Navigating the complexities of student loan debt can feel overwhelming, but understanding your options is the first step towards financial freedom. A student loan refinance calculator empowers you to explore different repayment scenarios, compare lenders, and ultimately make informed decisions about lowering your monthly payments and potentially saving thousands of dollars in interest over the life of your loan. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of using a refinance calculator to effectively manage your student loans.
This exploration delves into the mechanics of student loan refinancing, covering everything from understanding different loan types and interest rates to identifying key factors that influence your eligibility. We’ll guide you through the process of using a refinance calculator to assess potential savings and risks, helping you determine if refinancing is the right choice for your unique financial situation. We’ll also explore how to compare lenders and find the best fit for your needs.
Understanding Student Loan Refinancing
Refinancing your student loans can be a strategic move to potentially lower your monthly payments and save money over the life of your loan. It involves taking out a new loan to pay off your existing student loan debt, often with more favorable terms. This guide will explore the key aspects of student loan refinancing to help you make an informed decision.
Benefits of Refinancing Student Loans
Refinancing offers several potential advantages. Lower interest rates are a primary benefit, leading to reduced monthly payments and a lower total amount paid over the loan’s term. Consolidating multiple loans into a single payment simplifies repayment and improves financial organization. Furthermore, refinancing can potentially shorten the loan repayment term, enabling you to become debt-free sooner. However, it’s crucial to carefully weigh these benefits against potential drawbacks, such as losing federal loan protections.
Types of Student Loan Refinancing Options
Several options exist for refinancing student loans. Private lenders are the most common source, offering various loan terms and interest rates. These lenders typically assess your creditworthiness and financial situation to determine eligibility and loan terms. Some lenders specialize in refinancing specific types of student loans, such as federal or private loans. Understanding the differences between these options is crucial in choosing the best fit for your circumstances.
Comparison of Interest Rates Offered by Various Lenders
Interest rates offered by different lenders vary considerably, influenced by factors like credit score, loan amount, and chosen loan term. Generally, borrowers with higher credit scores qualify for lower interest rates. Longer loan terms typically result in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest paid. It is essential to compare offers from multiple lenders to secure the most competitive interest rate. For example, Lender A might offer a 6% fixed rate for a 10-year loan, while Lender B might offer a 7% fixed rate for the same term. These differences can significantly impact the total cost of the loan.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying for Student Loan Refinancing
Applying for student loan refinancing involves several steps. First, check your credit report and score to understand your financial standing. Next, compare offers from multiple lenders, focusing on interest rates, fees, and loan terms. Once you’ve chosen a lender, gather the necessary documentation, which typically includes your credit report, income verification, and details of your existing student loans. Submit your application and wait for lender approval. Finally, once approved, sign the loan documents and await the disbursement of funds to pay off your existing loans.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates for Refinanced Loans
Choosing between fixed and variable interest rates is a critical decision.
| Lender | Interest Rate Type | Average Interest Rate | Loan Term Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Lender A | Fixed | 6.5% | 5, 7, 10 years |
| Example Lender B | Variable | 5.5% (initial) | 5, 10 years |
| Example Lender C | Fixed | 7.0% | 3, 5, 7 years |
| Example Lender D | Variable | 6.0% (initial) | 7, 10, 15 years |
Note: Interest rates are subject to change and are for illustrative purposes only. Actual rates will vary based on individual circumstances. Variable rates can fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially leading to higher or lower payments over time. Fixed rates remain consistent throughout the loan term.
Using a Refinance Calculator

Student loan refinance calculators are invaluable tools for exploring potential savings and determining the best refinancing options. They streamline the complex process of comparing different loan offers, allowing you to quickly see the impact of various interest rates and loan terms on your monthly payments and overall cost.
These calculators typically incorporate several key features designed to provide a comprehensive picture of your refinancing possibilities. Understanding these features and how to effectively utilize them is crucial to making informed decisions.
Calculator Features
A typical student loan refinance calculator will request information such as your current loan amount(s), interest rate(s), and remaining loan term(s). Beyond this basic data, many calculators also allow you to input multiple loans, consider different repayment options (like fixed or variable interest rates), and factor in potential fees associated with refinancing. Some advanced calculators even allow you to project potential savings based on different interest rate scenarios and incorporate tax implications where applicable. The results usually include estimated monthly payments, total interest paid, and the overall cost of the loan under various refinance options.
