
Summer break often presents a unique financial challenge for students. Balancing the need for supplemental income with the desire to pursue internships or enriching experiences can be difficult. Securing student loans for the summer of 2024 can alleviate financial pressures, allowing students to focus on their goals. However, navigating the world of student loans requires careful consideration of eligibility, application processes, repayment plans, and potential risks. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the landscape of summer student loans in 2024, equipping students with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
This guide will cover various aspects of obtaining student loans for the summer, including eligibility criteria for both federal and private loans, application procedures and deadlines, available loan types and their associated interest rates, and effective budgeting strategies. We’ll also address common scams and provide alternative funding options to consider. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to secure summer funding responsibly and effectively.
Eligibility Requirements for Summer 2024 Student Loans
Securing funding for your summer coursework requires understanding the eligibility criteria for student loans. Both federal and private loan options exist, each with its own set of requirements. This section will clarify the pathways to accessing financial aid for your summer studies.
General Eligibility Criteria for Federal Student Loans
To be eligible for federal student loans, you must be a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen, enrolled at least half-time in a degree or certificate program at an eligible institution, maintain satisfactory academic progress, and complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). Additional requirements may apply depending on the specific loan program. For example, demonstrating financial need is a factor for some subsidized loan programs. The Department of Education’s website provides the most up-to-date and comprehensive information.
Specific Requirements for Summer Loan Disbursement
Summer loan disbursement often follows the same general eligibility guidelines as the academic year, but with some key differences. Your school’s financial aid office will determine your eligibility for summer loans based on your enrollment status during the summer session. You’ll typically need to be enrolled in a minimum number of credit hours to qualify. The disbursement process itself might also differ slightly, with funds potentially released in a single payment or spread across the summer term according to your institution’s schedule. Direct communication with your financial aid office is crucial for precise details.
Federal vs. Private Loan Eligibility
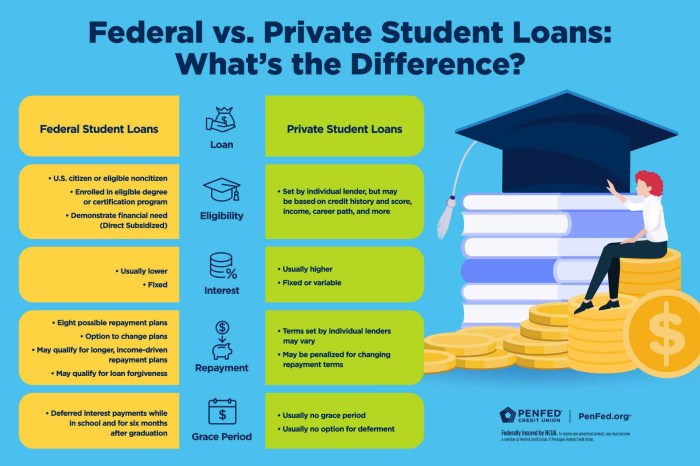
Federal student loans generally have more lenient eligibility requirements than private loans. Federal loans prioritize access based on need and enrollment status, while private lenders consider your credit history, income, and co-signer availability. Individuals with poor credit or limited income might find it more challenging to secure private loans, even if they meet the enrollment criteria. A strong credit history and a co-signer can significantly improve your chances of approval for a private loan. Federal loans, however, often come with more favorable repayment terms and protections against excessive interest rates.
Eligibility Factors for Different Loan Programs
| Loan Program | Credit History Required? | Income Verification Needed? | Co-signer Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Direct Subsidized Loan | No | Yes (FAFSA required) | No |
| Federal Direct Unsubsidized Loan | No | Yes (FAFSA required) | No |
| Private Student Loan (Example: Sallie Mae) | Usually Yes | Usually Yes | Often Yes |
| Private Student Loan (Example: Discover) | May vary | May vary | May vary |
Application Process and Deadlines for Summer 2024
Securing funding for your summer studies requires a timely and accurate application process. This section details the steps involved in applying for both federal and private student loans for the summer 2024 semester, including crucial deadlines to keep in mind. Careful planning and adherence to these deadlines are vital to ensuring a smooth funding process.
Federal Student Loan Application Process
Applying for federal student loans involves several key steps. The process is generally straightforward, but careful attention to detail is essential to avoid delays. The specific steps and deadlines may vary slightly depending on your institution and the type of federal loan you’re applying for. However, the general process remains consistent.
