
Navigating the landscape of student loan refinancing in 2023 requires careful consideration of various factors. Interest rates, a key determinant of your monthly payments and overall loan cost, fluctuate based on economic conditions, your creditworthiness, and the lender’s offerings. Understanding these dynamics empowers you to make informed decisions and potentially secure significant savings over the life of your loan.
This guide delves into the intricacies of student loan refinance interest rates in 2023, providing a comprehensive overview of the process, from eligibility requirements and lender comparisons to the potential benefits and risks involved. We’ll explore different interest rate types, help you understand how your credit score impacts your options, and equip you with the knowledge to navigate the refinancing process effectively.
Understanding 2023 Student Loan Refinance Rates
Student loan refinancing can significantly impact your monthly payments and overall loan cost. Understanding the factors that influence interest rates in 2023 is crucial for securing the best possible terms. This section will explore those factors, clarify the differences between fixed and variable rates, and provide a comparison of rates offered by various lenders.
Factors Influencing Student Loan Refinance Interest Rates
Several key factors determine the interest rate you’ll receive when refinancing your student loans. Your credit score is paramount; a higher score generally translates to a lower interest rate. The length of your loan term also plays a significant role; longer terms often come with higher rates but lower monthly payments. Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), representing your total debt compared to your income, is another critical factor. A lower DTI indicates lower risk to the lender and can result in a better rate. Finally, the type of loan you’re refinancing (e.g., federal vs. private) and the lender’s own risk assessment also influence the final rate. Lenders consider your loan amount and the overall health of the economy when setting rates.
Fixed Versus Variable Interest Rates
Choosing between a fixed and a variable interest rate is a critical decision. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan’s life, providing predictability and stability in your monthly payments. Variable interest rates, on the other hand, fluctuate based on market indexes like the prime rate or LIBOR. While variable rates might start lower, they could increase significantly over time, leading to unpredictable monthly payments and potentially a higher total cost. The best choice depends on your risk tolerance and financial outlook. Those seeking stability generally prefer fixed rates, while those comfortable with risk might consider variable rates if they anticipate a period of low interest rates.
Comparison of Interest Rates Offered by Various Lenders
Numerous lenders offer student loan refinancing options, each with its own rate structure. It’s crucial to compare offers from multiple lenders to find the most favorable terms. Factors such as lender fees, prepayment penalties, and customer service should also be considered. While specific rates change constantly, some lenders consistently offer competitive rates. It’s important to check directly with lenders for their most up-to-date rates and terms. Always review the fine print and understand all associated costs before committing to a loan.
Sample Interest Rates
The following table provides sample interest rates for different credit scores and loan amounts. These are illustrative examples and actual rates may vary depending on the lender and individual circumstances.
| Credit Score | Loan Amount ($100,000) – Fixed Rate | Loan Amount ($50,000) – Fixed Rate | Loan Amount ($100,000) – Variable Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 750+ (Excellent) | 6.00% | 6.25% | 5.00% |
| 700-749 (Good) | 7.00% | 7.25% | 5.75% |
| 660-699 (Fair) | 8.50% | 8.75% | 6.75% |
| Below 660 (Poor) | 10.00% or higher | 10.25% or higher | 7.75% or higher |
Eligibility Requirements for Refinancing
Refinancing your student loans can significantly reduce your monthly payments and overall interest costs, but it’s crucial to understand the eligibility criteria before applying. Lenders assess several factors to determine your eligibility, primarily focusing on your creditworthiness and financial stability. Meeting these requirements increases your chances of securing a favorable interest rate and loan terms.
Lenders generally have specific requirements regarding credit score and income, debt-to-income ratio, and the type of student loans you possess. Understanding these requirements is essential for a smooth application process.
Credit Score and Income Requirements
Most lenders require a minimum credit score of 660-700 for student loan refinancing. However, some lenders may accept applicants with lower scores, though they might offer less favorable interest rates or stricter terms. A higher credit score generally translates to better loan offers, reflecting a lower perceived risk to the lender. Simultaneously, lenders also assess your income to ensure you have the capacity to make consistent monthly payments. Sufficient income demonstrates your ability to repay the refinanced loan, minimizing the lender’s risk of default. The specific income requirements vary depending on the lender and the loan amount. For example, a lender might require a minimum annual income of $40,000 or more, depending on the loan size and your credit history.
