
Navigating the world of student loans can be daunting, especially in a state as diverse as Georgia. This guide delves into the complexities of Georgia’s student loan landscape, offering a clear understanding of available loan types, repayment options, and the overall economic impact of student debt within the state. We’ll explore both federal and private loan options, highlighting key differences in interest rates and repayment plans. Understanding these nuances is crucial for Georgia students and graduates aiming to manage their debt effectively and plan for a secure financial future.
From exploring eligibility for repayment assistance programs to examining the long-term effects of student loan debt on Georgia’s economy and workforce, this guide provides a holistic overview. We’ll also provide valuable resources and contact information for organizations offering support and guidance to borrowers throughout their journey.
Understanding Georgia’s Student Loan Landscape

Navigating the complexities of student loans in Georgia requires a clear understanding of the available options, associated costs, and repayment strategies. This section provides an overview of the key aspects of Georgia’s student loan system, aiming to equip prospective and current borrowers with essential information.
Types of Student Loans Available in Georgia
Georgia residents have access to both federal and private student loans. Federal loans, offered through the federal government, generally offer more favorable terms and protections for borrowers. These include subsidized and unsubsidized Stafford Loans, PLUS Loans for parents and graduate students, and Perkins Loans (though these are becoming less common). Private student loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks and other financial institutions and often come with higher interest rates and less borrower protection. The choice between federal and private loans depends on individual financial circumstances and creditworthiness.
Average Student Loan Debt for Georgia Graduates
The average student loan debt for Georgia graduates varies depending on the institution attended, the degree pursued, and the length of study. While precise figures fluctuate annually, data from sources like the Institute for College Access & Success (TICAS) and the Federal Reserve consistently show that Georgia graduates carry a significant amount of student loan debt, often exceeding national averages. This debt can significantly impact post-graduation financial planning and long-term economic stability. For example, a recent study might show an average debt of $30,000, but this is a broad generalization and actual figures can vary widely.
Interest Rates for Federal and Private Student Loans in Georgia
Interest rates for federal student loans are set by the government and are typically lower than those for private loans. These rates fluctuate based on market conditions and the type of loan. Private loan interest rates are determined by the lender and are often variable, meaning they can change over the life of the loan. Borrowers should carefully compare interest rates from multiple lenders before selecting a private loan. For example, a federal subsidized loan might have a fixed interest rate of 4%, while a private loan could have a variable rate starting at 7% and potentially rising higher.
Repayment Plans Offered to Georgia Student Loan Borrowrows
Federal student loans offer various repayment plans to accommodate different financial situations. These include standard repayment, graduated repayment, extended repayment, and income-driven repayment plans. Income-driven repayment plans tie monthly payments to a borrower’s income and family size, making them more manageable for those with lower incomes. Private loan repayment plans are generally less flexible and may offer fewer options than federal loans. It’s crucial for borrowers to understand the terms and conditions of their chosen repayment plan to avoid delinquency and potential negative consequences on their credit history.
Comparison of Key Features of Different Georgia Student Loan Programs
| Loan Type | Interest Rate | Repayment Options | Borrower Protections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Subsidized Stafford Loan | Variable, set by the government | Standard, Graduated, Extended, Income-Driven | Strong borrower protections, including deferment and forbearance options |
| Federal Unsubsidized Stafford Loan | Variable, set by the government | Standard, Graduated, Extended, Income-Driven | Strong borrower protections, including deferment and forbearance options |
| Federal PLUS Loan | Variable, set by the government | Standard, Extended | Borrower protections, but potentially less flexible than Stafford Loans |
| Private Student Loan | Variable or Fixed, set by the lender | Typically fewer options than federal loans | Fewer borrower protections than federal loans |
Georgia’s Student Loan Repayment Assistance Programs
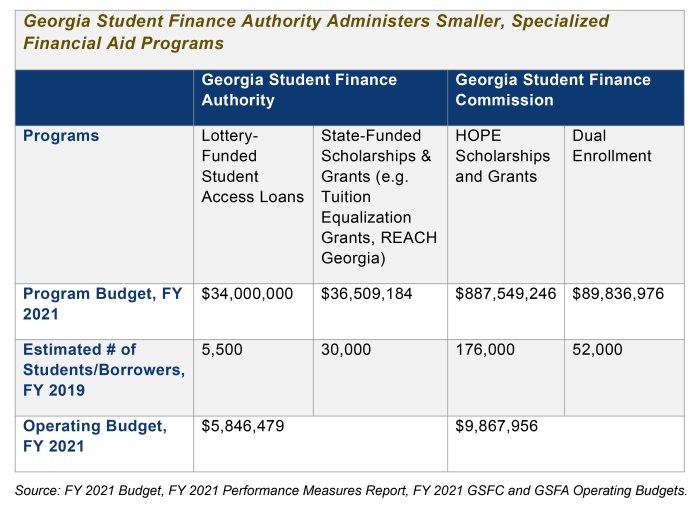
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be challenging, but Georgia offers several programs designed to provide assistance to borrowers. These programs aim to alleviate the financial burden of student loan debt and help borrowers manage their repayments effectively. Understanding the eligibility requirements, application processes, and potential challenges associated with these programs is crucial for maximizing their benefits.
