Navigating the complexities of federal student loans can feel overwhelming, but understanding the resources available through studentloans.gov is key to successful repayment. This website serves as the central hub for managing your federal student loans, offering a range of tools and services designed to guide you through the entire process, from application to repayment and beyond. This guide will explore the key features and functionalities of studentloans.gov, empowering you to confidently manage your student loan debt.
From exploring various repayment plans tailored to individual financial situations to understanding loan forgiveness programs and avoiding potential scams, we will delve into the practical aspects of utilizing this vital government resource. We aim to provide a clear and concise overview, equipping you with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate your student loan journey effectively.
Understanding the Website
StudentAid.gov, now consolidated into studentloans.gov, serves as the central hub for managing federal student loans in the United States. This website provides a comprehensive suite of tools and resources for borrowers to understand, manage, and repay their student loan debt. Its primary goal is to streamline the process, offering a single point of access for all federal student loan-related activities.
Studentloans.gov offers a range of services designed to assist borrowers throughout the entire loan lifecycle. These services include accessing loan details, making payments, exploring repayment plans, applying for deferment or forbearance, and consolidating loans. The site also provides educational resources on loan management, financial literacy, and navigating the complexities of student loan repayment. The website aims to be user-friendly and informative, guiding borrowers through the often-confusing process of managing their federal student loans.
Website Interface and Navigation
The website’s user interface is generally considered straightforward and intuitive, although some users may find certain aspects challenging depending on their technological proficiency. Navigation relies primarily on clear menus and a logical organizational structure. Users can easily access their account information, payment options, and loan details through clearly labeled buttons and links. However, the sheer volume of information available on the site can sometimes make finding specific information challenging for first-time users. A robust search function and frequently asked questions (FAQ) section help to mitigate this. The visual design is clean and uncluttered, using a consistent color scheme and font style to enhance readability. The website is responsive, adapting to various screen sizes, making it accessible across different devices (desktops, tablets, and smartphones).
User Roles and Access Levels
Studentloans.gov caters to several user roles, each with varying levels of access. Borrowers have full access to their loan information, payment options, and account settings. Servicers, the companies that manage student loans on behalf of the government, have access to borrower data to process payments and manage accounts. Government officials and authorized personnel have broader access for administrative tasks and oversight. The website employs robust security measures to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of user data, protecting sensitive personal and financial information. Access is controlled through secure login credentials and multi-factor authentication where applicable.
Comparison to Similar Government Websites
Compared to other government websites, studentloans.gov generally fares well in terms of user-friendliness and functionality. While some government websites can be notoriously difficult to navigate, studentloans.gov strives for a more intuitive experience. However, it’s worth noting that the complexity of federal student loan programs inherently makes the website more intricate than some other government online services. The website’s design and functionality are comparable to other federal online portals, employing similar security protocols and accessibility features. Continuous improvements and updates aim to enhance the overall user experience and keep pace with evolving technological standards and user feedback.
Loan Repayment Options
Understanding your repayment options is crucial for successfully managing your student loans. StudentLoans.gov offers a variety of repayment plans designed to fit different financial situations and budgets. Choosing the right plan can significantly impact your monthly payments and the total amount of interest you pay over the life of your loan.
Several repayment plans are available, each with its own set of features and eligibility requirements. These plans fall into two main categories: standard repayment plans and income-driven repayment plans. Standard plans offer fixed monthly payments over a set period, while income-driven plans adjust your payments based on your income and family size. Carefully considering your financial circumstances and long-term goals will help you select the most appropriate plan.
