
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can feel overwhelming. Understanding your options and projecting your future financial picture is crucial for responsible debt management. A student loan calculator is an invaluable tool that empowers you to take control of your repayment journey, allowing you to explore different scenarios and make informed decisions about your financial future.
This guide delves into the functionality of student loan calculators, exploring various types, influencing factors, and effective usage strategies. We’ll examine how interest rates, repayment periods, and loan types impact your monthly payments and overall cost, providing you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the often-daunting world of student loan debt.
Understanding Student Loan Calculators
Student loan calculators are invaluable tools for prospective and current borrowers. They provide a clear picture of potential repayment scenarios, helping individuals make informed decisions about their education financing. Understanding how these calculators work and the factors they consider is crucial for effective financial planning.
Student loan calculators function by taking several key input variables and using them to compute estimated monthly payments and total interest paid over the loan’s lifespan. This allows borrowers to explore different repayment options and their associated costs.
Input Variables and Their Impact
A typical student loan calculator requires several pieces of information to generate accurate estimates. These inputs significantly influence the final calculated figures. The most common input variables include the loan amount (principal), the annual interest rate, the loan term (repayment period), and the repayment plan type. Let’s examine how these variables affect the outcome.
For example, a $20,000 loan at a 5% interest rate over 10 years will result in a significantly lower monthly payment than the same loan amount at a 7% interest rate over the same period. Similarly, extending the repayment period from 10 years to 15 years will reduce the monthly payment but increase the total interest paid over the life of the loan. This trade-off is a critical consideration for borrowers. A higher interest rate directly increases the total cost of borrowing, while a longer repayment term reduces the monthly burden but ultimately increases the total interest paid.
Repayment Plan Comparison
The choice of repayment plan dramatically impacts both monthly payments and the total interest paid. Different plans offer varying terms and conditions. Below is a comparison illustrating the effect of different repayment plans on a hypothetical $30,000 loan at a 6% interest rate.
| Repayment Plan | Loan Term (Years) | Approximate Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 10 | $330 | $9,800 |
| Extended | 20 | $220 | $20,800 |
| Graduated | 10 | $250 (increasing gradually) | $12,000 (approximate, due to variable payments) |
| Income-Driven | Variable | Variable (based on income) | Variable (potentially higher overall) |
Note: These figures are approximate and may vary based on the specific lender and loan terms. Income-driven repayment plans are particularly complex and require individual calculation based on income and family size. It’s important to consult the lender’s specific repayment plan details.
Types of Student Loan Calculators

Choosing the right student loan calculator can significantly impact your understanding of repayment options and overall financial planning. Different calculators offer varying levels of complexity and features, catering to diverse needs and levels of financial literacy. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about your student loan debt.
Student loan calculators generally fall into three main categories: simple calculators, advanced calculators, and calculators specifically designed for either federal or private loans. Each type provides a unique set of functionalities, advantages, and disadvantages.
Simple Student Loan Calculators
Simple calculators offer a basic overview of potential repayment scenarios. They typically require input of the total loan amount, interest rate, and loan term to estimate monthly payments and total interest paid. These calculators are ideal for individuals seeking a quick, high-level understanding of their repayment options without delving into intricate details. They are user-friendly and require minimal financial knowledge to operate.
Advantages include ease of use and quick results. Disadvantages include a lack of sophisticated features, such as the ability to factor in different repayment plans or variable interest rates. They also often fail to account for potential changes in income or unexpected life events.
Advanced Student Loan Calculators
Advanced calculators provide a more comprehensive analysis of repayment options, incorporating additional variables such as different repayment plans (e.g., standard, extended, income-driven), variable interest rates, and potential for refinancing. These calculators often allow users to explore various “what-if” scenarios, simulating the impact of different payment amounts or loan consolidation strategies. This level of detail empowers users to make more informed and strategic decisions about managing their student loan debt.
Advantages include detailed analysis and the ability to model various repayment scenarios. Disadvantages include a steeper learning curve and the potential for overwhelming users with complex information. The accuracy of the calculations depends heavily on the accuracy of the input data provided by the user.
Federal vs. Private Student Loan Calculators
Calculators designed specifically for federal or private loans often incorporate features relevant to the specific loan type. Federal loan calculators might include information on income-driven repayment plans, loan forgiveness programs, and deferment options. Private loan calculators, on the other hand, may focus on refinancing options and the impact of different interest rates offered by various lenders.
The following key differences highlight the distinctions between calculators tailored for federal and private student loans:
- Repayment Plan Options: Federal loan calculators typically include options for income-driven repayment plans (IBR, PAYE, REPAYE, ICR), whereas private loan calculators usually only show standard repayment options.
- Loan Forgiveness Programs: Federal loan calculators often incorporate features to estimate eligibility for loan forgiveness programs (e.g., Public Service Loan Forgiveness), while private loan calculators do not.
- Deferment and Forbearance: Federal loan calculators can account for periods of deferment or forbearance, reflecting the impact on the overall repayment schedule. Private loan calculators may offer limited or no such functionality.
- Refinancing Options: Private loan calculators often emphasize refinancing options and their potential to lower interest rates, while federal loan calculators may not directly address this.