Data Input and Calculation
To use a refinance calculator, you’ll first need to gather your loan information. This includes the principal balance (the remaining amount you owe) for each student loan, the current interest rate for each loan, and the number of months remaining in the repayment period for each. For example, let’s say you have two loans: Loan A with a $20,000 balance, a 7% interest rate, and 60 months remaining; and Loan B with a $10,000 balance, a 6% interest rate, and 48 months remaining. You would input this data into the appropriate fields on the calculator. Once all the information is entered accurately, the calculator will process the data and present you with various refinancing scenarios and their projected outcomes.
Scenario Examples and Impact on Monthly Payments
Let’s consider two refinance scenarios using the example loans above. Scenario 1: You refinance both loans into a single loan with a 5% interest rate and a 72-month repayment term. The calculator might show a significantly lower monthly payment compared to your current payments on both loans individually. Scenario 2: You refinance with a 4% interest rate but choose a shorter 60-month term. While the monthly payment might be higher than in Scenario 1, the total interest paid over the life of the loan would be substantially less, potentially saving you a significant amount of money in the long run. The calculator will present these differences clearly.
Step-by-Step Tutorial: Determining Potential Savings
1. Gather your loan information: Compile the principal balance, interest rate, and remaining term for each student loan.
2. Find a reputable refinance calculator: Many banks and online lenders offer free calculators.
3. Input your loan details: Enter the information accurately into the calculator’s designated fields.
4. Explore different refinance scenarios: Adjust the interest rate and loan term to see how they impact your monthly payment and total interest paid.
5. Compare scenarios: Analyze the results to identify the option that best balances your monthly payment affordability with long-term cost savings.
6. Consider additional fees: Remember to factor in any potential refinancing fees when comparing options.
Factors Influencing Calculator Results
Several factors can influence the results a refinance calculator provides. These include the interest rate offered by the lender, the length of the new loan term, any associated fees (origination fees, prepayment penalties), and your credit score (which significantly impacts the interest rate you qualify for). Additionally, the type of loan (fixed vs. variable interest rate) will affect the predictability of your monthly payments and overall cost. Finally, the inclusion or exclusion of multiple loans in a single refinance application will impact the overall outcome presented by the calculator.
Factors Affecting Refinancing Eligibility
Securing a student loan refinance hinges on several key factors that lenders carefully evaluate. Understanding these criteria is crucial for a successful application and securing the best possible interest rate. This section details the critical elements lenders consider, highlighting the influence of your creditworthiness and financial stability on the refinancing process.
Credit Score’s Influence on Loan Approval and Interest Rates
Your credit score serves as a primary indicator of your creditworthiness to lenders. A higher credit score generally translates to a greater likelihood of approval and more favorable interest rates. Lenders view a strong credit history as evidence of responsible financial management, reducing their perceived risk. Conversely, a lower credit score can lead to rejection or significantly higher interest rates, potentially negating the benefits of refinancing. For example, a borrower with a credit score above 750 might qualify for a significantly lower interest rate compared to a borrower with a score below 650. The difference could be several percentage points, leading to substantial savings or added costs over the life of the loan.
Debt-to-Income Ratio’s Role in Refinancing
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), calculated by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income, is another crucial factor. A lower DTI demonstrates your ability to manage existing debt while taking on additional financial obligations. Lenders prefer borrowers with a lower DTI as it suggests a reduced risk of default. A high DTI might lead to loan rejection or less favorable terms. For instance, a borrower with a DTI of 30% might be viewed more favorably than a borrower with a DTI of 50%, especially if the additional loan increases their DTI significantly.
Comparison of Eligibility Requirements Across Lenders
Eligibility requirements vary across different lenders. Some lenders may prioritize credit score, while others might place greater emphasis on DTI or income stability. Some may have minimum loan amounts or specific requirements regarding the type of student loans being refinanced. It’s essential to compare offers from multiple lenders to find the most suitable option. For example, Lender A might require a minimum credit score of 680 and a DTI below 40%, while Lender B might accept borrowers with a score as low as 650 but with a more stringent DTI limit of 35%.
Scenarios Where Refinancing Might Not Be Beneficial
Refinancing isn’t always the optimal choice. For example, if your credit score is low, you might only qualify for higher interest rates, potentially increasing your overall borrowing costs. Similarly, if your current interest rates are already exceptionally low, refinancing might not result in significant savings. Additionally, prepayment penalties associated with your existing loans could outweigh any potential benefits from refinancing. Finally, if you are close to paying off your loans, the fees associated with refinancing might negate any long-term savings.