Standard Repayment Plan
The Standard Repayment Plan is the default plan for most federal student loans. It involves fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period. While this plan results in the shortest repayment timeline, it often leads to higher monthly payments compared to income-driven plans. For example, a $30,000 loan at a 5% interest rate would have a monthly payment of approximately $316. This plan is suitable for borrowers who have a stable income and prefer a shorter repayment period despite higher monthly payments.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
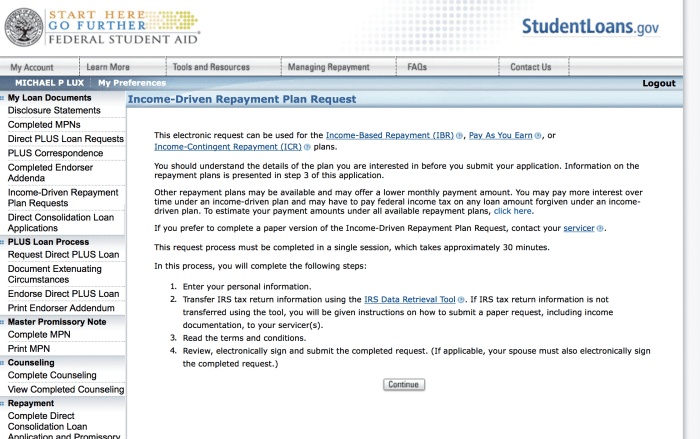
Income-driven repayment plans are designed to make student loan repayment more manageable by basing your monthly payments on your income and family size. These plans generally offer lower monthly payments than standard repayment plans, but they extend the repayment period, potentially leading to higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. There are several types of income-driven repayment plans, each with its own eligibility requirements and payment calculation methods.
Applying for Income-Driven Repayment
Applying for an income-driven repayment plan typically involves these steps:
- Log in to your StudentLoans.gov account.
- Navigate to the “My Loans” section.
- Select the loan(s) you wish to enroll in an income-driven repayment plan.
- Choose the specific income-driven repayment plan you want (e.g., ICR, PAYE, REPAYE,IBR).
- Provide your income and family size information. You’ll likely need to submit tax returns or other documentation to verify your income.
- Review and submit your application. You’ll receive confirmation once your application is processed.
Examples of Repayment Plan Impacts
Let’s consider a borrower with a $40,000 loan at a 6% interest rate. Under a Standard Repayment Plan (10 years), their monthly payment would be approximately $422, and they would pay around $10,660 in interest. Under an income-driven plan, assuming a lower monthly payment of $250, the repayment period would be significantly longer (potentially 20-25 years), and the total interest paid would likely be much higher, potentially exceeding $20,000. This illustrates the trade-off between lower monthly payments and increased total interest paid.
Comparison of Income-Driven Repayment Plans
The following table compares key features of several income-driven repayment plans. Note that eligibility requirements and payment calculation methods can change, so it’s always best to consult the official StudentLoans.gov website for the most up-to-date information.
| Plan Name | Eligibility Requirements | Payment Calculation Method | Maximum Repayment Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Income-Based Repayment (IBR) | Federal student loans; meets specific income requirements | 15% of discretionary income | 25 years |
| Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR) | Federal student loans; meets specific income requirements | Based on income, family size, and loan amount | 25 years |
| Pay As You Earn (PAYE) | Federal student loans disbursed after June 30, 2014; meets specific income requirements | 10% of discretionary income | 20 years |
| Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) | Most federal student loans; meets specific income requirements | 10% of discretionary income | 20 or 25 years, depending on loan type |
Loan Forgiveness and Cancellation Programs

Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be daunting. Fortunately, several federal programs offer loan forgiveness or cancellation opportunities for borrowers who meet specific criteria. Understanding these programs and their eligibility requirements is crucial for borrowers seeking to reduce or eliminate their student loan debt. This section Artikels key programs, their eligibility requirements, and the application process.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program forgives the remaining balance on your Direct Loans after you’ve made 120 qualifying monthly payments under a qualifying repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
Eligibility criteria include:
- Employment by a qualifying government organization or non-profit organization.
- Repayment under a qualifying repayment plan (e.g., Income-Driven Repayment plan).
- Consolidation of all federal student loans into a Direct Consolidation Loan.
- Making 120 qualifying monthly payments.
The application process involves:
- Confirming employment with a qualifying employer.
- Submitting an Employment Certification Form annually.
- Submitting a PSLF application after making 120 qualifying payments.
Examples of professions that qualify include teachers, nurses, social workers, and government employees.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program
This program provides forgiveness of up to $17,500 on Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans, and Federal Stafford Loans.
Eligibility criteria are:
- Must have taught full-time for five complete and consecutive academic years in a low-income school or educational service agency.