Debt-to-Income Ratio’s Impact
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), which represents the proportion of your monthly income dedicated to debt repayment, significantly influences your approval chances. A lower DTI generally improves your eligibility. Lenders prefer applicants with a DTI below 43%, indicating a comfortable level of debt management. A high DTI suggests a greater risk of default, potentially leading to rejection or less favorable terms. For instance, an applicant with a high DTI might be offered a higher interest rate or a shorter repayment period to compensate for the increased risk. Managing your debt effectively before applying for refinancing can significantly improve your chances of approval.
Loan Type and Eligibility
The type of student loans you hold—federal or private—influences your eligibility for refinancing. Private lenders typically refinance both federal and private student loans into a single private loan. However, refinancing federal loans into a private loan means losing access to federal protections like income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs. Careful consideration of the potential benefits and drawbacks of losing these federal protections is crucial before deciding to refinance federal student loans.
Required Documents for Application
Before applying, gather the necessary documents to streamline the process. This typically includes:
- Government-issued photo identification (e.g., driver’s license, passport)
- Social Security number
- Proof of income (e.g., pay stubs, tax returns)
- Student loan details (loan amounts, interest rates, lenders)
- Current credit report
Providing complete and accurate documentation ensures a faster and smoother application process. Missing or incomplete documentation can delay the approval or even lead to rejection.
Comparing Lenders and Their Offers

Choosing the right lender for student loan refinancing is crucial, as rates and fees can significantly impact your overall repayment costs. A thorough comparison of lenders and their offerings is essential before making a decision. This section will explore various aspects to consider when comparing lenders, highlighting key differences and helping you make an informed choice.
Comparing lenders involves more than just looking at interest rates. Factors like fees, customer service, and the lender’s overall reputation should all be taken into account. Understanding the nuances of different lender types can also be beneficial in finding the best fit for your individual circumstances.
Lender Fees and Charges
Fees associated with student loan refinancing can vary considerably between lenders. These fees can include origination fees, application fees, and potentially prepayment penalties. Origination fees are typically a percentage of the loan amount, while application fees are a flat fee charged for processing your application. Prepayment penalties, while less common, can charge you extra for paying off your loan early. It’s vital to compare these fees across multiple lenders to determine the true cost of refinancing.
For example, Lender A might charge a 1% origination fee and a $50 application fee, while Lender B might charge a 0.5% origination fee and a $100 application fee. On a $50,000 loan, Lender A’s fees would total $550 ($500 + $50), while Lender B’s fees would total $350 ($250 + $100). In this scenario, Lender B appears less expensive in terms of fees, although the interest rate needs to be considered as well.
Large Banks versus Smaller Lenders
Refinancing with a large bank often offers the perceived benefit of stability and established processes. These institutions generally have extensive resources and well-defined procedures. However, they may also have less flexible underwriting guidelines and potentially less personalized customer service compared to smaller lenders. Smaller lenders, on the other hand, might offer more competitive rates and a more personalized experience but may have less robust resources or a smaller track record.
A large bank’s advantage lies in its established infrastructure and potentially lower interest rates due to economies of scale. However, a smaller lender might offer a faster application process and more flexibility in terms of loan terms. The choice depends on your priorities: stability and established processes versus potentially lower rates and a more personalized approach.
Key Features of Refinancing Programs
Different lenders offer various features within their refinancing programs. Understanding these features is critical to finding a program that aligns with your financial goals and repayment preferences.
- Interest Rates: Fixed vs. Variable. Fixed rates offer predictable monthly payments, while variable rates fluctuate with market conditions.
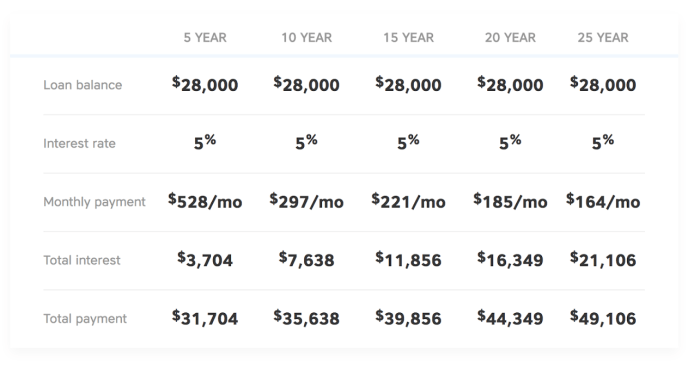
- Loan Terms: The length of the loan, typically ranging from 5 to 20 years, affects monthly payments and total interest paid.
- Fees: Origination fees, application fees, and prepayment penalties should all be considered.
- Customer Service: Look for lenders with responsive and helpful customer support channels.