- Complete the FAFSA: The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the first step. You’ll need to create an FSA ID and provide information about your income, assets, and family details. The FAFSA determines your eligibility for federal student aid, including loans. Submit your FAFSA well in advance of the deadline to allow ample processing time.
- Review Your Student Aid Report (SAR): After submitting the FAFSA, you’ll receive a SAR. This report summarizes your information and indicates your eligibility for federal aid. Carefully review this report for accuracy.
- Accept Your Loan Offer: Your school will notify you of your loan offer based on your FAFSA information and your school’s cost of attendance. You’ll need to accept the loan offer through your school’s financial aid portal.
- Complete Master Promissory Note (MPN): For federal student loans, you’ll need to sign a Master Promissory Note (MPN). This is a legal agreement outlining your responsibilities as a borrower.
- Complete Entrance Counseling: Before receiving your first federal student loan disbursement, you’ll likely need to complete entrance counseling. This online session educates you about your rights and responsibilities as a borrower.
Federal Student Loan Deadlines for Summer 2024
Deadlines for federal student loan applications vary by institution. However, generally, applications for summer funding are due earlier than those for the fall or spring semesters. Aim to complete the FAFSA by early spring (March or April) to ensure timely processing for summer disbursement. Contact your school’s financial aid office for specific deadlines. Late submissions may result in delays or denial of funding. For example, a university might set a deadline of April 15th for summer loan applications.
Private Student Loan Application Process
Private student loans are offered by banks and other financial institutions. The application process for private loans typically involves a credit check (for the student or co-signer), and requires more detailed financial information than federal loans.
- Research Lenders: Compare interest rates, fees, and repayment options from different private lenders.
- Complete the Application: Each lender has its own application process, typically requiring personal and financial information.
- Provide Documentation: You’ll likely need to provide documentation such as tax returns, bank statements, and proof of enrollment.
- Credit Check and Approval: The lender will conduct a credit check and review your application. Approval depends on your creditworthiness (or that of your co-signer).
Private Student Loan Deadlines for Summer 2024
Deadlines for private student loans vary greatly depending on the lender. Unlike federal loans, there isn’t a centralized application system. It’s crucial to check each lender’s website for specific deadlines. Generally, private lenders require applications well in advance of the start of the semester, often several weeks before the disbursement date. For example, a lender might have a deadline of May 1st for summer loan applications. Procrastination could significantly impact your ability to secure funding in time.
Types of Student Loans Available for Summer 2024
Securing funding for your summer education can significantly impact your ability to complete your studies. Understanding the various loan options available is crucial for making informed financial decisions. This section details the different types of student loans you might consider for the summer of 2024, highlighting their key features and differences.
Federal Student Loan Programs for Summer Borrowing
The federal government offers several student loan programs designed to assist students with their educational expenses, including summer courses. These programs generally offer more favorable terms and borrower protections compared to private loans. Key federal loan programs typically available for summer borrowing include Federal Direct Subsidized Loans and Federal Direct Unsubsidized Loans. Eligibility for these loans depends on factors such as financial need (for subsidized loans), enrollment status, and credit history.
Subsidized vs. Unsubsidized Federal Loans
Subsidized and unsubsidized federal student loans differ primarily in how interest accrues. With subsidized loans, the government pays the interest while you’re enrolled at least half-time and during certain grace periods. Unsubsidized loans, however, accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed, regardless of your enrollment status. This means that with unsubsidized loans, the total amount you repay will be higher than the original loan amount unless you pay the interest as it accrues. Choosing between subsidized and unsubsidized loans depends on your financial need and ability to manage interest payments.
Private Student Loans Compared to Federal Options
Private student loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. While they can be a viable option, they often come with higher interest rates, less flexible repayment options, and fewer borrower protections compared to federal loans. Federal loans typically offer benefits such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs, which are not always available with private loans. Before considering a private loan, it’s crucial to exhaust all federal loan options and carefully compare the terms and conditions of both federal and private loans to make an informed choice.