Eligibility Criteria for Georgia’s Student Loan Repayment Assistance Programs
Eligibility for Georgia’s student loan repayment assistance programs varies depending on the specific program. Generally, criteria often include factors such as income level, type of loan, and employment in specific fields (e.g., public service). Some programs may prioritize borrowers facing financial hardship or those working in critical professions with a demonstrated need for assistance. Specific requirements are detailed on the program’s official website and application materials. It’s essential to carefully review these documents to determine eligibility before applying.
The Application Process for Georgia’s Student Loan Repayment Assistance Programs
The application process for Georgia’s student loan repayment assistance programs typically involves completing an application form, providing supporting documentation (such as tax returns, pay stubs, and loan details), and undergoing a review process. The length of the review process can vary depending on the program and the volume of applications. Applicants should be prepared to provide thorough and accurate information to expedite the process. Many programs utilize online portals for application submission, streamlining the process and facilitating communication between the applicant and the program administrator.
Examples of Successful Cases Where Borrowers Benefited from These Programs
While specific case details are often kept confidential due to privacy concerns, anecdotal evidence suggests that many borrowers have successfully leveraged these programs to reduce their debt burden. For example, a teacher working in a low-income school district may have qualified for a program offering loan forgiveness after a certain number of years of service. Similarly, a nurse working in a rural hospital might have benefited from a program designed to support healthcare professionals in underserved areas. These examples highlight the positive impact these programs can have on individuals pursuing careers in public service or critical fields.
Potential Challenges Faced by Borrowers Applying for Assistance
Borrowers may encounter several challenges during the application process. These can include navigating complex eligibility requirements, gathering necessary documentation, and dealing with potentially lengthy processing times. Difficulties in understanding the program guidelines or completing the application correctly can also lead to delays or rejection. Furthermore, the availability of funds for these programs can be limited, leading to competitive application processes. Understanding these potential hurdles allows borrowers to proactively address them and increase their chances of successful application.
Steps to Apply for Assistance
- Step 1: Identify the relevant Georgia student loan repayment assistance program based on your circumstances and eligibility criteria.
- Step 2: Carefully review the program guidelines and requirements available on the official program website.
- Step 3: Gather all necessary documentation, such as tax returns, pay stubs, and student loan information.
- Step 4: Complete the application form accurately and thoroughly, ensuring all information provided is up-to-date and correct.
- Step 5: Submit the completed application form and supporting documentation through the designated channels (typically an online portal).
- Step 6: Follow up on the application status through the program’s communication channels to track the progress of your application.
The Impact of Student Loans on Georgia’s Economy

Student loan debt significantly impacts Georgia’s economy, affecting various sectors and influencing the state’s overall economic health. The burden of repayment influences workforce participation, homeownership rates, entrepreneurial activity, and overall economic growth, creating ripple effects across the state. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective policies and support systems.
Student Loan Debt and Workforce Participation in Georgia
High levels of student loan debt can discourage graduates from pursuing certain career paths, particularly those with lower starting salaries but potentially higher long-term earning potential, such as teaching or social work. The weight of repayment can also lead to delayed entry into the workforce as graduates prioritize paying down debt before committing to full-time employment. This can reduce the overall workforce participation rate and limit Georgia’s access to a skilled workforce in various sectors. Furthermore, the stress associated with managing student loan debt can negatively impact productivity and job performance among employed graduates.
Student Loan Debt and Homeownership Rates in Georgia
The substantial monthly payments associated with student loan debt often compete with other significant financial commitments, such as saving for a down payment on a house. This makes homeownership more challenging for many Georgia residents burdened with student loan repayments, impacting their ability to build wealth and contribute to the stability of their communities. The reduced homeownership rates can also indirectly affect the housing market, potentially slowing down growth and reducing property tax revenues for the state. Data comparing homeownership rates among Georgia residents with and without significant student loan debt would highlight this disparity.
