each option, comparing and contrasting their features to help you identify the best fit for your circumstances. Understanding the implications of loan repayment and building sound financial habits are key components of this discussion, ensuring you’re well-prepared for the journey ahead.
Types of Non-Interest Student Loans
Securing funding for higher education is a significant undertaking, and understanding the nuances of available financial aid is crucial. While interest-bearing loans are common, several non-interest student loan programs offer alternative avenues for financing your studies. These programs, offered by both government entities and private organizations, vary in their eligibility criteria, loan amounts, and repayment terms. This section will explore the different types of non-interest student loans available, comparing and contrasting their features to help you make informed decisions.
Government-Sponsored Non-Interest Student Loan Programs
Government-sponsored non-interest student loan programs are generally designed to provide financial assistance to students based on demonstrated financial need. These programs often have stricter eligibility requirements but typically offer more favorable repayment terms. Access to these programs can vary depending on your country of residence and specific educational institution.
Private Non-Interest Student Loan Programs
Private organizations, such as certain charities or foundations, may also offer non-interest student loans. These programs often have more flexible eligibility criteria but may also have stricter lending limits or more stringent repayment terms compared to government programs. Funding sources for private non-interest loans are diverse and may include endowments, donations, and specific grant programs. The availability and specifics of these loans vary greatly depending on the organization offering them.
Eligibility Criteria for Non-Interest Student Loans
Eligibility criteria for non-interest student loans differ significantly depending on the source of the funding. Government programs typically prioritize students from low-income backgrounds, demonstrating significant financial need, and may also consider academic merit or specific fields of study. Private programs may focus on factors like academic achievement, community involvement, or demonstrated leadership qualities. Some programs may require specific affiliations with the sponsoring organization, such as membership in a particular professional association or religious affiliation.
Comparison of Non-Interest Student Loan Programs
The following table compares several hypothetical examples of non-interest student loan programs. Note that the specifics of actual programs vary considerably, and this table serves as a general illustration. Always refer to the official program guidelines for the most up-to-date and accurate information.
| Loan Type | Eligibility Requirements | Typical Loan Amounts | Repayment Terms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Grant Program A | Demonstrated financial need, US citizenship, enrollment in accredited institution | $5,000 – $10,000 | Grant, no repayment required |
| Government Scholarship Program B | High academic achievement, specific field of study, enrollment in participating institution | $2,000 – $5,000 | Scholarship, no repayment required |
| Private Foundation Loan C | Demonstrated financial need, community involvement, essay submission | $1,000 – $3,000 | Repayment over 5 years, interest-free |
| University-Specific Grant D | Enrollment at the university, demonstrated financial need, application submission | Varies by university, typically $1,000-$5,000 | Grant, no repayment |
| Religious Organization Loan E | Religious affiliation, demonstrated financial need, participation in community service | Varies by organization, typically $1,000 – $2,000 | Repayment over 3 years, interest-free |
Eligibility and Application Process

Securing a non-interest student loan often involves a straightforward application process, though specific requirements can vary depending on the lending institution and the type of loan. Understanding the eligibility criteria and meticulously following the application steps are crucial for a successful outcome.
The application procedure generally involves several key stages, from initial eligibility checks to final loan disbursement. Factors such as your academic standing, credit history (if applicable), and the type of loan you’re applying for will significantly influence the approval process. Let’s delve into the details.
Application Requirements
The necessary documentation for a non-interest student loan application typically includes proof of enrollment in an eligible educational program, a completed loan application form, and possibly financial need documentation. Some lenders may also request additional supporting documents, such as transcripts, letters of recommendation, or parent/guardian financial information (depending on the loan type and the applicant’s age). Always refer to the specific requirements Artikeld by the lender.
Step-by-Step Application Guide
- Preliminary Check: Begin by verifying your eligibility for the specific non-interest loan program. This often involves checking the lender’s website for detailed eligibility criteria, such as minimum GPA requirements or enrollment status.
- Gather Documentation: Compile all necessary documents, including proof of enrollment (acceptance letter, enrollment verification), transcripts (if required), and any other supporting documents requested by the lender. Ensure all documents are accurate and up-to-date.
- Complete the Application Form: Carefully complete the loan application form, providing accurate and truthful information. Double-check all entries before submitting the form to avoid delays or rejection.
