
The pursuit of higher education often involves navigating the complex world of student financing. While federal student loans provide a crucial foundation, many students find themselves turning to private student loan providers to bridge the funding gap. Understanding the nuances of this market is critical for securing the best possible terms and avoiding potential pitfalls. This guide explores the diverse landscape of private student loan providers, offering insights into their lending practices, eligibility criteria, and the crucial considerations borrowers should keep in mind.
From traditional banks and credit unions to innovative fintech companies, the options for private student loans are numerous and varied. Each provider offers unique loan features, interest rates, and repayment options, making it essential for prospective borrowers to conduct thorough research and compare offers before committing to a loan. This comprehensive overview will empower you to make informed decisions, ensuring a smoother path towards your educational goals.
Types of Private Student Loan Providers

Navigating the world of private student loans can feel overwhelming, given the variety of lenders available. Understanding the different types of providers and their lending practices is crucial for securing the best loan terms for your individual circumstances. This section will clarify the landscape of private student loan providers, highlighting key differences and considerations.
Private student loans are offered by a range of institutions, each with its own approach to lending. These providers can be broadly categorized, and understanding these categories can help you make informed decisions.
Categorization of Private Student Loan Providers
| Provider Type | Examples | Typical Loan Features | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banks | Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Citizens Bank | Variable and fixed interest rates, competitive terms for borrowers with good credit, various repayment options. | Borrowers with established credit history seeking competitive rates and a wide range of options. |
| Credit Unions | Navy Federal Credit Union, Alliant Credit Union | Often lower interest rates than banks, member-centric approach, potential for personalized service. | Borrowers who are members of the credit union, often prioritizing lower rates and community-focused service. |
| Online Lenders | SoFi, Sallie Mae (private loans), Discover | Streamlined application processes, potentially faster funding, variable and fixed interest rates, may offer additional features like autopay discounts. | Borrowers who prefer digital convenience and quick application processes, often including those with varying credit profiles. |
| Specialized Lenders | Lenders focusing on specific professions or demographics (e.g., medical professionals) | Loan features tailored to specific needs and repayment plans, potentially offering income-driven repayment options. | Borrowers within the specific niche targeted by the lender, often those with unique financial situations or career paths. |
Comparison of Lending Practices
A direct comparison of interest rates, fees, and repayment options across different providers is challenging due to the constantly changing market and the personalized nature of loan offers. However, we can highlight some general trends observed among three major providers:
- Sallie Mae: Often offers a range of loan options, including variable and fixed rates. Fees can vary depending on the loan type and borrower profile. Repayment options typically include standard, graduated, and extended repayment plans.
- SoFi: Known for its user-friendly online platform and potentially competitive interest rates. They may offer additional benefits such as unemployment protection and career services. Fees and repayment options are generally clearly Artikeld on their website.
- Wells Fargo: A traditional bank offering private student loans, typically with competitive rates for borrowers with strong credit. Fees and repayment plans are similar to other major banks, often providing a range of choices to suit different needs.
It’s crucial to note that the specific interest rates, fees, and repayment options offered by each lender will vary based on factors such as credit score, co-signer availability, and the loan amount.
The Role of Fintech Companies in the Private Student Loan Market
Fintech companies are significantly impacting the private student loan market by introducing innovative technologies and approaches to lending. These companies often leverage data analytics and automated processes to streamline the application and approval process, offering potentially faster funding and more personalized loan options.
For example, many fintech lenders utilize sophisticated algorithms to assess creditworthiness, potentially providing access to loans for borrowers who might be overlooked by traditional lenders. They often offer flexible repayment options and integrated tools for budgeting and financial management, adding value beyond the loan itself. The increased competition from fintech lenders has also contributed to a more competitive pricing environment in the private student loan market, benefiting borrowers overall.
