
Navigating the complexities of student loan debt can feel overwhelming, but understanding the process of applying for cancellation offers a path towards financial relief. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the student loan cancellation application, covering eligibility, required documentation, potential impacts on your credit score, and strategies for a successful application.
From understanding the various federal and private loan programs to addressing common challenges and post-application procedures, we aim to demystify the process and empower you to make informed decisions. We’ll explore the financial implications, both short-term and long-term, and offer valuable resources to support your journey.
Understanding the Application Process
Applying for student loan cancellation can seem daunting, but breaking down the process into manageable steps makes it significantly easier. This section details the application procedure, required documentation, and common pitfalls to avoid ensuring a smooth and successful application.
The application process is designed to be straightforward, however, careful attention to detail is crucial for a successful outcome. Thorough preparation and accurate completion of all forms are key to avoiding delays and potential rejection.
Application Steps
The application process typically involves several key stages. Following these steps carefully will help streamline the process and increase the likelihood of approval.
| Step | Action | Timeline | Supporting Documents |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gather all required documents (see below). | Prior to application submission. | Tax returns, transcripts, employment verification, etc. |
| 2 | Complete the application form accurately and thoroughly. | Allow ample time for completion. | Application form itself. |
| 3 | Review the completed application for errors. | Before submission. | Completed application form. |
| 4 | Submit the application and all supporting documents. | Follow specified submission instructions. | All completed forms and supporting documentation. |
| 5 | Track your application status. | Ongoing until decision is received. | Application tracking number. |
| 6 | Respond to any requests for additional information promptly. | As needed. | Any requested documentation. |
Required Documentation
Providing complete and accurate documentation is essential for a timely and successful application. Missing or incorrect documents can lead to delays or rejection.
Generally, you will need to provide documentation such as:
- Completed application form.
- Official transcripts from all colleges and universities attended.
- Tax returns for the relevant years.
- Proof of income (e.g., pay stubs, tax returns).
- Documentation supporting any claimed hardship or extenuating circumstances.
Common Application Errors
Many applications are delayed or rejected due to preventable errors. Understanding these common mistakes and how to avoid them is crucial.
- Incomplete applications: Failing to complete all sections of the application form accurately and thoroughly. Solution: Carefully review the application form and ensure all sections are filled out completely and accurately before submission.
- Missing documentation: Not providing all required supporting documents. Solution: Create a checklist of all required documents and ensure you have copies before submitting the application.
- Inaccurate information: Providing incorrect or misleading information on the application or supporting documents. Solution: Double-check all information for accuracy. If unsure, seek clarification from the relevant authorities.
- Late submissions: Submitting the application after the deadline. Solution: Submit the application well in advance of the deadline to allow for unforeseen delays.
Eligibility Criteria for Loan Cancellation
Student loan cancellation programs offer a potential pathway to debt relief, but eligibility is carefully defined. Understanding the specific requirements for each program is crucial for determining your potential for forgiveness. This section details the eligibility criteria for various loan cancellation programs, highlighting key differences and considerations.
Types of Student Loan Cancellation Programs
Several federal programs offer pathways to student loan cancellation, each with its own set of eligibility requirements. These programs are not mutually exclusive; you might qualify for more than one. The key programs include Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), Teacher Loan Forgiveness, and Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans leading to forgiveness after a specific period. Eligibility often depends on the type of loan, your employment, and your income.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program Requirements
The PSLF program forgives the remaining balance on your Direct Loans after you’ve made 120 qualifying monthly payments under an income-driven repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer. Qualifying employers include government organizations (federal, state, local, or tribal) and not-for-profit organizations. Crucially, your employment must be continuous for the entire 120-month period. Income limitations are not directly applied to PSLF; eligibility focuses on employment and repayment history.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program Requirements
The Teacher Loan Forgiveness program can forgive up to $17,500 of your federal student loans if you teach full-time for five complete and consecutive academic years in a low-income school or educational service agency. This program specifically targets educators in underserved communities. Again, income limitations aren’t directly a factor; the focus is on the type of school and the duration of employment.
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans and Forgiveness
Several IDR plans, such as Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), Income-Based Repayment (IBR), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR), calculate your monthly payment based on your income and family size. After a set number of years (typically 20 or 25), any remaining balance may be forgiven. These plans inherently incorporate income limitations as the monthly payment amount is directly tied to your income. However, the forgiven amount may be considered taxable income.