Factors Influencing Loan Repayment
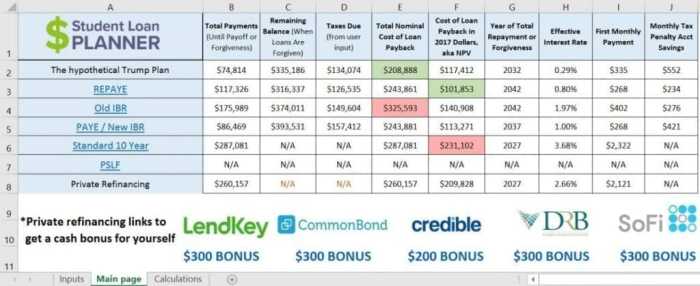
Understanding the factors that influence student loan repayment is crucial for effective financial planning. Several key elements significantly impact the total cost and duration of your repayment journey. These include interest rates, loan repayment periods, and the potential benefits of loan consolidation.
Interest Rates and Total Loan Cost
Interest rates directly affect the total amount you’ll pay back on your student loans. A higher interest rate means you’ll pay more in interest over the life of the loan, increasing the overall cost. Conversely, a lower interest rate reduces the total interest paid, leading to significant savings. The interest accrues on the principal loan amount, and the longer the repayment period, the more interest you will accumulate.
Interest Rate Impact on Monthly Payments and Repayment Time
Let’s consider two scenarios: Scenario A involves a $20,000 loan with a 5% interest rate, and Scenario B involves the same loan amount but with a 7% interest rate. Both loans have a 10-year repayment period. Scenario A would result in lower monthly payments and a smaller total repayment amount compared to Scenario B. The difference, while seemingly small initially, compounds over time, resulting in a substantial difference in the total amount paid. For example, a 2% difference in interest rate can translate to thousands of dollars more in interest paid over the life of the loan.
Repayment Period’s Effect on Total Interest Paid
The length of your repayment period significantly impacts the total interest paid. Choosing a shorter repayment period means higher monthly payments but lower overall interest costs. Conversely, a longer repayment period leads to lower monthly payments but significantly higher total interest costs.
| Repayment Period (Years) | Monthly Payment (Example: $20,000 loan at 5%) | Total Interest Paid (Example: $20,000 loan at 5%) | Total Repayment Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | $377 | $2,820 | $22,820 |
| 10 | $211 | $5,060 | $25,060 |
| 15 | $156 | $7,300 | $27,300 |
| 20 | $126 | $9,540 | $29,540 |
*Note: These are example calculations and actual amounts will vary based on the specific loan terms.*
Loan Consolidation and Debt Management
Loan consolidation involves combining multiple student loans into a single loan with a new interest rate and repayment schedule. This can simplify repayment by reducing the number of payments and potentially lowering the monthly payment amount. However, it’s crucial to carefully consider the new interest rate offered. If the new rate is higher than the weighted average of your existing loans, consolidation could increase your total interest paid. A lower interest rate, however, can result in significant long-term savings. Consolidation may also offer the benefit of extending the repayment period. While this lowers monthly payments, it can result in paying significantly more interest over the life of the loan.
Last Recap
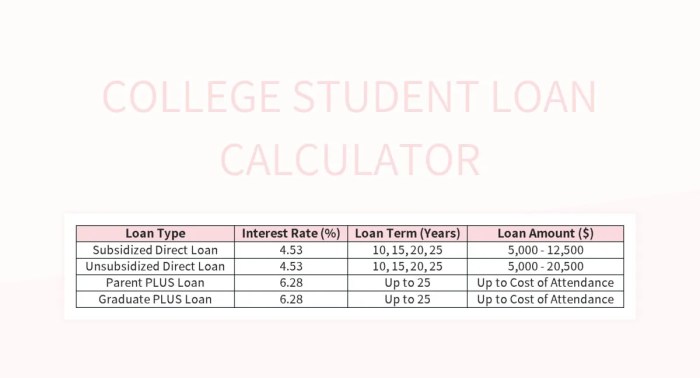
Mastering the art of student loan repayment involves more than just understanding the numbers; it’s about proactive financial planning. By utilizing a student loan calculator effectively and integrating it into a broader financial strategy, you can gain a clearer perspective on your debt, optimize your repayment plan, and pave the way for a more secure financial future. Remember, informed decision-making is key to successfully managing your student loans and achieving your long-term financial goals.
FAQ Explained
What is the difference between a simple and an advanced student loan calculator?
Simple calculators offer basic calculations based on loan amount, interest rate, and repayment period. Advanced calculators incorporate additional factors like loan consolidation, variable interest rates, and different repayment plans.
Can I use a student loan calculator to compare different loan refinancing options?
Yes, many advanced calculators allow you to input details of potential refinancing offers to compare monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall loan costs.
How often should I use a student loan calculator to track my progress?
It’s beneficial to use the calculator periodically (e.g., annually or whenever your financial situation changes significantly) to assess your progress and make necessary adjustments to your repayment plan.
What if my interest rate is variable? How does that affect the calculator’s accuracy?
Some calculators accommodate variable interest rates, allowing you to input an estimated average or range. However, remember that projections with variable rates are less precise than those with fixed rates.