Interest Rates and Fees

Understanding the interest rates and fees associated with private student loans is crucial for prospective borrowers. These costs significantly impact the overall cost of your education and your repayment burden. Careful consideration of these factors is essential before committing to a private loan.
Private student loan interest rates are determined by several factors, primarily the borrower’s creditworthiness. Lenders assess your credit history, credit score, and debt-to-income ratio to gauge your risk of default. A strong credit history and a high credit score generally translate to lower interest rates, reflecting the lender’s lower perceived risk. Other factors influencing interest rates include the loan term (longer terms often mean higher rates), the type of loan (variable vs. fixed), and the prevailing market interest rates. For example, a borrower with excellent credit might secure a lower rate than someone with a limited credit history. The lender’s current risk assessment models and the overall economic climate also play a significant role.
Private Student Loan Fees
Private student loans often involve various fees that add to the total cost of borrowing. Understanding these fees is vital for budgeting and financial planning.
| Fee Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Origination Fee | A one-time fee charged by the lender upon loan disbursement. This fee typically represents a percentage of the loan amount and covers the lender’s administrative costs associated with processing the loan. For example, a 1% origination fee on a $10,000 loan would be $100. |
| Late Payment Fee | A penalty charged if a payment is not received by the lender on or before the due date. The amount of the late fee varies by lender, but it can range from a fixed dollar amount to a percentage of the missed payment. Consistent on-time payments are crucial to avoid incurring these charges. |
| Prepayment Penalty | Some private student loans may include a prepayment penalty, which is a fee charged if you pay off the loan early. While less common now, it’s essential to check your loan agreement for any such clauses. This fee is designed to compensate the lender for lost interest income. |
| Returned Payment Fee | A fee charged if a payment is returned due to insufficient funds or incorrect account information. This fee helps cover the administrative costs associated with processing the returned payment. |
Fixed-Rate vs. Variable-Rate Loans
Private student loans are offered with two primary interest rate structures: fixed-rate and variable-rate. Understanding the differences is crucial for managing your repayment plan.
A fixed-rate loan maintains a consistent interest rate throughout the loan’s term. This provides predictability and allows for easier budgeting. Borrowers know exactly how much they will owe each month. Conversely, a variable-rate loan has an interest rate that fluctuates based on an underlying index, such as the prime rate or LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate). While variable-rate loans may initially offer lower interest rates, the rate can increase over time, leading to unpredictable monthly payments. A borrower might start with a low rate but face higher payments as the index increases. The choice between a fixed-rate and a variable-rate loan depends on individual risk tolerance and financial circumstances.
Repayment Options and Plans
Choosing the right repayment plan for your private student loan is crucial, as it directly impacts your monthly budget and the total amount you’ll pay over the life of the loan. Different plans offer varying levels of flexibility and may result in significantly different total interest costs. Understanding these options is key to responsible borrowing and repayment.
Several repayment options are typically available for private student loans, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The best choice depends on your individual financial circumstances and long-term goals.
Private Student Loan Repayment Plan Options
Private student loan providers offer a range of repayment plans designed to accommodate different financial situations. These plans primarily differ in their monthly payment amounts and the overall repayment period. Consider these factors carefully when selecting a plan.
- Standard Repayment: This is the most common plan, requiring fixed monthly payments over a set period (typically 10-15 years). Payments remain consistent throughout the repayment term. This option generally leads to lower total interest paid compared to longer-term plans.
- Graduated Repayment: With this plan, monthly payments start low and gradually increase over time. This can be beneficial in the early stages of your career when income may be lower. However, the total interest paid will likely be higher due to the longer repayment period and the compounding effect of interest on the outstanding balance.
- Extended Repayment: This option stretches the repayment period over a longer timeframe (potentially up to 25 years or more). Lower monthly payments are a key advantage, making the loan more manageable in the short term. However, this significantly increases the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Impact of Repayment Plans on Total Interest Paid
The choice of repayment plan has a substantial impact on the total interest you’ll pay. Longer repayment periods, while offering lower monthly payments, allow interest to accrue over a longer time, resulting in significantly higher total interest costs. Conversely, shorter repayment periods, while demanding higher monthly payments, minimize the total interest paid.