- Submit the Application: Submit the completed application form along with all supporting documents. This might be done online, via mail, or in person, depending on the lender’s procedures.
- Review and Approval: The lender will review your application and supporting documents. This process can take several weeks or even months. You may be contacted if additional information is needed.
- Loan Disbursement: Upon approval, the loan funds will be disbursed according to the lender’s schedule, often directly to the educational institution to cover tuition fees or other eligible expenses.
Factors Influencing Loan Approval
Several factors significantly impact the approval of a non-interest student loan application. While credit history is not always a major factor for certain types of non-interest student loans (especially those directly tied to the educational institution), academic performance, enrollment status, and the completeness of the application itself play crucial roles. For example, a student with a consistently strong academic record and a complete application package is more likely to be approved than a student with a poor academic record and an incomplete application. In cases where a co-signer is required, their credit history would also be considered. Some institutions may also consider family income for need-based non-interest loans.
Repayment Options and Terms
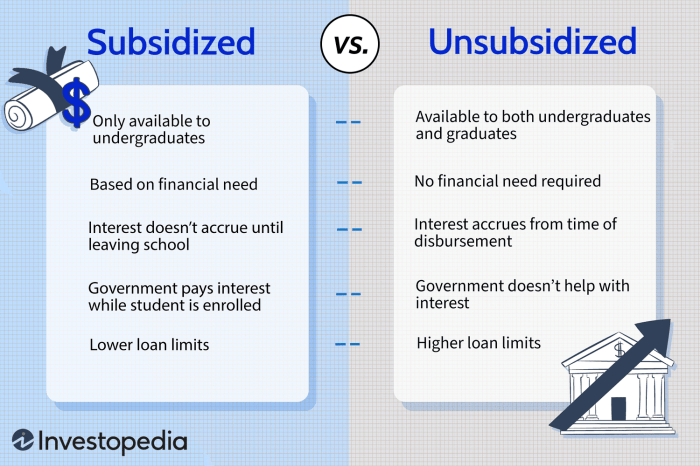
Understanding the repayment options and terms for your non-interest student loan is crucial for successful financial planning. Different repayment plans offer varying levels of flexibility, impacting your monthly payments and overall repayment period. Choosing the right plan depends on your individual financial circumstances and long-term goals.
Non-interest student loans typically offer several repayment plans, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. These plans often allow for flexibility in payment amounts and schedules, aiming to accommodate varying income levels and financial situations. However, it’s important to carefully consider the implications of each plan to avoid potential financial hardship.
Repayment Plan Options
Common repayment plans for non-interest student loans may include options such as a standard repayment plan, an extended repayment plan, and possibly income-driven repayment plans (though these are less common with non-interest loans, which often come with stricter terms). A standard repayment plan typically involves fixed monthly payments over a set period (e.g., 5-10 years), while an extended repayment plan stretches the repayment period, resulting in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest (although, again, this is not applicable to non-interest loans; the total amount owed remains the same). Some lenders might also offer graduated repayment plans where payments increase over time as it’s assumed income will also increase.
Repayment Schedule Examples and Implications
Let’s illustrate with examples. A $10,000 loan repaid over 5 years with a standard repayment plan might involve monthly payments of approximately $167. However, extending the repayment period to 10 years would reduce the monthly payment to roughly $83, but you’d be paying for a longer duration. The total amount paid remains the same in the case of a non-interest loan; only the timing of the payments changes. Choosing a longer repayment period might provide short-term financial relief, but it could lead to increased overall interest paid if interest were involved (it is not, in this case). Conversely, a shorter repayment period means higher monthly payments but quicker debt elimination.
Consequences of Defaulting on a Non-Interest Student Loan
Defaulting on a non-interest student loan can have severe consequences. This includes damage to your credit score, making it harder to obtain loans, credit cards, or even rent an apartment in the future. Lenders may also pursue legal action to recover the outstanding debt, which could involve wage garnishment or legal judgments. The impact on your financial well-being can be significant and long-lasting.
Hypothetical Repayment Plan for a $10,000 Loan
Let’s consider a hypothetical repayment plan for a $10,000 non-interest student loan. We’ll assume a standard repayment plan spread over 5 years (60 months).
| Month | Payment Amount | Remaining Balance |
|---|---|---|
| 1-60 | $166.67 | Decreasing monthly |
This results in a total repayment of $10,000 over 5 years. This is a simplified example; actual repayment schedules may vary depending on the lender and loan agreement. Always review the specific terms of your loan agreement carefully.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Choosing a non-interest student loan presents a unique set of advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional loans. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making an informed decision about your student financing. Weighing the benefits against the potential drawbacks will help you determine if a non-interest loan is the right choice for your specific financial circumstances.