Summary Table of Eligibility Criteria
| Program | Loan Type | Employment Requirements | Income Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) | Direct Loans | 120 qualifying payments under an IDR plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer | None (focus on employment) |
| Teacher Loan Forgiveness | Federal Student Loans | 5 consecutive years of full-time teaching at a low-income school or educational service agency | None (focus on employment and school type) |
| Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans | Federal Student Loans | None (focus on repayment and income) | Income-based calculation for monthly payments; forgiveness after 20-25 years |
Types of Student Loans Covered

This section details the types of student loans eligible for cancellation under the program, clarifying which loans qualify and which do not. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for a successful application. We will also Artikel the differences in the cancellation process depending on the loan type.
Federal Student Loan Eligibility
Federal student loans, disbursed by the U.S. Department of Education, generally have a more straightforward cancellation process than private loans. This is because the federal government directly manages these loans and establishes the cancellation programs. The specific eligibility criteria can vary based on the type of federal loan and the specific cancellation program being applied to.
Types of Federal Student Loans and Cancellation
Several types of federal student loans may be eligible for cancellation, depending on the specific program. These commonly include Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, Direct PLUS Loans (for parents and graduate students), and Federal Stafford Loans (older loans that have been consolidated into Direct Loans). However, eligibility is not guaranteed and depends on the specific cancellation program requirements.
Private Student Loan Eligibility
Private student loans, offered by banks and other private lenders, typically have more complex cancellation processes. Cancellation is not a standard feature of private loans, and the terms of cancellation are determined by the individual lender. Eligibility often depends on the loan agreement and specific circumstances. It’s crucial to check your loan agreement and contact your lender to understand their policies regarding loan cancellation. Few private lenders participate in government-sponsored loan forgiveness programs.
Examples of Ineligible Loans
Certain types of loans are generally not eligible for cancellation under most federal programs. These include loans taken out for purposes other than education, such as personal loans or home equity loans. Furthermore, loans with defaulted status may not qualify for cancellation programs, often requiring a rehabilitation process before eligibility is considered. Loans obtained from non-accredited institutions may also not qualify for federal programs. Always check with the specific cancellation program’s guidelines for detailed information.
Loan Type Cancellation Eligibility
| Loan Type | Federal Eligibility | Private Eligibility | Cancellation Process Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Subsidized Loan | Potentially Eligible (depending on program) | Generally Not Eligible | Follows federal guidelines for specific programs. |
| Direct Unsubsidized Loan | Potentially Eligible (depending on program) | Generally Not Eligible | Follows federal guidelines for specific programs. |
| Direct PLUS Loan | Potentially Eligible (depending on program) | Generally Not Eligible | Follows federal guidelines for specific programs; eligibility may vary based on borrower type (parent or graduate student). |
| Private Student Loan | Generally Not Eligible | Dependent on lender’s policies and terms | Contact your lender directly; cancellation is less common and usually based on individual circumstances. |
| Federal Perkins Loan | Potentially Eligible (depending on program) | Generally Not Eligible | May be eligible under specific cancellation programs, though these are less common now due to the loan’s phase-out. |
Impact of Loan Cancellation on Credit Score
Student loan cancellation can have a significant impact on your credit score, although the effect isn’t always straightforward. It depends on how the cancellation is reported to the credit bureaus and your overall credit history. While it can be beneficial in some ways, understanding the potential consequences is crucial for managing your financial well-being.
Credit Reporting of Loan Cancellation
The way your loan cancellation is reported to credit bureaus directly influences your credit score. The most common scenario is that the cancelled loan will be marked as “paid in full.” This is generally positive for your credit score, as it demonstrates responsible debt management. However, there are scenarios where the loan might be reported differently, potentially leading to a temporary decrease in your score. For example, if the loan was previously in default, the cancellation might initially show as a “paid charge-off,” which can have a more negative short-term effect. It’s important to note that the impact is usually temporary; as new positive credit activity is added, the effect diminishes.
Examples of Loan Cancellation on Credit Reports
Let’s consider two examples. In the first, Sarah had a student loan in good standing. When her loan was cancelled, it was reported as “paid in full,” immediately boosting her credit utilization ratio and improving her credit score. In contrast, Mark had a defaulted student loan. His cancellation was initially reported as a “paid charge-off,” which temporarily lowered his score. However, over time, as he established a positive payment history on other accounts, the negative impact faded. These examples highlight the importance of monitoring your credit report after a cancellation.
