
Navigating the world of student loans can be daunting, especially when considering private options. This guide delves into the specifics of PNC private student loans, offering a clear understanding of interest rates, repayment plans, eligibility requirements, and the application process. We’ll also compare PNC’s offerings to those of other lenders, helping you make an informed decision about financing your education.
Understanding the nuances of private student loans is crucial for responsible borrowing. This guide aims to demystify the process, providing you with the tools and information needed to confidently manage your student loan journey with PNC. From exploring various repayment options to understanding potential fees and risks, we cover all the essential aspects to empower you in making the right financial choices.
PNC Private Student Loan Interest Rates
Understanding the interest rates associated with PNC private student loans is crucial for prospective borrowers. These rates directly impact your monthly payments and the overall cost of your education. Factors such as your creditworthiness and the loan term significantly influence the interest rate you’ll receive.
PNC private student loan interest rates vary depending on several key factors. The loan term—the length of time you have to repay the loan—is a primary determinant. Generally, shorter loan terms (like 5 years) come with lower interest rates than longer terms (like 10 years). This is because the lender is exposed to less risk over a shorter repayment period. However, shorter terms often result in higher monthly payments.
Interest Rate Determination
PNC uses a variety of factors to determine your individual interest rate. Your credit history and credit score are paramount. A higher credit score typically indicates lower risk to the lender, resulting in a more favorable interest rate. The presence of a creditworthy co-signer can also significantly improve your chances of securing a lower rate, as the co-signer shares responsibility for repayment. Other factors considered may include your income, debt-to-income ratio, and the type of degree you are pursuing. It’s important to note that interest rates are not fixed and can change over time, depending on market conditions.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes
Fluctuations in interest rates directly affect both your monthly payments and the total cost of your loan. A higher interest rate translates to higher monthly payments for the same loan amount. Conversely, a lower interest rate results in lower monthly payments. The cumulative effect of even a small difference in interest rates can be substantial over the life of the loan, leading to a significant difference in the total amount repaid. For example, a 1% increase in the interest rate on a $30,000 loan over 10 years could add thousands of dollars to the total repayment amount.
Interest Rate Comparison Table
The following table provides a hypothetical illustration of how interest rates might vary based on loan amount and credit profile. These are examples and actual rates may differ.
| Loan Amount | Credit Score (Excellent) | Credit Score (Good) | Credit Score (Fair) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | 6.00% | 7.50% | 9.00% |
| $20,000 | 6.50% | 8.00% | 9.50% |
| $30,000 | 7.00% | 8.50% | 10.00% |
Note: These rates are hypothetical examples and do not represent actual PNC interest rates. Actual rates will vary based on individual circumstances and prevailing market conditions. Contact PNC directly for current rate information.
Repayment Options for PNC Student Loans
Choosing the right repayment plan for your PNC private student loan is crucial for managing your debt effectively and minimizing the total interest paid. PNC offers several repayment options, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial circumstances.
PNC offers a range of repayment plans to accommodate borrowers’ varying financial situations. These plans typically include options for fixed or variable interest rates, influencing both monthly payments and the total cost of repayment.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rate Repayment Plans
The primary difference between fixed and variable interest rate repayment plans lies in how your interest rate is determined. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan’s life, providing predictability in your monthly payments. A variable interest rate, however, fluctuates based on market indices, leading to potentially changing monthly payments.
Fixed-rate loans offer stability and predictability. You know exactly how much you’ll be paying each month, making budgeting easier. However, you might pay more in total interest over the life of the loan compared to a variable-rate loan if interest rates decline significantly during the repayment period. For example, if you choose a 10-year fixed-rate loan at 7%, your monthly payment will remain consistent for the entire 10 years, but your total interest paid will be higher than if interest rates dropped to 5% during that time.
Variable-rate loans may offer lower initial interest rates, leading to potentially lower monthly payments in the early stages of repayment. However, this advantage can quickly disappear if interest rates rise. Fluctuations can make budgeting more challenging, and you could end up paying significantly more in interest if rates increase substantially during your repayment period. For instance, a variable-rate loan starting at 5% could increase to 8% over time, resulting in higher monthly payments and a greater total interest cost.