The primary advantage of non-interest student loans lies in the absence of accruing interest. This significantly reduces the overall cost of borrowing, leading to lower repayment amounts and less financial burden in the long run. This contrasts sharply with interest-bearing loans, where the principal amount grows over time due to accumulating interest, potentially doubling or tripling the original loan amount by the time it is repaid.
Comparison of Long-Term Financial Implications
The long-term financial impact of a non-interest loan is considerably more favorable than that of an interest-bearing loan. For example, a $10,000 non-interest loan requires repayment of only $10,000. In contrast, a $10,000 loan with a 5% annual interest rate over 10 years could easily balloon to over $16,000 due to accumulated interest. This difference becomes even more pronounced with larger loan amounts and longer repayment periods. The absence of interest significantly lowers the total repayment amount and frees up more financial resources for other priorities after graduation.
Advantages of Non-Interest Student Loans
The benefits of securing a non-interest student loan are substantial. It offers a clear path to debt-free education, allowing students to focus on their studies without the added stress of accumulating debt. The reduced financial burden after graduation allows for greater flexibility in career choices and financial planning. The predictable and manageable repayment schedule promotes better financial stability.
Disadvantages of Non-Interest Student Loans
While the absence of interest is a major advantage, it’s important to acknowledge potential limitations. Non-interest loans are often more difficult to obtain due to their limited availability and stringent eligibility requirements. The loan amounts may be smaller compared to traditional loans, potentially leaving a funding gap for students with higher educational expenses. The eligibility criteria might exclude some students who might otherwise qualify for interest-bearing loans. Furthermore, the repayment schedule may be inflexible, making it challenging for borrowers facing unforeseen financial difficulties.
Advantages and Disadvantages Summary
Understanding the complete picture requires a balanced view of both the pros and cons. The following list summarizes the key advantages and disadvantages:
- Advantages: Lower total repayment amount, reduced financial burden, predictable repayment schedule, improved financial stability after graduation, focus on studies without debt stress.
- Disadvantages: Limited availability, stringent eligibility criteria, potentially smaller loan amounts, inflexible repayment terms, potential difficulty securing funding for high educational costs.
Finding and Evaluating Loan Providers
Securing non-interest student loans requires careful consideration of the lending institution. Choosing a reputable provider is crucial to ensure a smooth and ethical borrowing experience, protecting you from potential scams and unfair practices. This section will guide you through identifying trustworthy organizations and evaluating their offerings.
Reputable Organizations Offering Non-Interest Student Financial Assistance
Many organizations offer non-interest student financial assistance, but their availability and specifics vary significantly by location and eligibility criteria. It’s vital to research thoroughly and verify information independently. Examples include specific university-sponsored programs, certain religious charities (such as those affiliated with specific denominations), and established non-profit organizations dedicated to educational support. These organizations often operate with limited funding and may have highly competitive application processes. It is important to note that government-backed, non-interest loan programs are less common and usually targeted toward specific demographics or situations. Directly contacting educational institutions and relevant community organizations is the best way to uncover these opportunities.
Criteria for Evaluating Loan Provider Trustworthiness and Legitimacy
Evaluating the trustworthiness of a loan provider involves several key steps. Firstly, verify the organization’s legitimacy through independent research. Check if they are registered as a non-profit or charity with the relevant authorities in your jurisdiction. Look for evidence of their past performance, including reviews and testimonials from previous recipients. Be wary of organizations with vague or unverifiable claims, and always scrutinize their financial transparency. A reputable organization will be open about its funding sources and operational costs. Furthermore, review their terms and conditions carefully, paying close attention to fees, repayment schedules, and any potential hidden costs.
Strategies for Avoiding Loan Scams and Predatory Lending Practices
Avoiding loan scams and predatory lending practices requires vigilance. Be wary of unsolicited offers that seem too good to be true, particularly those promising extremely low or no interest rates with minimal documentation. Legitimate organizations will generally require some level of verification of your identity and financial situation. Never provide sensitive personal information, such as banking details, unless you are absolutely certain of the organization’s legitimacy and the security of the platform used for information exchange. If an organization pressures you to make a quick decision or requests upfront payments, proceed with extreme caution. Thorough research and a healthy dose of skepticism are your best defenses against predatory lending.