- Eligibility Requirements: Check the lender’s criteria regarding credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio.
- Repayment Options: Some lenders offer options like accelerated repayment or flexible payment plans.
Lender Pre-qualification Processes
Most lenders offer a pre-qualification process, allowing you to check your eligibility and receive a rate estimate without impacting your credit score. This process typically involves providing basic personal and financial information, such as your income, credit score, and the amount of student loan debt you wish to refinance. The lender will then use this information to provide you with a personalized rate estimate and an indication of your eligibility.
For example, one lender might require a credit score of at least 680 and a debt-to-income ratio below 45%, while another lender may have more lenient requirements. Some lenders might offer a quick online pre-qualification tool, while others may require a more extensive application process. Understanding these differences will help you efficiently navigate the pre-qualification stage.
The Refinancing Process Step-by-Step
Refinancing your student loans can significantly reduce your monthly payments and overall interest paid. However, navigating the process requires careful planning and understanding of the steps involved. This section Artikels the key stages of refinancing your student loans, from initial research to securing your new loan.
The refinancing process generally involves several key steps, each requiring attention to detail to ensure you achieve the best possible outcome. Understanding these steps and the timelines involved will empower you to make informed decisions throughout the process.
Gathering Necessary Information
Before you begin the application process, it’s crucial to gather all the necessary information. This includes your current student loan details (loan amounts, interest rates, lenders, and remaining balances), your credit score, and your income information. Having this information readily available streamlines the application process and helps lenders assess your eligibility quickly. A strong credit score is often a key factor in securing favorable interest rates. The higher your credit score, the better your chances of qualifying for lower interest rates. You can obtain your credit score from various credit reporting agencies.
Comparing Lenders and Loan Offers
Once you have gathered your information, it’s essential to compare offers from multiple lenders. Don’t settle for the first offer you receive. Different lenders offer varying interest rates, repayment terms, and fees. Carefully review the terms and conditions of each offer, paying close attention to the annual percentage rate (APR), which reflects the total cost of the loan. Use online comparison tools or contact lenders directly to obtain personalized quotes. A detailed comparison will help you identify the lender that best suits your financial situation and needs. For example, consider Lender A offering a 6% APR with a $500 origination fee versus Lender B offering a 6.2% APR with no origination fee. The seemingly smaller difference in APR could be offset by the fee, depending on the loan amount.
Completing the Application
Once you’ve chosen a lender, you’ll need to complete their application. This usually involves providing personal information, employment history, and details of your student loans. Be sure to accurately and completely fill out the application to avoid delays. Many lenders offer online applications, simplifying the process. Providing all necessary documentation upfront will help expedite the approval process. This may include tax returns, pay stubs, and proof of residency.
Loan Approval and Disbursement
After submitting your application, the lender will review your information and determine your eligibility. This process can take several days or weeks, depending on the lender and the complexity of your application. Upon approval, the lender will disburse the funds, paying off your existing student loans. You will then begin making payments on your new refinanced loan according to the agreed-upon terms. It’s important to carefully read the loan agreement before signing it to ensure you understand all the terms and conditions.
Timeline for the Refinancing Process
The entire refinancing process, from initial research to loan disbursement, typically takes between 4 to 8 weeks. However, this timeline can vary depending on several factors, including the lender’s processing time, the complexity of your application, and the volume of applications they are currently handling. Unexpected delays may occur, so it’s advisable to allow for some flexibility in your planning. For example, a lender experiencing a high volume of applications might take longer to process your application than a lender with lower application volume.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Refinancing
Refinancing student loans can offer significant advantages, but it’s crucial to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the inherent risks before making a decision. Understanding the impact on your monthly payments, loan forgiveness programs, and overall financial situation is paramount. This section will explore both the positive and negative aspects of refinancing to help you make an informed choice.
Lower Monthly Payments
Refinancing can substantially reduce your monthly student loan payments. By securing a lower interest rate or extending the loan term, you can lower your monthly obligations, freeing up cash flow for other financial priorities like saving, investing, or paying down other debts. For example, someone with a $50,000 loan at 7% interest might see their monthly payment drop by hundreds of dollars by refinancing to a 4% interest rate, even if the loan term is slightly extended. This relief can be particularly beneficial for individuals struggling with high monthly payments.
Risks of Refinancing Federal Student Loans
Refinancing federal student loans carries significant risks. The most prominent risk is the loss of federal protections and benefits. Federal loans often come with income-driven repayment plans, deferment options, and potential loan forgiveness programs (like Public Service Loan Forgiveness). Once you refinance into a private loan, these protections disappear. This means you lose the safety net provided by federal programs if you experience financial hardship. For instance, if you lose your job, you might not be able to defer your payments as you could with a federal loan.