Choosing a Repayment Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the optimal repayment plan requires careful consideration of your financial situation and long-term goals. The following steps can help guide you through this process.
- Assess your current financial situation: Evaluate your monthly income, expenses, and overall debt load to determine your affordability.
- Compare interest rates: Obtain quotes from PNC for both fixed and variable interest rate options to understand the potential cost differences.
- Consider your risk tolerance: Determine your comfort level with fluctuating payments. If you prefer predictability, a fixed-rate loan might be more suitable.
- Project your future income: Anticipate any potential changes in your income that might affect your ability to make payments.
- Calculate the total cost: Compare the total interest paid over the life of the loan for both fixed and variable rate options.
- Review the terms and conditions: Carefully read the loan agreement to fully understand all fees, penalties, and repayment terms.
- Make your decision: Choose the repayment plan that best aligns with your financial circumstances and risk tolerance.
Eligibility Requirements for PNC Private Student Loans
Securing a PNC private student loan involves meeting specific eligibility criteria. These requirements help PNC assess the applicant’s ability to repay the loan and manage the associated financial responsibility. Understanding these requirements beforehand can streamline the application process and increase the chances of approval.
Credit History and Credit Score
A strong credit history and a favorable credit score are significant factors in the PNC private student loan application process. Lenders use this information to gauge the applicant’s creditworthiness and repayment potential. Generally, a higher credit score indicates a lower risk to the lender, potentially leading to more favorable loan terms, such as a lower interest rate. Applicants with limited or poor credit history may find it more challenging to qualify for a loan or may be offered less attractive terms. In some cases, a co-signer with a strong credit history might be necessary to secure loan approval.
Co-Signer Requirements
If an applicant lacks a sufficient credit history or possesses a low credit score, a co-signer may be required. A co-signer is an individual who agrees to share responsibility for repaying the loan if the primary borrower defaults. PNC will assess the co-signer’s creditworthiness in addition to the applicant’s. The co-signer should have a strong credit history and a good credit score to improve the chances of loan approval. It is important to note that co-signing a loan carries significant financial responsibility for the co-signer.
Eligibility Checklist
The following checklist summarizes key eligibility requirements for PNC private student loans. It is advisable to review these criteria before initiating the application process.
- U.S. citizenship or permanent residency
- Enrollment or acceptance at an eligible school
- Satisfactory credit history (or a co-signer with satisfactory credit)
- Sufficient income or demonstrated ability to repay the loan
- Valid Social Security number
- Valid email address and phone number
Application and Approval Process for PNC Private Student Loans

Applying for a PNC private student loan involves a straightforward process designed to be completed online. The application requires providing accurate information and necessary documentation to facilitate a timely review and approval. The entire process, from application submission to loan disbursement, is generally efficient, though the exact timeframe can vary based on individual circumstances.
The online application process is user-friendly and guides applicants through each step. Applicants are required to create an online account and complete the application form, providing details about their educational background, financial information, and co-signer information (if applicable). The system allows for easy tracking of application progress. After submission, PNC reviews the application and supporting documentation.
Required Documents for Application
To ensure a smooth and efficient application process, having the necessary documents readily available is crucial. These documents verify your identity, academic standing, and financial stability, enabling PNC to assess your eligibility for a loan.
- Government-issued photo identification: Such as a driver’s license or passport.
- Social Security number: This is essential for verifying your identity and credit history.
- Proof of enrollment: An acceptance letter or enrollment confirmation from your chosen institution.
- Information on your chosen degree program: Including the program’s length and expected cost.
- Financial information: This may include tax returns, pay stubs, or bank statements to demonstrate your income and ability to repay the loan.
- Co-signer information (if applicable): If you require a co-signer, their identification and financial information will also be needed.
Online Application Steps
The online application process is designed for ease of use. Following these steps will help you navigate the application efficiently.
- Create an account: Visit the PNC website and create a secure online account.
- Complete the application form: Provide accurate and complete information in the online application form. Double-check all entries for accuracy.
- Upload required documents: Securely upload the necessary supporting documents as Artikeld above.
- Review and submit: Carefully review your application for any errors before submitting it electronically.
- Track your application: Use your online account to monitor the status of your application.