Loan Provider Evaluation Table
| Provider Name | Contact Information | Reputation/Reviews | Loan Terms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example University Financial Aid Office | Phone number, email address, physical address | Check university website for student reviews and feedback. | Refer to the university’s financial aid website for details on eligibility, repayment terms, and any applicable fees. |
| [Name of a reputable non-profit organization] | Website contact form, email address, possibly a phone number. | Check independent charity evaluation websites and online reviews. | Review the organization’s website for details on their loan program, eligibility criteria, and repayment terms. |
Impact on Future Financial Planning
Securing a non-interest student loan can significantly influence your long-term financial health, offering a pathway to education but also presenting responsibilities in managing debt and building a strong financial future. Careful planning and understanding of the implications are crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing potential drawbacks.
Obtaining a non-interest student loan, while advantageous due to the absence of accruing interest, still requires responsible financial management to avoid hindering future financial goals. The loan amount represents a debt that needs to be repaid, impacting available funds for other financial priorities like saving, investing, or purchasing a home. Failing to plan for repayment can lead to financial strain and potentially damage your credit score, affecting your ability to secure loans or credit cards in the future.
Budgeting and Financial Literacy in Repayment
Effective budgeting and strong financial literacy are paramount to successful loan repayment. A detailed budget, outlining income and expenses, helps allocate sufficient funds for loan payments while ensuring other essential needs are met. Understanding concepts like interest, credit scores, and debt management empowers informed decision-making regarding financial choices. Financial literacy resources, such as online courses, workshops, and financial advisors, provide valuable tools and knowledge to improve financial management skills. Without a well-defined budget and financial awareness, managing loan repayment becomes challenging and can lead to missed payments or accumulating additional debt.
Strategies for Minimizing Debt and Building Good Credit
Several strategies contribute to minimizing debt and building a positive credit history after loan repayment. Prioritizing loan repayment through consistent, on-time payments is crucial for establishing a good credit score. Exploring options like debt consolidation or refinancing, if available, might simplify repayment and potentially lower the overall cost. Building an emergency fund provides a safety net for unexpected expenses, preventing the need to borrow more money. Moreover, responsible credit card usage, maintaining low balances and timely payments, further strengthens creditworthiness.
Hypothetical Scenario: Managing Finances After a Non-Interest Student Loan
Imagine Sarah, a student who received a $10,000 non-interest student loan for her education. She created a detailed budget, allocating a portion of her post-graduation income towards loan repayment. She consistently made her monthly payments, ensuring on-time repayment within the agreed-upon timeframe. Simultaneously, she diligently saved a portion of her income for an emergency fund and made minimal, responsible credit card purchases, paying them off promptly. By combining disciplined budgeting with responsible financial practices, Sarah successfully repaid her loan, established a strong credit score, and laid a solid foundation for achieving her long-term financial goals, such as saving for a down payment on a house or investing for retirement.
Concluding Remarks

Securing a non-interest student loan can significantly impact your financial trajectory, offering a path to higher education without the added pressure of accumulating interest. By carefully considering the eligibility requirements, application processes, and repayment terms of various programs, you can make informed choices that align with your financial goals. Remember, diligent financial planning and a proactive approach to repayment are crucial for long-term financial success. This guide serves as a starting point for your research; further investigation into specific programs and consultations with financial advisors are highly recommended.
FAQ Section
What happens if I can’t repay my non-interest loan?
Consequences vary depending on the lender and loan type. They may include damage to your credit score, wage garnishment, or legal action. Contact your lender immediately if you anticipate difficulty repaying.
Are there any hidden fees associated with non-interest loans?
While the loan itself may be non-interest bearing, some lenders might charge administrative fees or origination fees. Carefully review the loan agreement to identify all costs involved.
Can I consolidate multiple non-interest student loans?
The possibility of consolidation depends on the lenders involved. Contact your lenders to inquire about consolidation options and their potential impact on your repayment plan.
How do non-interest loans affect my credit score?
Responsible repayment of a non-interest loan can positively impact your credit score, demonstrating your ability to manage debt. However, defaulting can severely damage your credit.