Comparison of Loan Types
The following table provides a general comparison of interest rates, repayment terms, and fees for different loan types. Keep in mind that actual rates and fees can vary depending on the lender, your creditworthiness, and the specific loan program. This table should be considered a general guideline and not a definitive source for current rates. Always consult the lender directly for the most up-to-date information.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate (Example – Subject to Change) | Repayment Terms (Example) | Fees (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Direct Subsidized Loan | Variable, based on the current market rate (e.g., 5% – 7%) | Standard repayment plans (e.g., 10-20 years) | Typically none |
| Federal Direct Unsubsidized Loan | Variable, based on the current market rate (e.g., 5% – 7%) | Standard repayment plans (e.g., 10-20 years) | Typically none |
| Private Student Loan | Variable or fixed, typically higher than federal loans (e.g., 7% – 12% or higher) | Variable, depending on the lender (e.g., 5-15 years) | May include origination fees, late payment fees, etc. |
Repayment Plans and Interest Rates for Summer 2024 Loans

Securing funding for your summer studies requires understanding the repayment options and interest rates associated with student loans. This section details the various repayment plans available after graduation and provides information on interest rates for summer 2024 loans, differentiating between federal and private loan options. Accurate information is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Federal Student Loan Repayment Plans
Federal student loans offer several repayment plans designed to fit different budgets and financial situations. The specific plan that best suits an individual will depend on their income, loan amount, and financial goals. Choosing the right plan can significantly impact the total amount repaid and the length of the repayment period.
Federal Student Loan Interest Rates for Summer 2024
Interest rates for federal student loans are set annually by the government. For Summer 2024, the interest rates will likely be similar to those set for the academic year. These rates vary depending on the loan type (e.g., subsidized, unsubsidized). It’s essential to check the official Federal Student Aid website for the most up-to-date interest rate information. For example, a subsidized Stafford Loan might have a fixed rate of around 5%, while an unsubsidized loan might have a slightly higher rate. These rates are typically fixed, meaning they remain constant throughout the loan’s life.
Private Student Loan Interest Rates for Summer 2024 and Lender Comparison
Private student loans offer an alternative funding source but typically come with variable interest rates that can fluctuate based on market conditions. These rates are usually higher than federal loan rates and vary significantly among lenders. For instance, Lender A might offer a rate of 7% while Lender B offers 9%, depending on the borrower’s creditworthiness and other factors. Comparing rates from multiple lenders is crucial before committing to a private loan. Consider factors beyond interest rates such as fees, repayment terms, and customer service when comparing options.
Repayment Plan Comparison Table
The following table illustrates various repayment plans and their associated costs. Note that these are examples and actual costs will depend on the loan amount, interest rate, and chosen repayment plan.
| Repayment Plan | Monthly Payment (Example) | Total Interest Paid (Example) | Repayment Period (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Repayment | $300 | $5,000 | 10 years |
| Extended Repayment | $200 | $7,000 | 20 years |
| Graduated Repayment | $200 (increasing over time) | $6,500 | 10 years |
| Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) | Variable (based on income) | Variable | 20-25 years |
Budgeting and Financial Planning for Summer Loans
Securing a student loan for the summer can significantly ease financial burdens, but effective budgeting is crucial to avoid accumulating unnecessary debt. Careful planning ensures your loan funds are used responsibly and that repayment is manageable. This section Artikels strategies for creating a realistic budget, tracking loan payments, minimizing interest, and accelerating repayment.
Creating a Realistic Budget
Developing a comprehensive budget involves carefully listing all anticipated income and expenses. Start by estimating your summer income from part-time jobs, internships, or other sources. Then, list all your anticipated expenses, categorizing them into necessities (rent, groceries, utilities) and discretionary spending (entertainment, dining out). Remember to allocate a specific amount for your student loan repayment. A helpful tool is a budgeting spreadsheet or app, allowing for easy tracking and analysis of your spending habits. For example, if your summer income is $3000 and your estimated expenses (excluding loan repayment) are $2000, you have $1000 available for loan repayment and any remaining discretionary spending.
Tracking Loan Payments and Managing Debt
Effective debt management begins with consistent tracking. Use a spreadsheet, budgeting app, or even a simple notebook to record all loan payments. Note the payment date, amount paid, and the remaining balance. This helps you stay organized and monitor your progress. Consider setting up automatic payments to ensure on-time repayments and avoid late fees. Regularly review your loan statements to ensure accuracy and identify any potential discrepancies. For instance, a monthly payment tracking sheet could include columns for “Date,” “Payment Amount,” “Payment Method,” and “Remaining Balance.”
Minimizing Interest Charges and Accelerating Loan Repayment
Minimizing interest charges is key to reducing the overall cost of your loan. Making extra payments whenever possible significantly reduces the principal balance and, consequently, the total interest accrued over the life of the loan. Even small additional payments can make a substantial difference over time. For example, paying an extra $50 per month on a $10,000 loan could save hundreds of dollars in interest and shorten the repayment period. Explore options for refinancing your loan if interest rates fall after you’ve secured the loan. Always prioritize paying down high-interest loans first.