Mitigating Negative Impacts on Credit
Even if a cancellation initially results in a temporary dip in your score, there are steps you can take to mitigate the negative effects and build a strong credit profile.
- Maintain a good payment history on all other credit accounts. Consistent on-time payments demonstrate financial responsibility, outweighing the temporary negative impact of a loan cancellation.
- Keep your credit utilization low. Aim to use less than 30% of your available credit. This shows lenders you are managing your debt effectively.
- Monitor your credit report regularly. Check for inaccuracies and ensure the cancellation is reported correctly. You can obtain free credit reports annually from AnnualCreditReport.com.
- Diversify your credit. Having a mix of credit accounts (credit cards, loans, etc.) can improve your credit score over time.
Financial Implications of Loan Forgiveness
Student loan forgiveness can have significant financial consequences, both positive and negative, impacting your immediate finances and long-term financial well-being. Understanding these implications is crucial before applying for any loan cancellation program. It’s important to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the potential drawbacks.
Tax Implications of Student Loan Cancellation
The tax implications of student loan forgiveness can be complex and depend on the specific program under which the forgiveness is granted. In some cases, forgiven student loan debt may be considered taxable income, meaning you will owe federal income taxes on the amount forgiven. This can significantly impact your tax liability for the year the forgiveness occurs. It’s crucial to consult a tax professional to determine the tax implications specific to your situation and the loan forgiveness program you are utilizing. They can help you navigate the complexities of tax reporting and potentially minimize your tax burden.
Long-Term Financial Benefits and Drawbacks of Loan Forgiveness
Loan forgiveness offers immediate relief from the burden of monthly student loan payments, freeing up cash flow for other financial priorities like saving, investing, or paying down other debts. This increased financial flexibility can contribute to improved long-term financial stability. However, the potential tax liability associated with loan forgiveness can offset some of these benefits. Furthermore, the long-term financial impact depends on how you utilize the freed-up funds. Mismanagement of this extra income could negate the positive effects of loan forgiveness.
Impact of Loan Cancellation on Future Borrowing
The impact of student loan cancellation on future borrowing can vary. While it removes the existing debt burden, the tax implications could affect your credit score temporarily. A significant tax liability might increase your debt-to-income ratio, potentially impacting your ability to secure loans in the future, such as mortgages or auto loans. However, the positive impact of eliminating monthly loan payments, increasing your credit score in the long run due to reduced debt, can significantly improve your borrowing capacity over time. Lenders generally view a lower debt-to-income ratio favorably.
Example of Potential Savings After Loan Cancellation
Let’s consider a hypothetical example. Suppose a borrower has $50,000 in student loan debt with a 6% interest rate and a 10-year repayment plan. Their monthly payment would be approximately $580. If their loan is forgiven, they would save $580 per month, or $6,960 per year. Over the 10-year repayment period, the total savings would be $69,600, excluding interest. However, if the forgiven amount is considered taxable income, they would need to factor in the additional tax liability to calculate their net savings. This illustrates the need for a careful calculation considering all relevant factors. The actual savings will vary depending on the interest rate, loan amount, repayment plan, and individual tax situation.
Resources and Support for Applicants
Navigating the student loan cancellation application process can feel overwhelming. Fortunately, numerous resources are available to guide you through each step and provide assistance when needed. Understanding these resources is crucial for a successful application. This section details the support available to applicants, ensuring a smoother and more informed experience.
We understand that applying for student loan cancellation can be complex. Therefore, we’ve compiled a list of resources designed to assist you throughout the process. These resources range from government agencies offering direct support to non-profit organizations providing valuable guidance and advocacy. Remember to thoroughly review all provided information to ensure you meet the eligibility criteria and understand the potential implications.
Government Agencies and Their Contact Information
The federal government offers various avenues for assistance with student loan applications. Direct contact with these agencies can clarify ambiguities and provide personalized support.
- Federal Student Aid (FSA): FSA is the primary source of information regarding federal student loans. Their website provides comprehensive details on loan programs, repayment plans, and the application process itself. Contact information can be found on their website. They offer a wealth of resources, including online tutorials and FAQs. They can be reached via phone and mail.