Student Loan Debt and Entrepreneurship in Georgia
While some argue that student loan debt can fuel entrepreneurship by providing graduates with the skills and knowledge needed to start businesses, the reality is often more complex. The significant financial burden of loan repayments can deter graduates from taking the financial risks associated with starting a business. Many aspiring entrepreneurs may choose more stable, albeit potentially less fulfilling, employment options to prioritize debt repayment. This can limit the growth of small businesses and stifle innovation within Georgia’s economy. Studies comparing entrepreneurial rates among graduates with varying levels of student loan debt would provide further insight into this relationship.
Comparison of Georgia’s Student Loan Debt Impact with Other States
Comparing Georgia’s economic impact of student loan debt to other states requires analyzing various economic indicators such as workforce participation rates, homeownership rates, entrepreneurial activity, and per capita income. States with similar demographics and economic structures should be selected for a more meaningful comparison. Data from the U.S. Census Bureau, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, and other relevant sources would be crucial for this comparative analysis. A detailed analysis could reveal whether Georgia’s situation is more or less severe than in comparable states and identify potential areas for improvement.
Graphical Representation of Student Loan Debt and Economic Indicators in Georgia
A scatter plot would effectively illustrate the relationship between student loan debt and key economic indicators in Georgia. The x-axis would represent the average student loan debt per borrower in Georgia (data from the Federal Reserve or the Department of Education), while the y-axis would represent various economic indicators, such as workforce participation rate, homeownership rate, and the number of new businesses started. Each data point would represent a specific year, with the data collected from reliable sources such as the U.S. Census Bureau and the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The graph’s title would be “Correlation between Student Loan Debt and Economic Indicators in Georgia (Year X to Year Y)”. The axes would be clearly labeled with units, and a trendline could be added to show the overall correlation. The graph would visually demonstrate the potential negative impact of rising student loan debt on Georgia’s economy.
Resources and Support for Georgia Student Loan Borrowers
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be challenging. Fortunately, numerous resources and support systems exist in Georgia to help borrowers manage their debt effectively and make informed financial decisions. This section details the available support, including counseling services, government assistance, financial literacy programs, and the advantages of seeking professional financial guidance.
Reputable Student Loan Counseling Organizations in Georgia
Several non-profit organizations offer free or low-cost student loan counseling services in Georgia. These organizations provide guidance on repayment plans, debt management strategies, and financial literacy resources. Choosing a reputable organization is crucial to ensure you receive accurate and unbiased advice. Consider organizations accredited by the National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC) or other reputable accrediting bodies. These organizations typically offer personalized counseling sessions and workshops.
Contact Information for Relevant Georgia Government Agencies
The Georgia Student Finance Commission (GSFC) is the primary state agency responsible for administering student aid programs and providing resources to borrowers. They can offer information on repayment options, available programs, and potential assistance. The federal government also plays a significant role. The Federal Student Aid website provides comprehensive information on federal student loan programs and repayment options.
Georgia Student Finance Commission: [Insert Phone Number Here], [Insert Email Address Here], [Insert Website Address Here]
Federal Student Aid: [Insert Website Address Here], [Insert Phone Number for Federal Student Aid Here (if applicable)]
Financial Literacy Resources for Georgia Students and Borrowers
Georgia offers various financial literacy resources to help students and borrowers understand personal finance principles and make informed decisions about managing student loan debt. Many community colleges, universities, and non-profit organizations offer workshops, seminars, and online resources focused on budgeting, debt management, and financial planning. These resources often include practical tools and strategies to help borrowers create a realistic repayment plan and improve their financial well-being. The GSFC may also offer or direct you to such resources.
Benefits of Seeking Professional Financial Advice Regarding Student Loans
Seeking professional financial advice can significantly benefit Georgia student loan borrowers. A financial advisor can provide personalized guidance tailored to individual circumstances, helping borrowers navigate complex repayment options, explore debt consolidation strategies, and develop a long-term financial plan. This personalized approach can lead to better debt management, reduced stress, and improved financial outcomes. They can also help you understand the implications of different repayment plans on your credit score and overall financial health. The cost of professional advice should be weighed against the potential long-term benefits.
Resource Guide
This guide provides contact information and website addresses (represented textually, not as active links) for accessing further assistance.
