
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, especially with the frequent changes to available plans. This update provides a clear overview of recent modifications to student loan save plans, including Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) and Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) programs. We’ll explore how these changes impact borrowers with different income levels and loan amounts, offering practical advice to help you make informed decisions about your repayment strategy.
Understanding these adjustments is crucial for borrowers to optimize their repayment journey and potentially save significant amounts of money over the life of their loans. This guide aims to demystify the process, offering a concise yet comprehensive analysis of the updated plans and their implications.
Recent Updates to Student Loan Save Plans

The past year has seen significant changes to federal student loan repayment plans, impacting millions of borrowers. These updates, largely driven by the ongoing economic climate and shifts in government policy, offer both new opportunities and potential challenges for borrowers navigating their student loan debt. Understanding these changes is crucial for making informed decisions about repayment strategies.
Key Changes in Student Loan Repayment Plans
Several key changes have been implemented recently. The most notable include the extension of the pause on federal student loan payments (which has since ended), the expansion of income-driven repayment (IDR) plans, and adjustments to the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program. The extended pause provided temporary relief to borrowers, but its termination necessitates a renewed focus on long-term repayment strategies. The expansion of IDR plans aims to make repayment more manageable for borrowers with lower incomes, while PSLF program adjustments aim to streamline the forgiveness process for qualifying public service employees. These changes have resulted in a more complex landscape of repayment options, requiring borrowers to carefully assess which plan best suits their individual circumstances.
Impact on Borrowers with Different Income Levels
The impact of these updates varies significantly based on income. Borrowers with higher incomes may find that the changes offer limited benefit, as they were already managing their payments effectively under existing plans. However, borrowers with lower incomes are likely to see substantial improvements, particularly through the expanded access to more affordable IDR plans. For example, the revised income calculation methods in some IDR plans may lead to significantly lower monthly payments for those with fluctuating or lower incomes. Conversely, those with higher incomes might find that the new plans offer less in terms of long-term savings or forgiveness compared to previous options. Careful evaluation of individual financial situations is paramount to determine the optimal repayment strategy.
Comparison of Student Loan Repayment Plan Benefits and Drawbacks
Choosing the right repayment plan requires careful consideration of both benefits and drawbacks. While income-driven repayment plans offer lower monthly payments, they often extend the repayment period, leading to higher overall interest payments. Standard repayment plans offer faster debt elimination but may result in higher monthly payments that strain budgets. PSLF offers complete loan forgiveness after 10 years of qualifying payments, but meeting the eligibility requirements can be challenging. Each plan presents a trade-off between affordability and repayment speed, demanding a personalized approach.
Summary of Key Student Loan Repayment Plan Features
| Plan Name | Eligibility Requirements | Payment Calculation Method | Forgiveness Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Repayment | All federal student loan borrowers | Fixed monthly payment over 10 years | None |
| Graduated Repayment | All federal student loan borrowers | Payments increase gradually over 10 years | None |
| Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) – ICR, PAYE, REPAYE,IBR | All federal student loan borrowers | Payment based on income and family size; repayment period extended to 20-25 years | Remaining balance forgiven after 20-25 years |
| Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) | Borrowers working full-time for qualifying government or non-profit organizations | Payment based on chosen IDR plan | Remaining balance forgiven after 120 qualifying payments |
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plan Changes
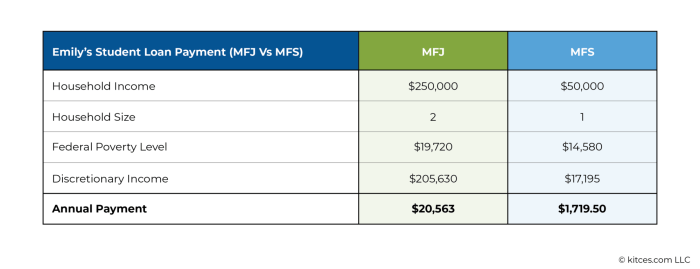
The Biden-Harris administration has made significant changes to Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans, aiming to make student loan repayment more manageable for borrowers. These modifications impact how monthly payments are calculated and, consequently, how much borrowers ultimately pay back over the life of their loans. Understanding these changes is crucial for borrowers to navigate their repayment options effectively.