Sample Budget Incorporating Student Loan Payments
This sample budget demonstrates how to incorporate student loan payments, summer expenses, and potential income. Remember to adjust the figures to reflect your individual circumstances.
| Category | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Summer Income (Part-time Job) | 2500 |
| Rent | 800 |
| Groceries | 300 |
| Utilities | 150 |
| Transportation | 100 |
| Student Loan Payment | 500 |
| Entertainment/Social | 250 |
| Savings | 400 |
Remember, this is a sample budget. Your actual budget will vary depending on your individual circumstances and spending habits.
Potential Scams and Avoiding Loan Fraud
Securing a student loan for summer courses can be a crucial step in your academic journey, but it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks involved. Unfortunately, unscrupulous individuals and organizations prey on students seeking financial assistance, employing deceptive tactics to steal money or obtain personal information. Understanding these scams and employing preventative measures is vital to protecting your financial well-being.
The landscape of student loans can be confusing, making it easy for students to fall victim to predatory lending practices and outright scams. These fraudulent schemes often involve promises of easy access to funds, exceptionally low interest rates, or guaranteed loan approvals, all designed to lure unsuspecting borrowers. It is crucial to approach loan offers with skepticism and diligence, verifying all information before committing to any agreement.
Common Student Loan Scams
Several common scams target students seeking summer loans. These include phishing emails that appear to be from legitimate lenders, requesting personal information under the guise of loan applications. Another tactic involves fraudulent websites mimicking legitimate loan providers, leading students to submit applications and personal data to criminals. Additionally, some scammers promise guaranteed loan approvals for a fee upfront, a practice that is always a red flag. Finally, there are instances of individuals posing as loan officers, contacting students directly with fraudulent loan offers.
Warning Signs of Loan Fraud and Predatory Lending
Several warning signs indicate potential loan fraud or predatory lending. High-pressure sales tactics, where you are urged to apply immediately without time to review the terms, are a significant red flag. Unusually low interest rates or fees that seem too good to be true should also raise suspicion. Loans with hidden fees or unclear terms are another major warning sign. If a lender demands payment upfront before disbursing funds, it is almost certainly a scam. Finally, a lender’s unwillingness to provide clear and concise information about the loan terms and conditions is a strong indicator of potential fraud.
Verifying the Legitimacy of Loan Offers and Lenders
To verify the legitimacy of a loan offer, begin by independently researching the lender. Check online reviews and verify the lender’s licensing and registration with relevant authorities. Compare interest rates and terms with those offered by reputable institutions. Never provide personal information until you have thoroughly verified the lender’s authenticity. Legitimate lenders will never pressure you into making a quick decision or request payment upfront. Always review the loan agreement carefully before signing, ensuring you understand all terms and conditions. If anything seems unclear or suspicious, seek a second opinion from a trusted financial advisor or counselor.
Resources for Reporting Suspected Loan Fraud
If you suspect you’ve encountered a loan scam or predatory lending practice, several resources are available to report it. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is a primary resource for reporting fraud. Your state’s attorney general’s office also handles consumer complaints, including those related to loan fraud. Additionally, you can report suspected fraud to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). These agencies investigate fraudulent activities and can provide assistance in recovering lost funds or protecting your personal information. Documenting all communication with the suspected fraudulent lender is crucial for reporting purposes.
Alternatives to Student Loans for Summer Funding
Securing funding for summer expenses doesn’t always necessitate student loans. Several viable alternatives exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Exploring these options allows students to make informed decisions about how to best finance their summer plans, potentially avoiding the long-term commitment and financial burden associated with loans.
Scholarships and Grants
Scholarships and grants represent a significant source of free money for educational expenses, including summer programs. Unlike loans, they don’t need to be repaid. Numerous organizations, from private foundations to government agencies, offer scholarships and grants based on various criteria such as academic merit, financial need, or specific talents and interests. Finding these opportunities often requires proactive searching and diligent application.
Part-Time Jobs
Working part-time during the summer is a straightforward way to earn money to cover expenses. This approach offers immediate financial support and provides valuable work experience, enhancing a student’s resume. However, the income generated may be limited depending on the available hours and wage, potentially impacting other summer activities or plans.
Summer Employment Programs
Many organizations offer structured summer employment programs specifically designed for students. These programs frequently provide valuable professional experience and mentorship opportunities, alongside a salary. Examples include internships, apprenticeships, and research assistant positions, often linked to specific fields of study.
