Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can feel overwhelming. This guide provides a clear and concise path towards responsible borrowing and repayment, focusing on identifying safe and reputable programs to help students manage their debt effectively. We’ll explore various federal loan programs, highlighting their features and eligibility requirements, and equip you with the knowledge to avoid common scams and navigate the repayment process confidently.
From understanding different repayment plans and identifying trustworthy loan servicers to building financial literacy and utilizing government resources, we aim to empower you with the tools and information necessary for a smooth and successful student loan journey. This comprehensive guide is designed to provide actionable strategies for managing your student loan debt responsibly and achieving long-term financial well-being.
Understanding Student Loan Programs
Navigating the world of student loans can feel overwhelming, but understanding the different programs available is the first step towards responsible borrowing and repayment. This section will Artikel the key federal student loan programs, their eligibility criteria, and a comparison of their interest rates and repayment plans. Choosing the right loan can significantly impact your financial future.
Federal Student Loan Program Types
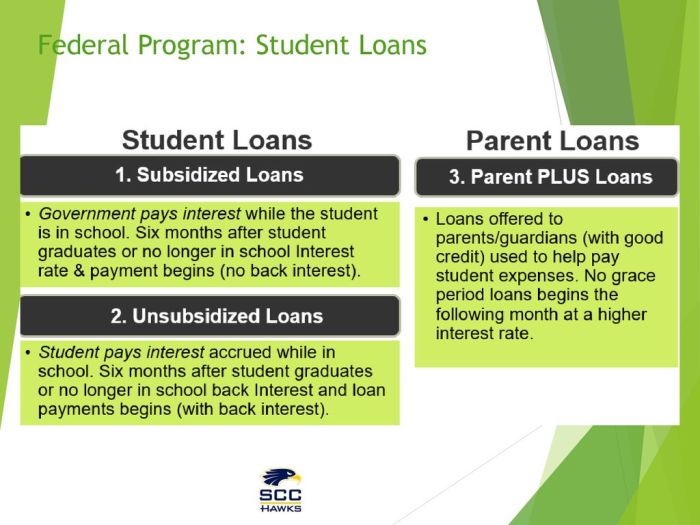
The federal government offers several student loan programs designed to help students finance their education. These programs differ in their eligibility requirements, interest rates, and repayment options. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed borrowing decisions. The main programs include Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, Direct PLUS Loans (for parents and graduate students), and Direct Consolidation Loans.
Eligibility Requirements for Federal Student Loan Programs
Eligibility for federal student loans depends on several factors, primarily including enrollment status, financial need (for subsidized loans), credit history (for PLUS loans), and citizenship or residency status. Specific requirements vary by program.
- Direct Subsidized Loans: These loans are based on financial need as determined by the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). Students must be enrolled at least half-time in an eligible degree or certificate program.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans: These loans are not based on financial need. Students must be enrolled at least half-time in an eligible degree or certificate program.
- Direct PLUS Loans: These loans are available to parents of dependent undergraduate students (Parent PLUS Loans) and to graduate or professional students (Graduate PLUS Loans). Credit checks are conducted, and borrowers must meet specific creditworthiness standards.
- Direct Consolidation Loans: This program allows borrowers to combine multiple federal student loans into a single loan with a new interest rate and repayment plan. Eligibility requires having existing federal student loans.
Interest Rates and Repayment Options
Interest rates for federal student loans vary depending on the loan type, the loan disbursement date, and whether the loan is subsidized or unsubsidized. Interest rates are typically fixed, meaning they remain the same throughout the loan’s life. Repayment options include standard repayment, graduated repayment, extended repayment, and income-driven repayment plans. Income-driven repayment plans tie monthly payments to your income and family size, making them potentially more affordable for borrowers with lower incomes.