The most significant change involves recalculating payments based on a borrower’s income and family size. Previously, some IDR plans used a formula that resulted in higher monthly payments for some borrowers, potentially leading to longer repayment periods and increased overall interest payments. The revised plans aim to address this by implementing a more borrower-friendly calculation method. This recalculation will also affect the amount of remaining loan balance eligible for forgiveness after a specified repayment period.
Revised Payment Calculation Methodology
The revised IDR plans utilize a more streamlined formula to determine monthly payments. Instead of complex calculations that varied across different plans, the new system employs a consistent approach. This involves dividing the borrower’s discretionary income (income above a certain poverty guideline) by 10, 15, or 20 percent, depending on the chosen plan, and applying that percentage to the total loan balance. For example, a borrower with a discretionary income of $20,000 on a 10% plan would have a monthly payment of approximately $166.67, assuming a loan balance of $20,000. This simplifies the process and makes it easier for borrowers to understand their monthly obligations. The specific formula used may vary slightly depending on the chosen IDR plan (Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR), and Income-Driven Repayment (IDR)).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Revised IDR Plans
The revised IDR plans offer several potential advantages. Lower monthly payments can make repayment more manageable, particularly for borrowers with lower incomes. The streamlined calculation method increases transparency and simplifies the process of understanding payment amounts. Furthermore, the potential for loan forgiveness after a certain number of qualifying payments is a significant benefit.
However, there are also potential disadvantages. While lower monthly payments are beneficial in the short term, they may lead to a longer repayment period and ultimately higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. The specific impact will depend on individual circumstances, including income level, loan amount, and interest rate. Borrowers should carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages before selecting a plan.
Examples of Impact on Borrowers with Varying Income and Loan Amounts
Consider two borrowers: Borrower A has a $50,000 loan balance and an annual discretionary income of $30,000. Borrower B has a $100,000 loan balance and an annual discretionary income of $60,000. Under a 10% IDR plan, Borrower A’s monthly payment would be significantly lower than Borrower B’s, even though Borrower B has a larger loan. However, Borrower B’s higher income might allow them to pay off their loan more quickly despite the larger payment. These examples highlight the importance of individual assessment based on personal financial situations. It is crucial to consult with a financial advisor or student loan counselor to determine the best plan based on your unique circumstances.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program Modifications
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program has undergone significant changes, making it more accessible to eligible borrowers while also clarifying the requirements for loan forgiveness. These modifications aim to streamline the application process and address previous ambiguities that led to many borrowers being denied forgiveness despite meeting the criteria. Understanding these updates is crucial for those working in public service and seeking loan forgiveness.
Recent updates to the PSLF program primarily focus on simplifying the application process and expanding eligibility. Previously, stringent requirements and a complex application process resulted in low forgiveness rates. The changes implemented aim to rectify this by broadening the definition of qualifying employment and providing more lenient interpretations of past repayment plans. The changes also offer a limited time waiver for past repayment periods, allowing borrowers who previously didn’t meet the stringent requirements to potentially qualify for forgiveness.
Revised PSLF Eligibility Requirements
The revised eligibility requirements focus on clarifying what constitutes qualifying employment and acceptable repayment plans. Previously, even minor discrepancies in employment or repayment plan details could disqualify borrowers. Now, there is a greater emphasis on the overall intent and substance of the borrower’s employment and repayment history. For example, the temporary waiver addresses past periods where borrowers may have been in ineligible repayment plans, such as those that were not income-driven repayment (IDR) plans. This waiver allows for previously non-qualifying payments to count towards the 120 payments required for forgiveness.
Modified PSLF Application Process
The application process has been streamlined to make it easier for borrowers to track their progress and submit their applications. The updated process emphasizes clear communication and provides borrowers with more frequent updates on the status of their applications. The goal is to improve transparency and reduce the uncertainty associated with the previous application process.