- StudentAid.gov: This website serves as the central hub for all federal student aid information. It contains detailed information about loan forgiveness programs, eligibility requirements, and the application process. The site provides a search function for easy navigation and access to numerous resources. This is the main website to consult for all things federal student aid related.
- Department of Education (ED): The Department of Education oversees federal student aid programs. Their website offers additional resources and contact information for resolving application-related issues. Their contact information can be found on their website. They offer a variety of support channels including phone, email, and mail.
Non-Profit Organizations Offering Assistance
Several non-profit organizations dedicate their efforts to assisting students with navigating the complexities of student loan repayment and cancellation. These organizations often offer free or low-cost services, including application assistance and financial counseling.
- National Consumer Law Center (NCLC): The NCLC provides legal assistance and advocacy for consumers, including those struggling with student loan debt. They offer resources and information on student loan rights and protections. Their contact information can be found on their website. They often publish articles and reports related to student loan issues.
- The Institute for College Access & Success (TICAS): TICAS conducts research and advocacy related to college affordability and student debt. Their website provides valuable information on student loan policies and trends. Their contact information can be found on their website. They publish research reports on various aspects of student debt.
- Student Loan Borrower Assistance Project (SLBAP): Many local and regional non-profit organizations provide assistance to student loan borrowers. These organizations often offer free workshops, counseling, and application assistance. Searching online for “student loan assistance [your state/city]” will help locate such organizations in your area.
Helpful Websites
Utilizing these websites can greatly simplify the application process and provide much-needed clarity. These resources are invaluable tools for applicants seeking to successfully navigate the complexities of student loan forgiveness.
- StudentAid.gov
- ED.gov
- NCLC.org (Example, replace with actual URL if available)
- ticas.org (Example, replace with actual URL if available)
Potential Challenges and Obstacles

Navigating the student loan cancellation application process can present several hurdles. Applicants may encounter difficulties gathering necessary documentation, understanding complex eligibility requirements, or dealing with unexpected delays from the processing agency. Understanding these potential challenges and developing proactive strategies is crucial for a successful application.
The application process itself can be lengthy and complex, requiring meticulous attention to detail. Errors or omissions in the application can lead to delays or outright rejection. Furthermore, changes in policy or unforeseen circumstances within the processing agency can also contribute to delays. Denials often stem from failing to meet specific eligibility criteria, providing insufficient documentation, or inaccuracies in the submitted information.
Application Errors and Omissions
Incomplete or inaccurate applications are a major source of delays and denials. Common errors include providing incorrect personal information, failing to upload all required documents, or omitting crucial details about your loan history. These errors can significantly delay processing, requiring corrections and resubmissions, potentially extending the timeline for approval. Careful review and double-checking of all information before submission is vital to avoid such issues.
Ineligible Loan Types
Not all student loans qualify for cancellation programs. Applicants may mistakenly believe their loans are eligible, only to discover during the application process that they are not covered under the specific program’s guidelines. Thoroughly researching the program’s eligibility criteria and understanding the types of loans covered is essential to avoid disappointment and wasted effort. Confirming loan eligibility through official sources before initiating the application process is strongly recommended.
Documentation Issues
Gathering and providing all the necessary documentation can be challenging. Applicants may struggle to locate old loan documents, obtain necessary verifications from previous institutions, or deal with missing or damaged paperwork. These issues can significantly impede the application process, potentially leading to delays or rejection. Proactive steps, such as organizing documents well in advance and contacting relevant institutions for assistance, can help mitigate these problems.
Processing Delays
Processing times can vary significantly, and unforeseen delays are possible due to high application volumes, system issues, or changes in government policy. These delays can be frustrating for applicants, but understanding that they are a possibility helps manage expectations and avoid unnecessary anxiety. Regularly checking the application status and contacting the processing agency if there are concerns can help keep the applicant informed.