Comparison of Federal Student Loan Programs
The following table summarizes key features of the different federal student loan programs. Remember that these are general guidelines, and specific details may change. Always consult the official government website for the most up-to-date information.
| Loan Type | Eligibility | Interest Rate | Repayment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Subsidized Loan | Financial need, half-time enrollment | Variable; check the official website for current rates | Standard, graduated, extended, income-driven |
| Direct Unsubsidized Loan | Half-time enrollment | Variable; check the official website for current rates | Standard, graduated, extended, income-driven |
| Direct PLUS Loan (Parent/Grad) | Credit check required, enrollment (for Grad PLUS) | Variable; check the official website for current rates | Standard, extended |
| Direct Consolidation Loan | Existing federal student loans | Fixed; weighted average of existing loans | Standard, graduated, extended, income-driven |
Identifying Reputable Loan Servicers
Choosing the right student loan servicer is crucial for a smooth repayment journey. A trustworthy servicer provides clear communication, accurate account information, and helpful assistance throughout the repayment process. Selecting a less-than-reputable servicer, however, can lead to significant frustration, potential financial harm, and unnecessary complications. Understanding how to identify a reliable servicer is therefore a vital step in responsible student loan management.
Navigating the world of student loan servicers requires careful consideration and due diligence. Several key factors contribute to determining a servicer’s trustworthiness, including their accreditation, customer feedback, and adherence to established industry standards. Ignoring these factors can lead to negative experiences, so understanding these key indicators is paramount.
Servicer Accreditation and Licensing
Accreditation and licensing demonstrate a servicer’s commitment to meeting specific industry standards and regulations. Reputable servicers will be transparent about their accreditation status, readily providing information on their licensing and any relevant certifications. This often involves verification through official government websites or independent accreditation bodies. Lack of transparency regarding licensing or accreditation should raise immediate concerns. For instance, a servicer that avoids providing clear details about their licensing or claims to be accredited by an unknown organization should be approached with caution.
Analyzing Customer Reviews and Complaints
Online reviews and complaint databases offer valuable insights into a servicer’s performance and customer service. Websites like the Better Business Bureau (BBB) and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) allow you to search for complaints filed against specific servicers. A high volume of negative reviews or a pattern of unresolved complaints should be a significant red flag. For example, consistent complaints about unresponsive customer service, inaccurate billing, or difficulty modifying repayment plans indicate potential problems. Conversely, a consistently positive track record suggests a higher level of reliability.
Identifying Red Flags of Fraudulent Servicers
Fraudulent servicers often employ deceptive tactics to lure unsuspecting borrowers. These tactics include unsolicited contact promising unrealistic benefits, pressure to provide personal information immediately, requests for upfront fees, and a lack of transparency about their fees and services. For instance, a servicer that contacts you out of the blue offering a drastically reduced interest rate or demands immediate payment for services before providing any details should be treated with extreme suspicion. Any servicer demanding payment before providing clear documentation and contracts should be avoided.
Checklist of Questions for Potential Loan Servicers
Before engaging a student loan servicer, it’s essential to ask specific questions to verify their legitimacy and assess their suitability for your needs. This proactive approach helps mitigate potential risks and ensures you make an informed decision.
- What is your company’s accreditation status and licensing information?
- Can you provide references or links to independent verification of your accreditation?
- What are your fees and how are they structured?
- What customer service options do you offer (phone, email, online portal)?
- What is your complaint resolution process?
- How do you protect my personal information?
- Can you provide examples of your repayment plans and their terms?
Safe Repayment Strategies
Navigating student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, but understanding your options and employing a strategic approach can significantly ease the burden and help you achieve financial freedom sooner. Choosing the right repayment plan and developing effective management habits are crucial for successful repayment.
Several repayment plans cater to different financial situations and priorities. Understanding their nuances is key to selecting the best fit for your circumstances. Careful consideration of your current income, future earning potential, and overall financial goals will help you determine the most appropriate strategy.
Standard Repayment Plan
The standard repayment plan is a fixed monthly payment spread over 10 years. This plan offers predictability and the fastest path to loan payoff. However, the fixed monthly payments might be challenging for those with fluctuating incomes or limited financial resources in the early years after graduation. For example, a $30,000 loan at a 5% interest rate would result in a monthly payment of approximately $317, leading to a total repayment of roughly $38,000.
Graduated Repayment Plan
Unlike the standard plan, graduated repayment starts with lower monthly payments that gradually increase over time. This approach can be beneficial for recent graduates who anticipate higher earnings in the future. The lower initial payments provide short-term relief, but it’s important to note that the total interest paid will likely be higher compared to the standard plan because of the longer repayment period. The same $30,000 loan example might start with payments around $200, increasing incrementally over the 10-year repayment period.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-driven repayment plans (IDR) tie your monthly payment to your income and family size. These plans, including plans like Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), offer lower monthly payments, potentially making them more manageable during periods of lower income. However, they typically extend the repayment period to 20 or 25 years, potentially leading to higher overall interest payments. Eligibility requirements vary depending on the specific plan. For example, a borrower earning $30,000 annually might have a significantly lower monthly payment than under a standard plan, perhaps only $150, but the repayment would extend far beyond 10 years.