Loan Approval and Disbursement Timeframe
The time it takes for loan approval and disbursement can vary depending on several factors, including the completeness of your application and the volume of applications PNC is processing at that time. While PNC aims for efficiency, applicants should allow for a reasonable timeframe for processing.
Generally, the process takes several weeks. Once approved, the loan disbursement is typically made directly to the educational institution to cover tuition and fees. In some cases, a portion of the funds may be disbursed directly to the borrower after verification of expenses. Applicants should always contact PNC directly if they have concerns about the processing time for their specific application.
Managing and Paying Back PNC Student Loans
Successfully managing and repaying your PNC student loan requires a proactive approach and understanding of your repayment options. This section details methods for making timely payments, the consequences of late payments, and how to contact PNC for assistance. Effective management minimizes financial stress and helps you achieve your financial goals.
Making Timely Payments on PNC Student Loans
PNC offers several convenient ways to make your student loan payments. You can choose the method that best suits your needs and schedule. Consistent and on-time payments are crucial for maintaining a good credit history and avoiding penalties.
- Online Payments: This is often the most convenient method. You can log into your PNC online banking account, locate your student loan account, and make a payment directly. This typically allows for immediate payment processing.
- Mail Payments: You can mail a check or money order to the address provided on your monthly statement. Remember to include your account number and allow sufficient processing time for the payment to be credited to your account. This method may take several days to process.
- Phone Payments: Some lenders offer phone payment options, although this may not be the case with all PNC student loans. Check your loan documents or contact PNC customer service to confirm availability.
Consequences of Late or Missed Payments
Late or missed payments can have significant negative consequences. These consequences can impact your credit score and overall financial well-being.
- Late Fees: PNC will likely charge late fees for payments made after the due date. These fees can add up over time, increasing the total amount you owe.
- Negative Impact on Credit Score: Late payments are reported to credit bureaus, negatively affecting your credit score. A lower credit score can make it more difficult to obtain loans, credit cards, or even rent an apartment in the future.
- Loan Default: Repeated missed payments can lead to loan default. This can result in serious financial consequences, including wage garnishment, legal action, and damage to your credit history.
Contacting PNC Customer Service
If you anticipate difficulty making a payment or have questions about your account, contacting PNC customer service is crucial. They can provide guidance, explore potential payment assistance options, and help you avoid late payment penalties. You can find their contact information on your loan documents or on the PNC website. Contacting them promptly is key to resolving any issues effectively.
Managing a PNC Student Loan Account: A Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart. The flowchart begins with “Login to PNC Account.” This branches into two paths: “Make Payment” and “Account Inquiry/Assistance.” “Make Payment” then branches into “Online Payment,” “Mail Payment,” and “Phone Payment” (if available). Each of these ends in “Payment Confirmation.” “Account Inquiry/Assistance” leads to “Contact Customer Service,” which leads to “Resolution/Information.” All paths ultimately lead to “Account Updated.” The flowchart visually represents the straightforward process of managing your account. This visual representation simplifies the steps involved in managing your PNC student loan account.
Comparing PNC Private Student Loans to Other Lenders
Choosing a private student loan involves careful consideration of several factors, including interest rates, fees, and repayment options. While PNC offers competitive private student loans, it’s crucial to compare their offerings against those of other major lenders to determine the best fit for your individual financial situation. This comparison will highlight key differences and help you make an informed decision.
Several key aspects differentiate PNC’s private student loans from those offered by other lenders. These differences primarily revolve around interest rates, which can significantly impact the overall cost of borrowing, fees associated with loan origination and servicing, and the flexibility of repayment options available to borrowers after graduation. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting a loan that aligns with your financial goals and repayment capabilities.
Interest Rates and Fees
Interest rates for private student loans vary depending on the lender, the borrower’s creditworthiness, and the loan terms. PNC typically offers a range of interest rates, often competitive with other major lenders like Sallie Mae and Discover. However, the specific rate you qualify for will depend on your credit score and other financial factors. Origination fees, which are charged upfront to cover the lender’s administrative costs, also differ between lenders. Some lenders may offer lower interest rates but higher fees, while others might have a higher interest rate but lower or no fees. Careful comparison of the total cost of borrowing, considering both interest and fees, is crucial.
