
Securing funding for higher education is a significant undertaking, and understanding the nuances of student loans is crucial for responsible borrowing. This guide delves into the specifics of private student loans with fixed interest rates, offering a clear and concise overview of their mechanics, advantages, and potential drawbacks. We’ll explore how these loans differ from federal options and examine the factors influencing interest rate determination, ultimately empowering you to make informed financial decisions.
From understanding the impact of credit scores and co-signers to exploring various repayment strategies and mitigating potential risks, we aim to provide a comprehensive resource for prospective borrowers. We’ll also compare private loans with alternative financing methods, such as federal loans, scholarships, and grants, to help you choose the best path towards your educational goals.
Understanding Fixed Interest Rates in Private Student Loans

Private student loans, unlike federal loans, offer both fixed and variable interest rates. Understanding the mechanics of a fixed interest rate is crucial for responsible borrowing and long-term financial planning. This section will clarify the advantages and disadvantages of fixed rates, compare them to federal loan options, and illustrate their impact on total loan repayment costs.
Fixed interest rates on private student loans mean that the interest rate remains constant throughout the loan’s repayment period. This contrasts with variable interest rates, which fluctuate based on market indexes. The fixed rate is determined at the time you take out the loan and is locked in, providing predictability in your monthly payments. The interest is calculated on the principal balance of the loan and is added to the principal, increasing the amount owed. This compounding effect is consistent throughout the loan term with a fixed rate.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Interest Rates
Choosing a fixed interest rate offers several key benefits. The most significant is the predictability of monthly payments. Knowing exactly how much you’ll owe each month simplifies budgeting and financial planning. This stability can be particularly valuable during periods of economic uncertainty, when variable rates might increase significantly. Furthermore, fixed rates provide a sense of security, allowing borrowers to focus on repayment rather than worrying about fluctuating interest costs. However, fixed rates may not always be the most cost-effective option, especially if interest rates are low and expected to remain so. Borrowers should compare fixed and variable rate options to determine the most suitable choice for their individual circumstances.
Comparison with Federal Student Loans
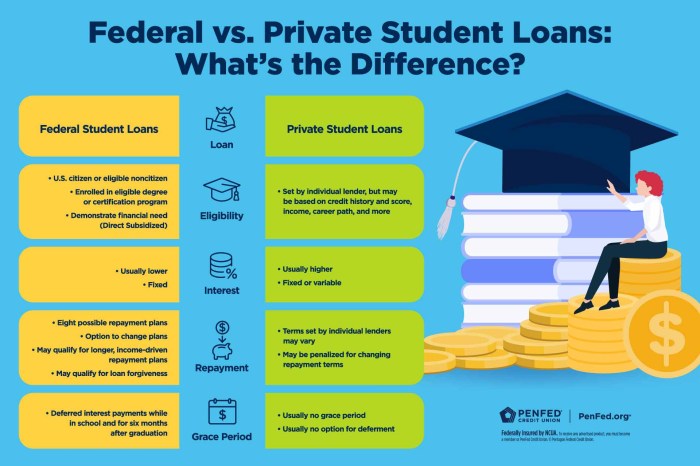
Federal student loans typically offer fixed interest rates, but these rates are set by the government and change annually. Private student loans, on the other hand, have fixed rates set by the lender, which can be influenced by factors such as credit score and market conditions. Federal loans often come with additional benefits such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs, which are generally not available with private student loans. Therefore, the choice between federal and private loans depends on individual financial circumstances, creditworthiness, and the availability of federal loan options.
Impact of Fixed Interest Rates on Total Repayment Cost
The fixed interest rate significantly impacts the total cost of borrowing over the loan term. A higher interest rate leads to a greater accumulation of interest charges, increasing the total amount repaid. Conversely, a lower interest rate results in lower total repayment costs. The length of the loan term also plays a crucial role; longer repayment periods generally lead to higher total interest payments, even with a fixed rate.
| Loan Amount | Interest Rate | Loan Term (Years) | Total Repayment Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| $20,000 | 6% | 10 | $25,500 (approx.) |
| $20,000 | 8% | 10 | $27,700 (approx.) |
| $30,000 | 6% | 15 | $43,000 (approx.) |
| $30,000 | 8% | 15 | $50,000 (approx.) |
*Note: These are approximate figures and do not include any fees or charges that may apply. Actual repayment costs may vary depending on the lender and individual loan terms.*
Factors Influencing Interest Rates on Private Student Loans
Securing a private student loan involves understanding the factors that determine your interest rate. Lenders assess several key aspects of your financial profile to determine the risk associated with lending you money. A lower risk profile typically translates to a lower interest rate, while a higher risk profile results in a higher rate.
Several key factors contribute to the interest rate you’ll receive on a private student loan. These factors are carefully weighed by lenders to assess the risk involved in lending to you. Understanding these factors can help you improve your chances of securing a more favorable interest rate.