Applying for Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Applying for an IDR plan generally involves these steps:
- Check your eligibility: Confirm you meet the requirements for the specific IDR plan you’re interested in.
- Gather necessary documents: This typically includes tax returns, proof of income, and family size information.
- Complete the application: Submit the application through your loan servicer’s website or portal.
- Monitor your account: Track your payment progress and ensure the payment amount aligns with your income.
Effective Student Loan Payment Management
Effective student loan management involves a multi-pronged approach:
- Understand your loans: Know the amount you owe, interest rates, and repayment terms for each loan.
- Budgeting and Prioritization: Create a realistic budget that includes your loan payments. Prioritize loan payments alongside essential living expenses.
- Automate Payments: Set up automatic payments to avoid late fees and ensure consistent repayments.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly check your loan accounts for accuracy and identify any potential issues.
- Explore Refinancing Options: Consider refinancing if you qualify for a lower interest rate to reduce your overall cost.
Avoiding Loan Scams and Fraud

Navigating the world of student loans can be complex, and unfortunately, this complexity makes it a fertile ground for scams and fraudulent activities. Understanding common tactics and knowing how to protect yourself is crucial to avoid financial hardship and maintain your academic progress. This section will equip you with the knowledge to identify and avoid these deceptive practices.
The student loan landscape is rife with individuals and organizations seeking to exploit borrowers. These schemes often prey on students facing financial pressures or those unfamiliar with the loan repayment process. Recognizing these tactics is the first step in safeguarding your financial well-being.
Common Tactics Used in Student Loan Scams
Student loan scams employ a variety of deceptive tactics to lure unsuspecting victims. These tactics often involve promises that sound too good to be true, creating a sense of urgency, or leveraging fear and confusion. For example, some scams may promise immediate loan forgiveness or consolidation at significantly reduced rates, requiring upfront fees or personal information. Others may impersonate legitimate loan servicers, sending phishing emails or text messages demanding immediate payment or account information. Be wary of any communication that pressures you to act quickly or share sensitive information without first verifying its legitimacy through official channels.
Identifying Fake Loan Servicers or Loan Forgiveness Schemes
Identifying fraudulent loan servicers or loan forgiveness schemes requires a critical and discerning eye. Legitimate loan servicers will never ask for upfront fees to process your loan application or to help you with loan forgiveness. They will also never request your personal banking information or Social Security number via email or text message. Always verify the identity of any entity contacting you regarding your student loans by independently contacting your lender or the Federal Student Aid website. Furthermore, be highly skeptical of any unsolicited offers of loan forgiveness that promise quick and easy solutions without requiring you to meet specific eligibility criteria. Legitimate loan forgiveness programs, like Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), have strict requirements and a rigorous application process.
Resources for Reporting Suspected Student Loan Fraud
If you suspect you have been a victim of a student loan scam or have encountered fraudulent activity, several resources are available to help you. You can report suspected fraud to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at ReportFraud.ftc.gov. Additionally, you can contact your state’s attorney general’s office, which often handles consumer protection complaints. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) also provides resources and assistance to individuals who have experienced financial fraud. These agencies can investigate your complaint and potentially take action against the perpetrators.
Verifying the Legitimacy of Loan Forgiveness Programs
Verifying the legitimacy of loan forgiveness programs is crucial to avoid falling prey to scams. Always independently research any program before engaging with it. Start by checking the official websites of government agencies, such as the Department of Education and the Federal Student Aid website. Look for information about the program’s eligibility requirements, application process, and any associated fees. If the information you find online is unclear or inconsistent, it’s best to err on the side of caution and avoid participating in the program. Remember, legitimate loan forgiveness programs will never require upfront payments or request your personal information through unofficial channels.
Financial Literacy and Budgeting for Loan Repayment

Successfully managing student loan debt requires a solid understanding of personal finance and the creation of a realistic budget. This involves tracking income and expenses, prioritizing loan payments, and developing strategies for long-term financial well-being. A well-structured budget allows you to visualize your financial situation, identify areas for improvement, and allocate funds effectively towards loan repayment.