Repayment Options and Customer Service
Repayment options can significantly influence the manageability of your student loan debt. PNC offers various repayment plans, including graduated, extended, and fixed repayment options. These plans allow borrowers to tailor their monthly payments to their financial circumstances. However, the specific options available and their terms may vary from those offered by competitors. Customer service quality also plays a significant role. Comparing lenders based on their customer service reputation, accessibility, and responsiveness is vital. Lenders with strong customer service support can provide valuable assistance during the loan application, repayment, and any potential financial hardship periods.
Comparative Table of Key Features
| Feature | PNC | Sallie Mae | Discover |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate (Example Range) | 6.00% – 12.00% | 6.50% – 13.00% | 7.00% – 14.00% |
| Origination Fee | Variable, check current rates | Variable, check current rates | Variable, check current rates |
| Repayment Options | Fixed, Graduated, Extended | Fixed, Graduated, Extended | Fixed, Graduated, Income-Based |
| Co-signer Requirements | May be required for borrowers with limited credit history | May be required for borrowers with limited credit history | May be required for borrowers with limited credit history |
Note: The interest rate ranges and fees provided in the table are examples and may not reflect current rates. It’s essential to check each lender’s website for the most up-to-date information. The availability of specific repayment options can also vary depending on individual circumstances and loan terms.
PNC Private Student Loan Fees and Charges

Understanding the fees associated with your PNC private student loan is crucial for accurately budgeting and managing your repayment. These fees, while seemingly small individually, can accumulate significantly over the life of the loan, impacting your overall borrowing cost. This section details the various fees you might encounter and their implications.
PNC Private Student Loans, like many other private student loans, include several potential fees that add to the total cost of borrowing. These fees aren’t always consistent and can vary based on factors such as the loan amount, your creditworthiness, and the specific terms of your loan agreement. It’s essential to review your loan documents carefully to understand the exact fees applicable to your situation. Failing to understand these charges can lead to unexpected expenses and financial strain during repayment.
Origination Fees
An origination fee is a one-time charge levied by PNC at the time your loan is disbursed. This fee compensates PNC for the administrative costs involved in processing your loan application and funding your education. The percentage of the origination fee can vary, but it’s typically expressed as a percentage of the total loan amount. For example, a 1% origination fee on a $10,000 loan would be $100. This fee is usually deducted from the total loan amount before it’s disbursed to you, meaning you receive slightly less than the total loan amount approved.
Late Payment Fees
Late payment fees are charged if you fail to make a payment by the due date specified in your loan agreement. The amount of the late fee can vary; PNC’s late payment fee structure will be clearly Artikeld in your loan documents. These fees can quickly add up if you consistently miss payments, significantly increasing the total cost of your loan. Consistent on-time payments are crucial to avoid incurring these additional charges.
Returned Payment Fees
If a payment is returned due to insufficient funds or incorrect account information, PNC will likely charge a returned payment fee. This fee covers the administrative costs associated with processing the returned payment and attempting to collect the funds again. It’s important to ensure you have sufficient funds in your account and that your payment information is accurate to avoid this fee.
Other Potential Fees
While less common, other fees may apply depending on your specific loan agreement. These could include fees for things like loan modifications or early payoff penalties. Always refer to your loan documents for a complete list of applicable fees.
Total Cost of Borrowing: Interest and Fees
The total cost of borrowing encompasses not only the principal loan amount but also the accumulated interest and any applicable fees. To illustrate, let’s consider an example: Suppose you borrow $20,000 with a 6% annual interest rate over 10 years, and a 1% origination fee ($200). The total interest paid over the life of the loan would depend on the repayment plan, but could be substantial. Adding the origination fee, late payment fees (if any), and the total interest paid together, you’ll arrive at the true cost of borrowing. This emphasizes the importance of comparing loan offers from different lenders and choosing the option with the lowest total cost.
Implications of Fees on Loan Repayment
Fees significantly impact the overall cost and duration of loan repayment. Each additional fee increases the total amount you need to repay, potentially extending the repayment period and increasing the total interest paid. Careful financial planning and responsible borrowing habits are essential to minimize the impact of these fees and manage your student loan debt effectively. Understanding the fee structure upfront allows for better budgeting and informed decision-making regarding your loan.
- Origination Fee: A one-time fee charged upon loan disbursement, typically a percentage of the loan amount.