It’s important to carefully weigh the benefits of lower monthly payments against the increased long-term cost of interest. A loan amortization schedule (available from your lender) can clearly illustrate the impact of different plans on the total cost.
Hypothetical Repayment Schedule for a $50,000 Loan at 7% Interest
This table demonstrates the differences in monthly payments and total interest paid for a hypothetical $50,000 private student loan with a 7% annual interest rate, assuming various repayment plans. These are simplified examples and actual figures may vary depending on the lender and specific loan terms.
| Repayment Plan | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard (10-year) | $560 | $16,800 |
| Graduated (10-year) | Starts at ~$400, increases gradually | ~$18,000 |
| Extended (20-year) | ~$360 | ~$37,000 |
Note: These are simplified estimates. Actual payments and interest may vary based on compounding frequency and other loan terms. Consult your lender for precise figures.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Private student loans, while offering access to crucial funds for higher education, present several potential risks that borrowers must carefully consider before accepting any loan offer. Understanding these risks and implementing proactive strategies for managing debt is essential for navigating the complexities of student loan repayment successfully. Failing to do so can lead to significant financial strain and long-term consequences.
High interest rates and the potential for substantial debt burdens are primary concerns. Unlike federal student loans, which often offer more favorable interest rates and repayment options, private loans can carry significantly higher interest rates, leading to a larger total repayment amount over the life of the loan. This can be particularly problematic for borrowers who may face unexpected job losses or other financial difficulties during repayment. The accumulation of substantial debt can negatively impact credit scores, making it difficult to secure loans or credit cards in the future, further hindering financial stability.
Comparison of Loan Offers
Before committing to a private student loan, it’s crucial to compare offers from multiple lenders. Different lenders offer varying interest rates, fees, repayment terms, and other conditions. By carefully reviewing several loan offers, borrowers can identify the most favorable terms that align with their individual financial circumstances and repayment capabilities. This comparative analysis allows borrowers to make informed decisions, potentially saving thousands of dollars in interest and fees over the loan’s lifetime. For example, a difference of even one percentage point in the interest rate can significantly impact the total amount repaid.
Strategies for Effective Debt Management
Effective management of private student loan debt requires a proactive approach. This includes creating a realistic budget that accounts for loan payments, other expenses, and potential financial emergencies. Borrowers should prioritize making on-time payments to avoid late fees and maintain a good credit score. Exploring options such as income-driven repayment plans (if available with the lender) can help manage payments during periods of financial hardship. Furthermore, proactively contacting the lender to discuss potential hardship situations or explore refinancing options can provide valuable assistance in mitigating financial stress. For instance, consolidating multiple loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate can simplify repayment and reduce the overall cost. Finally, careful financial planning and budgeting throughout the repayment period are crucial for avoiding default and maintaining long-term financial well-being.
Consumer Protection and Regulations
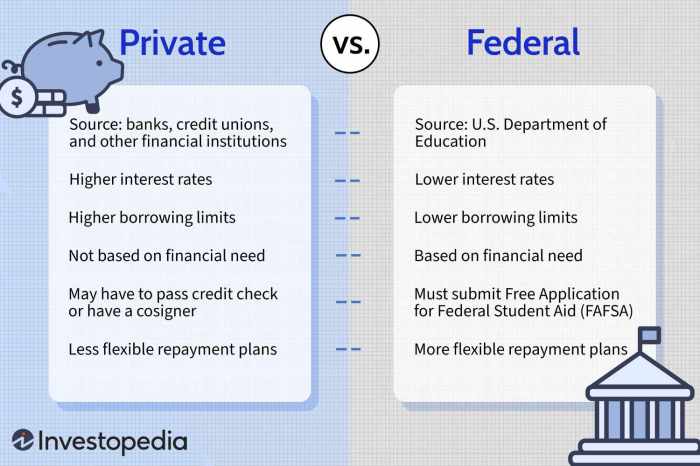
Navigating the world of private student loans requires understanding the legal protections in place to safeguard borrowers. Several federal and state laws regulate private student loan providers, aiming to ensure fair lending practices and prevent predatory behavior. While the government doesn’t directly lend through private loans, its oversight plays a crucial role in protecting consumers.