Family Contributions
Family members may be willing to contribute financially to support summer expenses. This option avoids accumulating debt, but it’s crucial to have open and honest conversations about financial expectations and responsibilities within the family.
Savings and Existing Funds
Students who have saved money from previous earnings or received gifts can utilize these funds to cover summer costs. This method avoids debt and interest payments but requires prior planning and financial discipline.
Comparison of Funding Alternatives
| Funding Source | Advantages | Disadvantages | Example Resources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scholarships/Grants | Free money, no repayment required | Competitive application process, limited availability | Fastweb, Scholarship America, Federal Student Aid website |
| Part-Time Jobs | Immediate income, work experience | Limited income potential, may restrict other activities | Indeed, LinkedIn, local job boards |
| Summer Employment Programs | Structured experience, potential for mentorship, salary | Competitive application process, limited availability, specific skills/qualifications often required | Company websites, university career services |
| Family Contributions | Avoids debt, potentially flexible | Dependent on family resources and willingness to contribute, potential for family conflict | Open communication with family |
| Savings | Avoids debt, interest payments | Requires prior planning and saving, limited funds may be available | Personal savings accounts |
Illustrative Example
Let’s consider the case of Sarah, a college student pursuing a summer internship in graphic design. She needs additional funding to cover her living expenses and commuting costs during the summer months. This example will illustrate how she navigates the process of applying for and utilizing a summer student loan, including the financial implications of her decisions.
Sarah researches different student loan options available to her, focusing on federal loans due to their generally lower interest rates and flexible repayment plans. She determines that she needs $3,000 to cover rent, utilities, transportation, and other living expenses for the three-month summer internship.
Loan Application and Approval
Sarah applies for a federal Direct Unsubsidized Loan, as she is not eligible for subsidized loans based on her financial situation. The application process is straightforward, involving completing an online form and providing supporting documentation, such as her financial aid award letter and tax information. Her application is approved for the full $3,000, and the funds are disbursed directly to her bank account.
Expense Management and Budgeting
Sarah meticulously budgets her loan funds. She creates a detailed spreadsheet tracking her income and expenses, ensuring that she allocates sufficient funds for each category. She prioritizes essential expenses like rent and utilities, setting aside a smaller portion for entertainment and discretionary spending. By diligently tracking her expenses, she avoids overspending and manages to stay within her budget.
Repayment Plan and Interest Accrual
Sarah chooses a standard repayment plan, which requires monthly payments over a 10-year period. While this extends the repayment period, it results in lower monthly payments, making them more manageable alongside her potential future student loan payments for the academic year. However, she understands that this longer repayment period means she will pay more in interest over the life of the loan. Understanding the interest rate associated with her loan, she calculates the total interest she will pay over the 10 years and incorporates this into her long-term financial planning.
Financial Implications and Potential Pitfalls
Sarah’s successful utilization of the summer loan hinges on her responsible budgeting and financial planning. A potential pitfall could have been overspending or failing to track her expenses, leading to debt accumulation beyond her repayment capabilities. Another risk is not understanding the implications of interest accrual, which could lead to a higher total repayment amount than anticipated. However, by carefully planning and managing her finances, Sarah successfully navigates the summer loan process, utilizing the funds to support her internship and gain valuable work experience. The experience provides her with valuable financial literacy skills that will be beneficial in the future.
Final Conclusion
Successfully navigating the process of securing student loans for summer 2024 requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of the available options. Remember to carefully compare loan terms, understand the repayment implications, and budget effectively to avoid overwhelming debt. By utilizing the resources and information provided in this guide, students can make informed decisions that support their academic and personal goals without compromising their financial future. Remember to always verify the legitimacy of any loan offers and seek assistance if needed from trusted financial advisors or educational institutions.
Helpful Answers
What is the interest rate on federal student loans for summer 2024?
Interest rates for federal student loans vary depending on the loan type and are set annually. Check the official Federal Student Aid website for the most up-to-date information.
Can I use summer loans to pay for living expenses?
Generally, yes, but it’s crucial to create a realistic budget and only borrow what you need. Consider other funding options first, such as part-time jobs or scholarships.
What happens if I can’t repay my summer loan?
Failure to repay your loan can result in negative impacts on your credit score and potential collection actions. Contact your lender immediately if you anticipate difficulties with repayment to explore options like deferment or forbearance.
Are there any grace periods for summer loans?
Grace periods for repayment typically begin after you graduate or cease at least half-time enrollment. Specific details depend on your loan type and lender. Consult your loan documents for exact details.