Potential Savings and Risks

Refinancing your student loans can offer significant financial benefits, but it’s crucial to carefully weigh the potential savings against the inherent risks. Understanding both sides of the equation is essential to making an informed decision that aligns with your long-term financial goals. This section will explore the potential savings you could realize through refinancing, as well as the potential downsides and risks involved.
Calculating Potential Savings
To estimate potential savings, you need to compare your current monthly payment and total interest paid with the projected figures after refinancing. This involves understanding your current loan terms (interest rate, principal balance, repayment period) and the terms offered by a potential refinance lender. The difference between the total interest paid under your current loans and the total interest paid under the refinanced loan represents your potential savings.
For example, let’s say you have $50,000 in student loans with a 7% interest rate and a 10-year repayment plan. Your monthly payment would be approximately $570 and your total interest paid over 10 years would be around $24,000. If you refinance to a 5% interest rate with the same repayment term, your monthly payment would drop to approximately $490, and your total interest paid would be approximately $14,000. This would result in a monthly savings of $80 and a total interest savings of $10,000. You can use a refinance calculator to easily perform these calculations with your specific loan details. Remember to factor in any fees associated with refinancing.
To calculate potential monthly savings: Subtract the refinanced monthly payment from your current monthly payment. To calculate total interest savings: Subtract the total interest paid under the refinanced loan from the total interest paid under your current loans.
Scenarios Where Refinancing Could Increase Long-Term Costs
Refinancing isn’t always the best option. Several scenarios can lead to higher long-term costs. For example, extending your loan term to lower your monthly payment will increase the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Additionally, if interest rates rise after you refinance, you might end up paying more interest than you would have under your original loan terms. Finally, some refinance lenders charge significant fees, which can offset potential savings.
Consider a scenario where you refinance a $30,000 loan at 6% interest over 10 years, resulting in a monthly payment of $320 and total interest of approximately $7,000. If you refinance to a 4% interest rate but extend the repayment term to 15 years to lower your monthly payments, your monthly payment would be around $220. However, your total interest paid would increase to approximately $9,000, a $2,000 increase despite the lower interest rate.
Risks Associated with Refinancing
Refinancing student loans carries several risks. A significant risk is the loss of federal loan benefits, such as income-driven repayment plans, loan forgiveness programs (like Public Service Loan Forgiveness), and deferment or forbearance options. These benefits are only available for federal loans and are lost when you refinance into a private loan. Furthermore, refinancing can make it harder to manage your debt if you experience unexpected financial hardship, as private lenders may not offer the same flexibility as federal loan programs. Finally, changes in your credit score could affect your ability to refinance at favorable terms.
Potential Savings and Risks Comparison
| Scenario | Monthly Savings | Total Interest Saved | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refinance from 7% to 5% (10-year term) | $80 | $10,000 | Loss of federal loan benefits |
| Refinance from 6% to 4% (10-year to 15-year term) | -$100 | -$2,000 | Increased total interest paid, loss of federal loan benefits |
| Refinance with high fees | $50 | $5,000 | High fees offsetting potential savings, loss of federal loan benefits |
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Before refinancing, carefully analyze your financial situation and long-term goals. Consider your current interest rate, remaining loan balance, repayment term, and financial stability. Compare offers from multiple lenders to secure the best possible terms. Evaluate the potential savings against the risks, including the loss of federal loan benefits. If you have concerns about your ability to manage your debt or anticipate potential financial difficulties, refinancing might not be the most prudent choice. Seeking advice from a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and help you make an informed decision.
Finding the Right Lender
Choosing the right lender for student loan refinancing is crucial for securing favorable terms and minimizing costs. A thorough comparison of lenders is essential to ensure you find the best fit for your individual financial situation and needs. This involves considering various factors beyond just the interest rate.
Different lenders offer varying services, interest rates, fees, and customer support. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed decision. Factors like your credit score, loan amount, and the type of loans you’re refinancing will significantly impact the offers you receive. Therefore, a proactive approach to lender research will significantly benefit your refinancing journey.