Sample Budget Template
Creating a budget is crucial for managing student loan payments. A simple budget categorizes income and expenses, allowing you to see where your money goes and make informed decisions. The following template demonstrates how to incorporate student loan payments:
| Income | Amount |
|---|---|
| Net Salary/Wages | $XXXX |
| Other Income (e.g., part-time job) | $XXX |
| Total Income | $XXXX |
| Expenses | Amount |
| Housing (Rent/Mortgage) | $XXX |
| Utilities (Electricity, Water, Gas) | $XXX |
| Food | $XXX |
| Transportation | $XXX |
| Student Loan Payment | $XXX |
| Healthcare | $XXX |
| Debt Payments (excluding student loans) | $XXX |
| Savings | $XXX |
| Entertainment | $XXX |
| Other Expenses | $XXX |
| Total Expenses | $XXXX |
| Net Income (Income – Expenses) | $XXX |
Remember to replace the “XXX” placeholders with your actual amounts. Regularly review and adjust your budget as needed.
Tips for Improving Financial Literacy and Responsible Money Management
Effective money management involves understanding your financial situation and making conscious decisions about spending and saving. This includes tracking your income and expenses, setting financial goals, and building an emergency fund.
- Track your spending: Use budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or even a notebook to monitor where your money goes. This awareness is the first step towards better financial control.
- Create a budget: Allocate funds for essential expenses, loan repayments, savings, and discretionary spending. Prioritize needs over wants.
- Set financial goals: Define short-term and long-term goals, such as paying off student loans, saving for a down payment on a house, or investing for retirement. These goals provide motivation and direction.
- Build an emergency fund: Aim for 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in a readily accessible savings account. This fund provides a safety net for unexpected events.
- Seek financial education: Utilize online resources, workshops, or financial advisors to enhance your understanding of personal finance.
Strategies for Reducing Monthly Expenses
Reducing monthly expenses frees up funds for loan repayment and other financial goals. Careful examination of spending habits can reveal areas where savings are possible.
- Identify non-essential spending: Analyze your spending patterns to pinpoint areas where you can cut back, such as dining out, entertainment, or subscriptions.
- Negotiate lower bills: Contact service providers (internet, phone, insurance) to negotiate lower rates or explore alternative, more affordable options.
- Reduce transportation costs: Consider carpooling, using public transportation, biking, or walking to reduce fuel costs and vehicle maintenance.
- Cook at home more often: Eating out frequently can significantly increase expenses. Preparing meals at home is a cost-effective alternative.
- Shop smart: Compare prices, use coupons, and take advantage of sales to save money on groceries and other purchases.
Benefits of Building a Strong Credit Score
A strong credit score is essential for securing favorable loan terms in the future. A higher credit score often translates to lower interest rates, better loan offers, and increased borrowing power.
A good credit score can save you thousands of dollars in interest payments over the life of a loan.
Maintaining a strong credit score involves responsible credit card usage, timely loan payments, and avoiding excessive debt. Consistent positive financial behavior contributes to a better credit history, which positively impacts your future borrowing opportunities.
Government Resources and Support

Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be daunting, but thankfully, various government resources and support systems are available to help borrowers manage their debt effectively. Understanding these resources and how to access them is crucial for successful repayment and avoiding potential pitfalls. This section will Artikel key government websites, contact information, and processes related to student loan forgiveness programs and the role of student loan counselors.
The federal government plays a significant role in managing and supporting student loan borrowers. Several agencies provide essential information, assistance, and programs designed to ease the burden of student loan debt. These resources are readily accessible online and through direct contact, offering a valuable lifeline for those struggling with repayment.
Key Government Websites and Contact Information
The primary source of information for federal student loans is the Federal Student Aid website (studentaid.gov). This website provides comprehensive information on loan types, repayment plans, forgiveness programs, and other relevant topics. It also offers tools and resources to help borrowers manage their loans, such as loan simulators and repayment calculators. For direct assistance, borrowers can contact the Federal Student Aid Information Center at 1-800-4-FED-AID (1-800-433-3243). Additionally, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) website (consumerfinance.gov) offers resources and guidance on avoiding student loan scams and understanding your rights as a borrower. The CFPB can be reached at 1-855-411-CFPB (1-855-411-2372).