Georgia Student Finance Commission Website: [Insert Website Address Here (text only)]
Federal Student Aid Website: [Insert Website Address Here (text only)]
National Foundation for Credit Counseling Website: [Insert Website Address Here (text only)]
Future Trends in Georgia Student Loan Policies
Georgia’s student loan landscape is dynamic, constantly evolving under the influence of shifting demographics, economic conditions, and changes in both state and federal legislation. Predicting the future with certainty is impossible, but analyzing current trends and potential pressures allows us to anticipate likely developments in the coming years. These predictions consider Georgia’s unique economic and social context, comparing it to similar states and factoring in the impact of national policy changes.
Georgia’s student loan policies are likely to face increasing pressure to address the growing burden of student loan debt on its residents. This pressure will stem from various sources, including rising tuition costs, a changing job market, and increasing awareness of the long-term financial consequences of student loans. Simultaneously, opportunities exist to improve access to affordable higher education and create more effective repayment assistance programs.
Potential Policy Changes in Georgia
Several potential changes to Georgia’s student loan policies are foreseeable. These include expansions of existing grant programs to increase affordability, the implementation of income-driven repayment plans mirroring or exceeding federal options, and the creation of targeted loan forgiveness programs for specific professions crucial to the state’s economy, such as healthcare and technology. Furthermore, increased transparency and consumer protection measures regarding private student loan options are also likely. For example, Georgia might adopt stricter regulations on predatory lending practices, mirroring policies seen in states like California, which has robust protections for borrowers.
Challenges and Opportunities in Georgia’s Student Loan Debt Landscape
A significant challenge lies in balancing the need for accessible higher education with the fiscal responsibility of managing state-funded programs. The state will need to find innovative funding solutions and carefully evaluate the long-term financial implications of any new initiatives. An opportunity lies in leveraging partnerships between the state, higher education institutions, and private sector employers to create apprenticeship programs and other alternative pathways to employment that reduce reliance on student loans. States like Oregon, with its strong emphasis on apprenticeships and vocational training, provide a potential model.
Comparison with Similar States
Comparing Georgia’s policies to those of states with similar demographics, such as North Carolina and South Carolina, reveals areas for improvement. These states often demonstrate variations in the scope and generosity of their state-level grant programs, income-driven repayment options, and loan forgiveness initiatives. Analyzing best practices from these states could inform Georgia’s future policy decisions. For example, if North Carolina implements a successful program to address loan forgiveness for teachers, Georgia could consider adopting a similar approach tailored to its specific needs.
Impact of Federal Student Loan Policy Changes
Changes in federal student loan policies, such as modifications to income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness programs, directly impact Georgia borrowers. For instance, a significant expansion of the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program at the federal level would immediately benefit many Georgia residents employed in public service. Conversely, reductions in federal funding for grant programs would necessitate adjustments in state-level programs to mitigate the negative effects on Georgia’s students. The recent changes to the PSLF program, expanding eligibility criteria, illustrate the direct influence of federal action on Georgia borrowers.
Potential Impact of Proposed State and Federal Legislation
Proposed legislation at both the state and federal levels could significantly reshape Georgia’s student loan landscape. For example, a state bill proposing increased funding for need-based grants would directly increase access to higher education for low-income students. Similarly, federal legislation aimed at strengthening consumer protections in the student loan market would affect Georgia borrowers by improving transparency and reducing the risk of predatory lending. The potential passage of the “Fair Access to Student Loans Act” (hypothetical example) could significantly alter the private student loan market in Georgia, resulting in more favorable terms for borrowers.
End of Discussion
Successfully managing student loan debt requires careful planning, understanding of available resources, and proactive engagement with available assistance programs. This guide has aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of the student loan landscape in Georgia, empowering borrowers with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed decisions. By understanding the various loan types, repayment options, and the economic implications of student debt, Georgians can navigate this crucial aspect of their financial lives more effectively and confidently plan for the future. Remember to actively seek assistance when needed and utilize the many resources available to support your financial well-being.
Helpful Answers
What is the average student loan debt in Georgia?
The average student loan debt for Georgia graduates varies depending on the degree pursued and the institution attended. Researching specific averages for different programs and schools is recommended.
Can I consolidate my federal and private student loans in Georgia?
Federal student loans can often be consolidated through the federal government’s programs. Private loans typically cannot be consolidated with federal loans, and consolidation options for private loans may vary depending on the lender.
What happens if I default on my student loans in Georgia?
Defaulting on student loans can have severe consequences, including damage to your credit score, wage garnishment, and potential legal action. Contact your loan servicer immediately if you are facing difficulties making payments to explore options like deferment or forbearance.
Are there income-driven repayment plans available for Georgia student loan borrowers?
Yes, several income-driven repayment plans are available for federal student loans. These plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. Eligibility criteria vary by plan.