The steps involved in applying for PSLF forgiveness are as follows:
- Consolidate your federal student loans: If your loans aren’t already consolidated into a Direct Consolidation Loan, you must consolidate them first. This step is crucial because only Direct Loans are eligible for PSLF.
- Complete the PSLF form: This form requires information about your employment and repayment history. Accurate and complete information is essential for a successful application.
- Submit your employment certification form: Your employer must complete and sign this form, verifying your employment in a qualifying public service role. This is often done annually.
- Track your progress: Regularly check your PSLF account to monitor your progress towards the 120 qualifying payments.
- Submit your application for forgiveness: Once you have made 120 qualifying payments, you can submit your application for loan forgiveness.
Impact on Public Service Borrowers
These changes are expected to significantly benefit public service borrowers. The streamlined application process and expanded eligibility criteria will likely lead to a higher forgiveness rate. For example, teachers, nurses, and social workers who previously were denied forgiveness due to technicalities might now be eligible. The limited-time waiver provides a crucial opportunity for those who may have made payments under ineligible plans in the past to finally see their loans forgiven. This can alleviate substantial financial burdens and allow these individuals to focus on their careers and communities.
Impact on Student Loan Borrowers
The recent updates to student loan repayment plans have significant implications for borrowers, potentially altering their monthly payments and long-term financial health. These changes, encompassing modifications to Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans and the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program, affect borrowers differently depending on their income, loan amount, and career path. Understanding these effects is crucial for borrowers to effectively manage their debt.
The primary impact is on monthly payment amounts. For some borrowers, particularly those with lower incomes or higher loan balances, the updated IDR plans may result in lower monthly payments. This immediate relief can significantly improve short-term affordability. Conversely, some borrowers might experience slightly higher payments under the new plans, depending on the specific changes implemented and their individual circumstances. The long-term financial implications, however, extend beyond monthly payment adjustments.
Monthly Payment Adjustments and Long-Term Financial Implications
The changes in IDR plans can lead to varying repayment periods and, consequently, differing total amounts paid over the life of the loan. Lower monthly payments, while beneficial in the short term, can extend the repayment period, potentially resulting in a higher total interest paid over the loan’s lifespan. Conversely, higher monthly payments, although initially burdensome, could lead to faster loan repayment and a reduction in overall interest paid. This trade-off necessitates careful consideration of individual financial circumstances and long-term goals.
Hypothetical Scenario: Old vs. New Repayment Plans
Let’s consider two borrowers, both with $50,000 in student loan debt at a 6% interest rate. Borrower A, under the old plan, had a monthly payment of $300, resulting in a 20-year repayment period and a total repayment of approximately $72,000 (including interest). Borrower B, under the new plan, experiences a lower monthly payment of $250 due to revised IDR calculations. This results in a 25-year repayment period and a total repayment of approximately $75,000. While Borrower B enjoys lower monthly payments, they ultimately pay $3,000 more in interest over the life of the loan. This scenario highlights the importance of carefully analyzing both short-term affordability and long-term financial implications.
Infographic Depicting Borrower Distribution Across Repayment Plans
An infographic illustrating the distribution of borrowers across different repayment plan categories before and after the update would visually represent the shifts in borrower demographics. The pre-update graphic might show a larger concentration of borrowers in standard repayment plans, with smaller segments in various IDR plans. The post-update graphic could demonstrate a potential shift towards increased participation in IDR plans, particularly income-driven options offering lower monthly payments. The infographic would use bar charts or pie charts to visually compare the proportions of borrowers in each repayment plan category before and after the implementation of the updates. For example, the pre-update graphic might show 60% in standard repayment, 20% in ICR, 10% in PAYE, and 10% in REPAYE. The post-update graphic could show a shift, perhaps 50% standard, 25% ICR, 15% PAYE, and 10% REPAYE, reflecting the impact of the modifications on borrower choices. This visual representation would provide a clear understanding of the changes in repayment plan usage among student loan borrowers.
Resources and Further Information
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be challenging, especially with the frequent changes to programs and plans. This section provides essential resources and practical tips to help you understand and manage your student loans effectively. We aim to empower you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions about your repayment strategy.