Accessing Government-Sponsored Student Loan Forgiveness Programs
Several government-sponsored programs offer loan forgiveness or cancellation options under specific circumstances. These programs typically target borrowers working in public service, those with disabilities, or those who have experienced specific hardships. Eligibility criteria vary depending on the program. For example, the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program forgives the remaining balance of federal student loans after 120 qualifying monthly payments under an income-driven repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying government or non-profit organization. To access these programs, borrowers must typically complete applications and provide documentation demonstrating their eligibility. Detailed information about eligibility requirements, application processes, and program specifics can be found on the Federal Student Aid website. It is important to note that meeting the requirements for these programs often takes significant time and careful planning.
The Role of Student Loan Counselors
Student loan counselors provide valuable guidance and support to borrowers navigating the complexities of loan repayment. These counselors can help borrowers understand their repayment options, explore available programs, and create personalized repayment plans. Many colleges and universities offer free counseling services to their students and alumni. Additionally, non-profit organizations and government agencies also provide counseling services, often at no cost. These counselors can assist with consolidating loans, applying for income-driven repayment plans, and exploring options for loan forgiveness or deferment. They can also help borrowers understand their rights and responsibilities as borrowers and avoid potential scams or predatory lending practices. Seeking guidance from a qualified counselor can significantly improve a borrower’s chances of successfully managing and repaying their student loans.
Visual Representation of Loan Repayment
Understanding the long-term financial implications of different student loan repayment plans is crucial. A visual representation can effectively demonstrate how choices made today impact the total cost of borrowing over time. This section will describe a chart illustrating the cumulative interest paid under various repayment scenarios.
This chart displays the total interest paid over the life of a hypothetical $30,000 student loan under three common repayment plans: Standard, Extended, and Income-Driven Repayment. The x-axis represents the repayment period in years, and the y-axis represents the cumulative interest paid in dollars.
Comparison of Repayment Plans and Cumulative Interest
The chart is a line graph. Three distinct lines represent the three repayment plans. The “Standard Repayment” line shows a steeper initial incline, reflecting higher monthly payments and quicker principal reduction, leading to less overall interest paid. This line plateaus relatively early, indicating a shorter repayment period. The “Extended Repayment” line shows a gentler incline, representing lower monthly payments and a longer repayment period. Consequently, this line extends further along the x-axis and reaches a significantly higher point on the y-axis, illustrating a substantially greater total interest paid. Finally, the “Income-Driven Repayment” line shows a variable incline, reflecting fluctuating monthly payments based on income. While the repayment period is potentially longer than the standard plan, the total interest paid falls somewhere between the standard and extended plans, demonstrating the trade-offs involved. Specific data points could include the total interest paid after 5, 10, and 15 years for each plan, clearly labeled on the graph. For example, a data point might be labeled “Standard Repayment, Year 10: $5,000 Interest Paid.” The overall trend shows a clear correlation between repayment duration and total interest paid: longer repayment periods generally result in higher total interest costs. This visual emphasizes the importance of choosing a repayment plan that balances affordability with minimizing long-term costs.
Epilogue
Successfully managing student loans requires proactive planning, informed decision-making, and a commitment to financial literacy. By understanding the various federal programs, identifying reputable servicers, and employing safe repayment strategies, you can significantly reduce the stress and financial burden associated with student loan debt. Remember to utilize available government resources and prioritize responsible financial habits to build a secure financial future. Taking control of your student loans is a crucial step towards achieving your long-term financial goals.
Essential Questionnaire
What happens if I can’t make my student loan payments?
Contact your loan servicer immediately. They can help you explore options like deferment, forbearance, or income-driven repayment plans to avoid default.
Can I consolidate my student loans?
Yes, loan consolidation combines multiple loans into one, potentially simplifying payments. However, it may not always lower your interest rate.
How can I improve my credit score while paying off student loans?
Make on-time payments consistently, keep credit utilization low, and maintain a diverse credit history. Paying down your student loans also positively impacts your credit score.
What is the difference between a subsidized and unsubsidized loan?
Subsidized loans don’t accrue interest while you’re in school (under certain conditions), while unsubsidized loans do.