Credit Score’s Impact on Interest Rates
Your credit score is a crucial factor in determining your interest rate. Lenders use your credit history to gauge your creditworthiness – your ability to repay borrowed money. A higher credit score demonstrates a history of responsible borrowing and repayment, signaling lower risk to the lender. Conversely, a lower credit score indicates a higher risk of default, leading to a higher interest rate to compensate for that increased risk. Lenders typically use a FICO score or a similar credit scoring model to assess your creditworthiness. A strong credit history, characterized by consistent on-time payments and low credit utilization, is highly beneficial in securing a lower interest rate.
The Role of a Co-signer in Reducing Interest Rates
A co-signer is an individual who agrees to share responsibility for repaying your loan if you fail to do so. Including a co-signer with a strong credit history significantly reduces the lender’s risk. Because the lender has an additional financially responsible individual backing the loan, they are more willing to offer a lower interest rate. This is particularly helpful for borrowers with limited or imperfect credit histories. The co-signer’s credit score and financial stability directly influence the interest rate offered on the loan.
Hypothetical Scenario: Interest Rates and Credit Scores
The following scenario illustrates how different credit scores can impact the interest rate on a $20,000 private student loan. These rates are hypothetical and should not be taken as precise representations of current market conditions. Actual rates vary widely depending on the lender, the specific loan terms, and the overall economic climate.
Let’s consider three borrowers applying for a $20,000 private student loan with similar loan terms (e.g., loan term, repayment schedule) but differing credit scores:
- Borrower A: Excellent Credit (750+): Interest Rate: 4.5%
- Borrower B: Good Credit (700-749): Interest Rate: 6.0%
- Borrower C: Fair Credit (650-699): Interest Rate: 8.5%
This hypothetical example demonstrates the significant impact of credit score on the interest rate. A borrower with excellent credit receives a considerably lower rate than a borrower with fair credit. This difference in interest rates can result in thousands of dollars in additional interest paid over the life of the loan.
Repayment Options and Strategies for Fixed-Rate Private Student Loans
Understanding your repayment options is crucial for effectively managing your private student loan debt. Fixed-rate loans offer predictable monthly payments, simplifying budgeting and long-term financial planning. However, various repayment plans exist, each with its own implications. Choosing the right plan depends on your individual financial situation and goals.
Available Repayment Plans
Private student loan lenders typically offer several repayment plans. These may include a standard repayment plan, an extended repayment plan, and potentially others such as graduated repayment plans (where payments increase over time) or income-driven repayment plans (though these are less common with private loans). The terms and conditions of each plan vary by lender, so it’s essential to review your loan agreement carefully. Standard plans usually involve shorter repayment periods and higher monthly payments, while extended plans offer lower monthly payments but stretch the repayment period over a longer timeframe.
Long-Term Financial Implications of Repayment Schedules
The choice between a standard and an extended repayment plan significantly impacts your long-term finances. A standard plan, while requiring higher monthly payments, results in paying less interest overall because the loan is repaid faster. Conversely, an extended plan, with its lower monthly payments, leads to significantly higher interest payments over the life of the loan. For example, a $50,000 loan at 7% interest with a 10-year repayment plan might have a monthly payment of approximately $570 and total interest paid around $14,000. The same loan on a 20-year plan might have a monthly payment of roughly $380, but the total interest paid would climb to over $36,000. This demonstrates the substantial cost of extending the repayment period.
Creating a Realistic Repayment Budget
Creating a realistic repayment budget is a critical step in managing your student loan debt. This involves a step-by-step process:
- Calculate your monthly income and expenses: List all sources of income and meticulously track all your monthly expenses, including housing, food, transportation, and entertainment.
- Determine your discretionary income: Subtract your essential expenses from your monthly income to determine how much money you have available for loan repayments and other non-essential spending.
- Allocate funds for loan repayment: Based on your discretionary income, determine a realistic amount you can comfortably allocate towards your student loan payments each month. Consider the interest rate and the overall cost of different repayment plans.
- Monitor and adjust your budget: Regularly review your budget to ensure it aligns with your financial situation. Adjust your spending habits or repayment plan if necessary to stay on track.
Calculating Monthly Payments and Total Repayment Costs
Accurately calculating your monthly payments is essential for effective budgeting. Several online loan calculators can assist with this process, but a basic understanding of the calculation is helpful. While precise calculation requires financial software or specialized formulas, a simplified estimate can be made using amortization calculators available online. These calculators use the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term to determine the monthly payment.
| Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid | Loan Term (Years) | Total Repayment Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| $570 | $14,000 (approx.) | 10 | $64,000 |
| $380 | $36,000 (approx.) | 20 | $86,000 |
| $450 | $22,000 (approx.) | 15 | $77,000 |
| $650 | $10,000 (approx.) | 8 | $60,000 |
Risks and Considerations Associated with Private Student Loans
While private student loans can offer a crucial funding source for higher education, they come with inherent risks, especially concerning fixed interest rates during periods of economic instability. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is paramount to responsible borrowing. This section will explore potential pitfalls and provide guidance on navigating the complexities of private student loan debt.