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) is a key federal agency overseeing private student lenders. Its authority stems from the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. The CFPB works to ensure lenders comply with federal consumer protection laws, investigating complaints, enforcing regulations, and promoting transparency in lending practices. State attorneys general also have jurisdiction over private lenders operating within their states, often enforcing state-specific consumer protection laws.
Relevant Consumer Protection Laws and Regulations
Several laws significantly impact private student loan practices. The Truth in Lending Act (TILA) mandates clear disclosure of loan terms, including interest rates, fees, and repayment schedules. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs how lenders collect and use credit information, protecting borrowers from inaccurate or discriminatory practices. The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) protects borrowers from abusive debt collection tactics. Violation of these laws can result in significant penalties for lenders. For instance, a lender failing to provide accurate TILA disclosures could face fines and legal action.
The Role of Government Agencies in Overseeing Private Student Loan Providers
Government agencies, primarily the CFPB and state attorneys general, play a vital role in overseeing private student loan providers. They monitor lenders’ compliance with federal and state consumer protection laws, investigating complaints from borrowers alleging unfair or deceptive practices. These agencies have the power to take enforcement actions against lenders who violate these laws, including issuing cease-and-desist orders, imposing fines, and even pursuing legal action. Furthermore, they regularly publish consumer advisories and educational materials to inform borrowers about their rights and responsibilities. The CFPB, for example, maintains a public database of consumer complaints, allowing borrowers to see trends and potential issues with specific lenders.
Resources Available to Borrowers Facing Difficulties with Repayment
Borrowers struggling with private student loan repayments have several resources available to them. Contacting the lender directly to explore options like forbearance, deferment, or loan modification is often the first step. Nonprofit credit counseling agencies can provide free or low-cost guidance on managing debt and exploring repayment options. State and local consumer protection agencies can offer assistance with resolving disputes with lenders. The CFPB website offers valuable information and tools for navigating private student loan difficulties. Finally, legal aid organizations may be able to provide legal representation to borrowers facing serious challenges with their loans. For example, a borrower facing financial hardship might contact a credit counselor to explore options like an income-driven repayment plan, if available with their lender.
Summary
Securing a private student loan requires careful planning and a comprehensive understanding of the market. By comparing loan offers, understanding the associated fees and repayment options, and proactively managing your debt, you can mitigate potential risks and successfully navigate the complexities of private student loan financing. Remember, responsible borrowing practices are key to achieving your educational aspirations without incurring undue financial strain. Utilize the resources and information provided here to make well-informed decisions that align with your financial well-being.
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between a fixed-rate and a variable-rate private student loan?
A fixed-rate loan maintains a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, making your monthly payments predictable. A variable-rate loan’s interest rate fluctuates based on market conditions, leading to potentially higher or lower payments over time.
Can I refinance my private student loans?
Yes, refinancing can consolidate multiple loans into one with a potentially lower interest rate or more favorable repayment terms. However, it’s crucial to compare offers from different lenders before refinancing.
What happens if I miss a payment on my private student loan?
Missing payments can result in late fees, damage your credit score, and potentially lead to default, which has serious financial consequences. Contact your lender immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment.
What are the consequences of defaulting on a private student loan?
Defaulting on a private student loan can severely damage your credit score, making it difficult to obtain future loans or credit cards. It can also lead to wage garnishment or legal action by the lender.