- Late Payment Fee: Charged for payments made after the due date.
- Returned Payment Fee: Charged when a payment is returned due to insufficient funds or incorrect information.
- Other Potential Fees: Fees may apply for loan modifications or early payoff, as detailed in your loan agreement.
Deferment and Forbearance Options for PNC Private Student Loans
Navigating the repayment of student loans can be challenging, and unforeseen circumstances may necessitate temporary pauses in your payments. PNC offers deferment and forbearance options to help borrowers manage their loans during difficult financial periods. Understanding the differences between these options and the application process is crucial for responsible loan management.
Deferment and forbearance are both temporary pauses in your loan repayment, but they differ significantly in their eligibility requirements and impact on your loan. While both can provide short-term relief, it’s important to understand that interest may still accrue during either, potentially increasing your overall loan cost.
Circumstances Qualifying for Deferment or Forbearance
PNC’s specific criteria for granting deferment or forbearance for private student loans may vary, and it’s essential to check your loan agreement or contact PNC directly for the most up-to-date information. Generally, however, deferment is typically granted for specific situations like unemployment, or enrollment in graduate school, while forbearance is often granted for more general financial hardship. For instance, a borrower experiencing unexpected medical expenses might qualify for forbearance, whereas a borrower who has lost their job and is actively seeking employment might be eligible for deferment. Documentation supporting the claimed circumstance is typically required.
Differences Between Deferment and Forbearance
Deferment and forbearance, while both offering temporary relief from loan payments, differ significantly. Deferment typically involves a temporary suspension of payments, and in some cases, the interest may be subsidized by the lender (though this is less common with private loans). Forbearance, on the other hand, usually involves a reduction in payments or a temporary suspension of payments, but interest typically continues to accrue. This means that the total amount owed at the end of the deferment or forbearance period will likely be higher than the original principal amount due to accumulated interest. The choice between these options depends heavily on the borrower’s specific circumstances and financial capabilities.
Application Process for Deferment or Forbearance
The application process for obtaining deferment or forbearance typically involves contacting PNC directly. This might be done through their online portal, by phone, or via mail. Borrowers will generally need to provide documentation supporting their claim for hardship or qualifying circumstance. This might include proof of unemployment, enrollment in a graduate program, or medical bills. PNC will review the application and supporting documentation, and then will notify the borrower of their decision. The processing time can vary, so it is advisable to apply well in advance of needing the relief.
Impact on Loan Repayment Schedule and Total Cost
Both deferment and forbearance will extend the overall repayment period of your loan. This is because the missed payments are added to the end of the loan term. However, the impact on the total cost varies. With deferment, if interest is subsidized, the total cost may not increase significantly. But with forbearance, where interest continues to accrue, the total cost will inevitably increase, as the borrower will be repaying both the original principal and the accumulated interest over a longer period. For example, a $20,000 loan with a 6% interest rate could accrue thousands of dollars in interest over a period of forbearance, leading to a significantly higher total repayment amount. Careful consideration of the potential long-term financial implications is crucial before opting for either option.
Potential Risks and Benefits of PNC Private Student Loans
Choosing a private student loan, like those offered by PNC, requires careful consideration of both the potential advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your financial situation and long-term goals. While private loans can offer flexibility, they also carry risks that shouldn’t be overlooked.
PNC private student loans, like other private loans, present a blend of potential benefits and inherent risks. The decision of whether or not to utilize them depends heavily on individual circumstances and responsible borrowing practices. Weighing the pros and cons carefully is essential before committing to a loan.
Potential Risks of PNC Private Student Loans
Private student loans, including those from PNC, carry several risks that borrowers should be aware of before applying. These risks can significantly impact your financial future if not properly managed.
Understanding these potential drawbacks is critical for making an informed decision about borrowing. Failing to adequately assess these risks could lead to unforeseen financial difficulties.