Potential Risks of Private Student Loans with Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates, while providing predictability, can still pose challenges. During periods of high inflation or economic recession, the real value of your fixed payments may decrease, meaning you are paying more in today’s dollars than you might have anticipated when the loan was taken out. Furthermore, if you experience unexpected job loss or a significant decrease in income, maintaining your fixed monthly payments can become incredibly difficult. This risk is heightened if you haven’t carefully considered your repayment plan and potential financial setbacks. The lack of government protections and benefits associated with federal student loans also contributes to the heightened risk involved with private student loans.
Strategies for Mitigating Private Student Loan Debt Risks
Effective risk mitigation begins with thorough planning. Before taking out a private student loan, carefully assess your current financial situation, including income, expenses, and existing debt. Develop a realistic budget that incorporates your anticipated loan payments. Consider exploring options for reducing your overall borrowing needs, such as scholarships, grants, or part-time employment. If possible, prioritize federal student loans due to their borrower protections. Moreover, maintaining a strong credit score is crucial, as it influences the interest rates you’ll qualify for. Regularly monitoring your credit report for errors is essential. Building an emergency fund can help you manage unexpected financial difficulties and prevent loan default.
Importance of Understanding Loan Agreements
Before signing any loan agreement, meticulously review all terms and conditions. Pay close attention to the interest rate, fees, repayment schedule, and any potential penalties for late or missed payments. Understanding the loan’s grace period, which is the period between graduation and the start of repayment, is also crucial. Don’t hesitate to ask questions if anything is unclear; it’s far better to clarify details beforehand than to face unexpected financial burdens later. Consider seeking advice from a financial advisor or student loan counselor to ensure you fully comprehend the implications of your loan agreement.
Warning Signs of Predatory Lending Practices
It’s essential to be aware of predatory lending practices that can trap borrowers in cycles of debt. Understanding these warning signs is crucial to protecting yourself.
- Unusually high interest rates compared to market averages.
- Hidden fees or charges not clearly disclosed in the loan agreement.
- Aggressive sales tactics or pressure to borrow more than needed.
- Lack of transparency regarding loan terms and conditions.
- Difficulty in contacting the lender or obtaining clear answers to questions.
- Requirements for co-signers with poor credit history, suggesting the lender has low confidence in the borrower’s ability to repay.
- Loans with prepayment penalties that discourage early repayment.
Comparison with Other Financing Options
Choosing the right financing method for higher education is crucial, as it significantly impacts your overall cost and long-term financial health. This section compares private student loans with fixed interest rates to other common financing options, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences will empower you to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial circumstances and educational goals.
Several avenues exist for funding higher education, each with its unique characteristics. Federal student loans, scholarships, and grants offer alternatives to private loans, each presenting a different balance of accessibility, cost, and repayment terms.
Comparison of Financing Options for Higher Education
The following table summarizes the key differences between private student loans with fixed interest rates and other common financing options for higher education. Note that specific interest rates, repayment terms, and eligibility requirements can vary depending on the lender or awarding institution.
| Financing Option | Interest Rate Type | Repayment Terms | Eligibility Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Student Loans (e.g., Subsidized/Unsubsidized Loans) | Fixed or Variable (depending on the loan type) | Varying repayment plans available (Standard, Graduated, Extended, Income-Driven) | US citizenship or eligible non-citizen status; enrollment in an eligible educational program; demonstration of financial need (for some loan types) |
| Private Student Loans (Fixed Interest Rate) | Fixed | Typically fixed repayment period, but some lenders may offer options; often shorter repayment periods than federal loans. | Creditworthiness (credit history and score); co-signer may be required; enrollment in an eligible educational program. |
| Scholarships | N/A (No interest) | Generally no repayment required | Academic merit, athletic ability, financial need, or other criteria set by the awarding institution. Highly competitive. |
| Grants | N/A (No interest) | Generally no repayment required | Financial need, specific demographics, or other criteria set by the awarding institution. Highly competitive. |
Wrap-Up
Choosing a private student loan with a fixed interest rate requires careful consideration of various factors, including your credit history, financial situation, and long-term financial goals. By understanding the mechanics of fixed interest rates, the influence of creditworthiness, and the available repayment options, you can navigate the complexities of private student loan borrowing and make informed decisions that align with your financial well-being. Remember to thoroughly research lenders, compare offers, and fully understand the terms and conditions before signing any loan agreement.
Question Bank
What is the difference between a fixed and variable interest rate on a private student loan?
A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term, while a variable rate fluctuates based on market conditions. Fixed rates offer predictability, while variable rates could potentially result in lower initial payments but higher overall costs if rates rise.
Can I refinance my private student loan with a fixed interest rate?
Yes, refinancing is an option, allowing you to potentially secure a lower interest rate or more favorable repayment terms. However, eligibility requirements vary among lenders, and refinancing may involve fees.
What happens if I miss a payment on my private student loan?
Missing payments can negatively impact your credit score and lead to late fees, increased interest charges, and potential loan default. Contact your lender immediately if you anticipate difficulty making payments to explore possible solutions.
How do I choose the best lender for a private student loan?
Compare interest rates, fees, repayment options, and customer service from multiple lenders. Read reviews and check the lender’s reputation before committing to a loan.