| Common Problem | Solution | Example | Additional Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incomplete Application | Thoroughly review all sections before submission; double-check all information for accuracy. | Missing income verification documents. | Use a checklist to ensure all required fields are completed. |
| Ineligible Loan Type | Verify loan type eligibility against program guidelines before applying. | Applying for cancellation of a Parent PLUS loan under a program only covering Federal Direct Loans. | Contact the loan servicer or government agency for clarification. |
| Missing Documentation | Gather and organize all necessary documents well in advance of application. | Missing transcripts or proof of enrollment. | Contact previous institutions to request missing documents. |
| Processing Delays | Regularly check application status; contact the processing agency if there are concerns. | Application stuck in “processing” status for an extended period. | Be patient and persistent; keep records of all communication. |
Post-Application Procedures
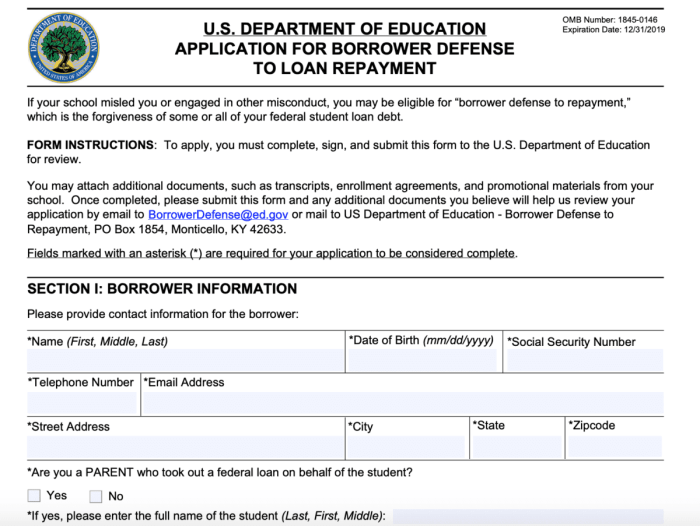
Submitting your student loan cancellation application is a significant step. However, the process doesn’t end there. Understanding the post-application procedures ensures a smoother path towards potential loan forgiveness. This section Artikels the key steps to take after submission, providing clarity on tracking your application and addressing potential appeals.
- Application Status Tracking: After submitting your application, you’ll receive a confirmation number. This number is crucial for tracking your application’s progress. Most loan cancellation programs offer online portals or dedicated phone lines where you can input your confirmation number to check the status. Regularly checking for updates will keep you informed about the review process. Expect delays; processing times can vary depending on the volume of applications and the complexity of individual cases. For example, a program might provide weekly updates via email or text message, detailing the stage your application has reached.
- Required Documentation and Follow-Up: The processing agency may request additional documentation after your initial submission. This is common, especially if your application requires further verification of information provided. Respond promptly to these requests. Failure to provide requested documentation within the specified timeframe could lead to delays or even rejection of your application. For instance, they might request official transcripts, tax returns, or employment verification.
- Appealing a Denied Application: If your application is denied, you typically have a right to appeal. The appeal process usually involves submitting a formal request outlining the reasons why you believe the denial was incorrect. This often requires providing additional evidence to support your case. Carefully review the denial letter to understand the specific reasons for the rejection and gather relevant documentation to address those concerns. Many programs provide detailed instructions and forms for the appeals process on their websites.
Understanding Appeal Processes
The appeal process varies depending on the specific student loan cancellation program. Generally, appeals require a formal written request, often with supporting documentation. This documentation may include updated financial information, corrected errors in the initial application, or new evidence supporting your eligibility. It’s essential to clearly and concisely explain why you believe the initial decision was wrong and provide compelling evidence to support your claim. The agency will review your appeal and notify you of their decision within a specified timeframe. For example, a program might allow you to submit an appeal within 30 days of receiving the denial notice, with a decision rendered within 60 days of the appeal submission.
Last Word
Securing student loan cancellation can significantly impact your financial future. By carefully reviewing the eligibility requirements, gathering necessary documentation, and understanding the potential consequences, you can increase your chances of a successful application. Remember to utilize the available resources and seek assistance when needed. This guide serves as a starting point; further research and personalized advice are recommended to navigate your specific circumstances effectively.
Helpful Answers
What happens if my application is denied?
Understand the appeals process and gather any additional documentation that might strengthen your case. Contact the relevant agency for guidance.
How long does the application process typically take?
Processing times vary depending on the program and the volume of applications. Expect potential delays and track your application status regularly.
Can I apply for cancellation if I have private student loans?
Eligibility for cancellation depends on the specific loan program and lender. Private loan cancellation options are less common than federal loan programs.
Will my tax liability change after loan cancellation?
Yes, loan cancellation may have tax implications. Consult a tax professional to understand the potential impact on your tax return.