Understanding your options and accessing reliable information are crucial steps in successfully managing your student loans. The following resources and tips are designed to guide you through this process.
Reliable Websites and Government Resources
The federal government provides several key websites dedicated to assisting student loan borrowers. These resources offer comprehensive information, tools, and support for navigating the student loan repayment system. Accessing these resources is the first step towards effectively managing your debt.
- StudentAid.gov: This is the official website of the Federal Student Aid, a part of the U.S. Department of Education. It provides information on federal student loan programs, repayment plans, and forgiveness options. You can access your loan information, make payments, and find answers to frequently asked questions.
- Federal Student Aid’s Repayment Estimator: This online tool allows you to estimate your monthly payments under different repayment plans, helping you determine which option best suits your financial situation. It takes into account your loan amount, interest rate, and income.
- National Student Loan Data System (NSLDS): This system provides a central location to access your federal student loan information from various lenders. It’s a valuable tool for tracking your loans and ensuring accuracy.
Tips for Navigating Student Loan Changes
Staying informed and proactive are key to successfully navigating changes in student loan programs. These tips will help you stay ahead of the curve and make the best choices for your financial future. Regularly reviewing your options is essential to ensure your plan remains aligned with your current financial situation.
- Regularly check StudentAid.gov for updates: Significant changes to student loan programs are often announced on this website. Make it a habit to visit the site periodically.
- Understand your loan terms and repayment options: Know the details of your loans, including interest rates, repayment periods, and any applicable fees. Explore different repayment plans to find the most suitable one.
- Consider income-driven repayment plans: If your income is low, these plans can significantly reduce your monthly payments.
- Explore loan forgiveness programs: Programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) may offer loan forgiveness after a certain period of qualifying employment. Meet all requirements for qualification.
- Budget carefully and prioritize loan payments: Include your student loan payments in your monthly budget to avoid delinquency and late fees.
Reviewing Your Repayment Plan
Regularly reviewing your repayment plan ensures it remains aligned with your financial circumstances. This proactive approach helps you avoid potential issues and take advantage of beneficial changes. It’s recommended to conduct this review at least annually, or whenever your financial situation changes significantly.
To review your repayment plan, you should first gather all relevant information, including your loan details, income, and expenses. Then, you should compare your current repayment plan with other available options to see if a different plan would better suit your financial situation. Finally, you should contact your loan servicer if you need to make changes to your repayment plan. This process will help you determine if your current plan is still the most effective one for your circumstances.
Staying Informed About Future Updates
The landscape of student loan programs is constantly evolving. Staying informed about future updates and changes is crucial for making informed decisions and avoiding potential pitfalls. This proactive approach ensures you remain aware of new opportunities and potential challenges.
By regularly checking official government websites and reputable financial news sources, you can stay abreast of any significant changes that may impact your repayment plan. This commitment to staying informed will help you manage your student loans effectively and make the best choices for your financial future. Subscribing to email alerts from StudentAid.gov can also be beneficial.
Closing Summary

The recent updates to student loan save plans represent a significant shift in the landscape of student loan repayment. By carefully reviewing the changes to IDR plans, PSLF eligibility, and other repayment options, borrowers can proactively manage their debt and potentially achieve loan forgiveness sooner. Staying informed about these updates and utilizing available resources is key to navigating this complex system effectively and achieving long-term financial stability.
FAQ Insights
What if I’m already enrolled in a repayment plan? Do I need to take action?
It’s advisable to review your current plan and compare it to the updated options to see if a change would benefit you. Contact your loan servicer to discuss your options.
Where can I find more detailed information on the changes?
The official websites of the Department of Education and your loan servicer are excellent resources. You can also consult with a financial advisor specializing in student loan debt.
What if I don’t qualify for PSLF? Are there other options?
Yes, several other income-driven repayment plans may be available, offering varying degrees of payment flexibility and potential for loan forgiveness based on your income and loan type. Explore your options with your loan servicer.
How often are these plans updated?
Student loan programs are subject to change, so it’s crucial to regularly check for updates from official sources. Staying informed is vital for making the best decisions for your financial future.