Lender Services Comparison
A comprehensive comparison of lenders requires analyzing several key aspects of their services. This includes examining interest rates, fees, loan terms, customer service responsiveness, and the overall borrower experience. Consider the availability of various loan types, such as fixed vs. variable rates, and whether they offer additional features like hardship programs or autopay discounts. A side-by-side comparison using a spreadsheet can greatly assist in this process.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Lender
Selecting a lender involves more than simply comparing interest rates. Several critical factors should be carefully evaluated to make a well-informed decision. Reputable lenders often prioritize transparency and clear communication throughout the refinancing process. A careful review of customer reviews and complaints can provide valuable insights into the lender’s reliability and customer service quality. Furthermore, understanding all associated fees is paramount to avoid unexpected costs.
- Interest Rates: Compare APRs (Annual Percentage Rates) across different lenders to identify the lowest rate available for your specific situation.
- Fees: Examine origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment fees. Some lenders offer no origination fees, which can significantly impact your overall cost.
- Customer Reviews and Ratings: Check online reviews on sites like the Better Business Bureau (BBB) and Trustpilot to gauge customer satisfaction and identify potential red flags.
- Loan Terms and Flexibility: Consider repayment terms, options for deferment or forbearance, and the lender’s policies on hardship situations.
- Customer Service: Evaluate the ease of contacting customer support, the responsiveness of representatives, and the clarity of their communication.
Reputable Student Loan Refinancing Lenders
Several reputable lenders offer student loan refinancing options. It’s important to note that this is not an exhaustive list, and the best lender for you will depend on your individual circumstances. Always independently verify the information provided by any lender before making a decision.
- SoFi
- Earnest
- Splash Financial
- CommonBond
- LendKey
Checklist of Questions to Ask Potential Lenders
Before applying for refinancing, it’s advisable to prepare a list of questions to ask potential lenders. This will ensure you have all the necessary information to make an informed decision. Asking direct and specific questions will help you avoid surprises and ensure the lender meets your needs.
- What is your current interest rate for my loan profile?
- What are all associated fees, including origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment fees?
- What are your repayment options and terms?
- What is your process for handling hardship situations?
- What is your customer service availability and responsiveness?
- Can you provide examples of successful refinancing cases similar to my situation?
Last Point
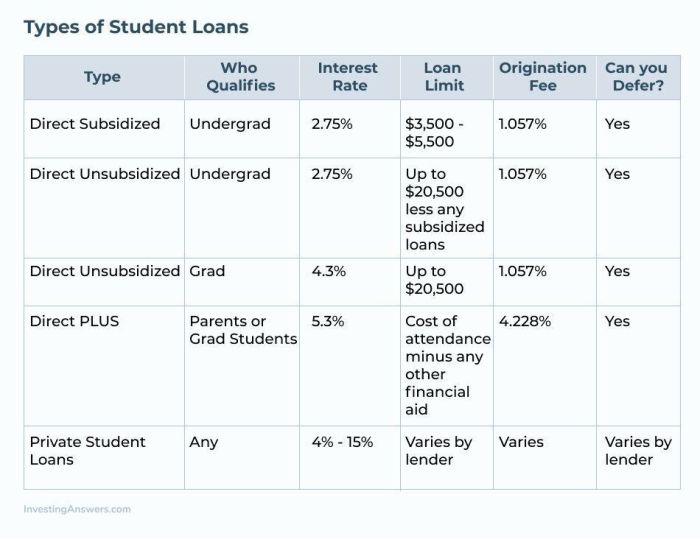
Ultimately, the decision to refinance student loans is a personal one that requires careful consideration of your individual circumstances. By leveraging the power of a refinance calculator and understanding the factors that influence your eligibility and potential savings, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your long-term financial goals. Remember to thoroughly research lenders, compare offers, and weigh the potential benefits against any associated risks before committing to a refinance plan. Taking control of your student loan debt is a significant step towards achieving financial stability and security.
Query Resolution
What is the impact of a poor credit score on refinancing?
A lower credit score can significantly impact your eligibility for refinancing and may result in higher interest rates or even loan denial. Lenders view a strong credit score as an indicator of your ability to repay the loan.
Can I refinance federal student loans?
Yes, you can refinance federal student loans, but be aware that doing so means you will lose the benefits associated with federal loans, such as income-driven repayment plans and potential government forgiveness programs.
How often should I check my refinance options?
Interest rates fluctuate, so it’s advisable to check your options at least annually, or even more frequently if your financial situation changes significantly (e.g., increased income, improved credit score).
What are the common fees associated with refinancing?
Common fees can include origination fees, prepayment penalties (in some cases), and potentially late payment fees. Carefully review the lender’s fee schedule before committing.