Impact on Loan Forgiveness Programs
Refinancing federal student loans can jeopardize your eligibility for loan forgiveness programs. Programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) require borrowers to make qualifying payments on federal loans. Refinancing eliminates your eligibility for these programs, potentially costing you thousands of dollars in forgiven debt over time. A borrower pursuing PSLF who refinances their federal loans would lose their progress toward forgiveness and have to start over with a private lender, a process that could take years.
Scenarios Where Refinancing May or May Not Be Beneficial
Refinancing can be beneficial for borrowers with good credit scores and stable incomes who are confident in their ability to consistently make payments. For example, a high-earning individual with excellent credit might find that refinancing significantly lowers their monthly payment and saves them money in the long run. However, refinancing is not suitable for those with inconsistent income, poor credit, or those pursuing loan forgiveness programs. A borrower with a low credit score might not qualify for favorable interest rates, negating the benefits of refinancing. Similarly, someone actively working towards loan forgiveness through a federal program should avoid refinancing to prevent jeopardizing their eligibility.
Illustrative Examples of Refinancing Scenarios
Refinancing student loans can significantly impact your overall repayment costs. The decision of whether or not to refinance hinges on several factors, including your current interest rate, credit score, and financial goals. Let’s examine scenarios where refinancing proves beneficial and where it might not be the best course of action.
Scenario: Significant Savings Through Refinancing
Imagine Sarah, a recent graduate with $50,000 in federal student loans at a 7% interest rate, resulting in a 10-year repayment plan with a monthly payment of approximately $600. Facing a high monthly payment, Sarah researches refinancing options and qualifies for a private loan with a 4% interest rate. By refinancing, she can secure a new 10-year loan with a monthly payment reduced to approximately $480, saving $120 per month. Over the life of the loan, this seemingly small monthly difference translates into substantial savings. The total interest paid on the original loan would be approximately $20,000. With the refinanced loan at 4%, the total interest paid would be approximately $10,000, resulting in a saving of $10,000. This significant reduction in interest paid frees up considerable funds for other financial goals.
Scenario: Refinancing Not Recommended
Consider David, who has $30,000 in federal student loans with a 5% interest rate. He is currently enrolled in an income-driven repayment plan, keeping his monthly payments low and manageable. While he might find a private lender offering a lower interest rate, refinancing his federal loans would mean losing access to crucial benefits such as income-driven repayment, deferment, and forbearance options. If David experiences unexpected financial hardship, the flexibility afforded by his federal loans could be essential. Refinancing into a private loan would eliminate these safety nets. In this case, the potential risk of losing these crucial protections outweighs the benefits of a slightly lower interest rate.
Visual Representation of Interest Paid
A bar graph would clearly illustrate the difference. The first bar would represent the total interest paid on the original high-interest loan (e.g., $20,000, as in Sarah’s example), significantly taller than the second bar. The second bar would represent the total interest paid on the refinanced loan with a lower interest rate (e.g., $10,000, as in Sarah’s example), showing a considerable reduction in the total interest paid over the life of the loan. The visual contrast would powerfully demonstrate the potential cost savings associated with refinancing when advantageous.
Closure
Refinancing your student loans can be a powerful tool for managing your debt, potentially leading to lower monthly payments and substantial long-term savings. However, it’s crucial to approach the process strategically, comparing offers from multiple lenders, carefully weighing the benefits against the potential risks, and ensuring the refinance aligns with your financial goals. By understanding the factors influencing interest rates and the steps involved, you can confidently navigate this important financial decision and secure the best possible terms for your situation.
FAQ Compilation
What is the average student loan refinance interest rate in 2023?
The average interest rate varies greatly depending on your credit score, loan amount, and the lender. It’s best to check rates from several lenders for a personalized estimate.
Can I refinance federal student loans?
Yes, but be aware that refinancing federal loans into private loans means you’ll lose access to federal protections and programs like income-driven repayment plans and potential forgiveness programs.
How long does the refinance process take?
The process typically takes several weeks, from application to loan disbursement. The exact timeline depends on the lender and the complexity of your application.
What is a good credit score for student loan refinancing?
Lenders generally prefer applicants with credit scores above 670-700, but some may consider applicants with lower scores. A higher score usually results in better interest rates.
What documents do I need to refinance my student loans?
You’ll typically need proof of income, identification, and details about your existing student loans. Specific requirements vary by lender.