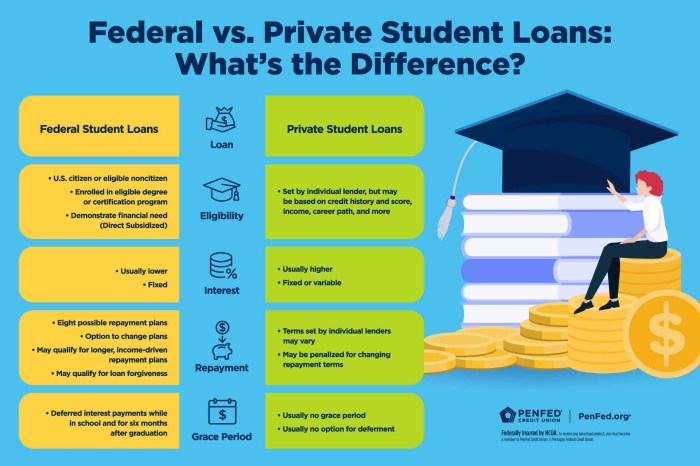
- Higher Interest Rates: Private loan interest rates are typically higher than federal student loan rates. This means you’ll pay more in interest over the life of the loan, increasing the total cost of your education.
- Variable Interest Rates: Some private loans offer variable interest rates, which fluctuate based on market conditions. This can lead to unpredictable monthly payments and potentially higher overall costs if rates rise.
- Lack of Federal Protections: Unlike federal student loans, private loans generally don’t offer the same borrower protections, such as income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness programs. This means you may have fewer options if you experience financial hardship.
- Stricter Eligibility Requirements: Private lenders often have stricter eligibility requirements than federal loan programs. Borrowers with less-than-perfect credit scores or limited income may find it difficult to qualify.
- Potential for Debt Accumulation: Borrowing more than necessary can lead to significant debt accumulation, impacting your ability to save for other financial goals like a down payment on a house or retirement.
Benefits of PNC Private Student Loans
While private student loans come with risks, they also offer certain advantages that may make them a suitable option for some borrowers. These benefits can help finance education costs and provide financial flexibility.
It’s important to remember that these benefits should be carefully weighed against the potential risks before making a borrowing decision. The suitability of a private loan depends heavily on your individual circumstances and responsible financial planning.
- Potential for Higher Loan Amounts: Private loans may offer higher borrowing limits than federal loans, potentially covering the full cost of education, including tuition, fees, and living expenses.
- No Requirement for Need-Based Assessment: Unlike federal loans, private loans are not need-based, making them accessible to students who may not qualify for federal aid.
- Co-signer Options: Having a co-signer with good credit can improve your chances of approval and potentially secure a lower interest rate.
- Flexible Repayment Options: Some private lenders, including PNC, may offer a variety of repayment options, such as fixed or variable interest rates, and potentially shorter repayment terms.
Comparison of Risks and Benefits
To help visualize the trade-offs, let’s summarize the risks and benefits in a concise format:
| Risks | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Higher interest rates than federal loans | Potentially higher loan amounts than federal loans |
| Variable interest rates (potential for increased costs) | No need-based assessment required |
| Lack of federal borrower protections | Co-signer option to improve approval chances and interest rates |
| Stricter eligibility requirements | Flexible repayment options (depending on the lender and loan terms) |
| Potential for significant debt accumulation | May cover the full cost of education |
Last Word
Securing funding for your education is a significant step, and choosing the right loan provider is equally important. This comprehensive guide on PNC private student loans has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate the process effectively. By understanding interest rates, repayment plans, eligibility criteria, and potential risks, you are better prepared to make informed decisions and manage your student loan debt responsibly. Remember to carefully consider your financial situation and explore all available options before committing to a loan.
Essential Questionnaire
What happens if I miss a payment on my PNC student loan?
Missing payments can result in late fees, damage to your credit score, and potential loan default. Contact PNC immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment to explore options like deferment or forbearance.
Can I refinance my PNC student loan?
Yes, you may be able to refinance your PNC student loan with another lender, potentially securing a lower interest rate or more favorable repayment terms. Shop around and compare offers before refinancing.
What is the difference between a co-signer and an endorser?
A co-signer shares responsibility for the loan with you, while an endorser only agrees to pay if you default. Both impact your approval chances, but a co-signer carries more financial risk.
Does PNC offer loan forgiveness programs?
PNC does not directly offer loan forgiveness programs. However, certain professions or government programs may offer loan forgiveness opportunities for federal student loans; private loans like those from PNC typically do not qualify.