- Must meet the requirements for a low-income school or educational service agency, as defined by the Department of Education.
The application process involves completing and submitting the Teacher Loan Forgiveness application.
This program benefits teachers committed to serving in underserved communities.
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans and Forgiveness
Several IDR plans, such as the Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) plans, can lead to loan forgiveness after a set period of time (typically 20 or 25 years), depending on the plan and your income.
Eligibility criteria include:
- Having federal student loans.
- Meeting the income requirements for the chosen IDR plan.
- Making timely payments according to the IDR plan’s terms.
The application process involves selecting an IDR plan and submitting the necessary documentation to your loan servicer.
These plans offer relief to borrowers with lower incomes, potentially leading to loan forgiveness after many years of repayment.
Other Loan Forgiveness and Cancellation Programs
Additional programs exist, often targeting specific circumstances or professions. These programs may have unique eligibility requirements and application processes. It’s crucial to thoroughly research these options through the official Department of Education website to determine eligibility. Examples could include programs related to specific types of disabilities or service in the military. Always refer to the official guidelines for the most up-to-date information.
Managing Student Loan Debt
Successfully navigating student loan repayment requires proactive planning and consistent effort. Understanding your loan details, developing a realistic budget, and employing effective debt management strategies are crucial for avoiding delinquency and ultimately achieving financial freedom. This section Artikels key strategies to help you manage your student loan debt effectively.
Budgeting and Financial Planning for Loan Repayment
Creating a comprehensive budget is paramount to successful student loan repayment. A well-structured budget allows you to visualize your income and expenses, ensuring that your loan payments are factored into your overall financial picture. This prevents unexpected shortfalls and helps you prioritize loan repayment alongside other essential expenses. Failing to budget adequately can lead to missed payments, negatively impacting your credit score and potentially resulting in default.
Sample Budget Incorporating Student Loan Payments
A sample budget might look like this:
| Income | Amount |
|---|---|
| Monthly Salary | $3000 |
| Expenses | Amount |
| Rent/Mortgage | $1000 |
| Utilities | $200 |
| Groceries | $300 |
| Transportation | $150 |
| Student Loan Payment | $350 |
| Other Expenses (Entertainment, Savings, etc.) | $1000 |
This example demonstrates a balanced budget where student loan payments are integrated without compromising essential living expenses. Remember to tailor your budget to your specific income and expenses.
Strategies for Effective Student Loan Debt Management
Several strategies can significantly improve your ability to manage student loan debt. These include exploring different repayment plans, considering income-driven repayment options, and prioritizing high-interest loans. Furthermore, actively monitoring your loan accounts and communicating with your loan servicer can help you avoid potential issues.
Avoiding Delinquency and Default on Student Loans
Delinquency and default on student loans have serious consequences, including damage to your credit score, wage garnishment, and potential legal action. To avoid these outcomes, consistently make on-time payments, stay in contact with your loan servicer, and proactively address any financial difficulties you may encounter. Consider exploring options like deferment or forbearance if you face temporary financial hardship, but remember these options may accrue interest. Proactive communication with your loan servicer is key to finding solutions before the situation escalates.
The Application Process

Applying for federal student loans through StudentAid.gov is a multi-step process that requires careful attention to detail. Understanding the requirements and potential hurdles can significantly improve your chances of a smooth and successful application. This section will guide you through the process, outlining the necessary steps, documentation, and potential challenges.
Steps Involved in the Application Process
The application process begins with completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). This form collects information about your financial situation and is used to determine your eligibility for federal student aid, including loans. Following FAFSA submission, you’ll receive a Student Aid Report (SAR) summarizing your information. Based on your SAR, you may be offered federal student loans. Accepting the offered loans involves completing a Master Promissory Note (MPN), which is a legal agreement outlining your responsibilities as a borrower. Finally, your school will certify your loan amount and disburse the funds directly to your account.
Required Documentation
The primary document required is the FAFSA form. This form requires information about you, your parents (if you are a dependent student), your income, assets, and other financial details. Accurate and complete information is crucial for a successful application. You’ll also need your Social Security number, Federal Tax Return information (yours and your parents’, if applicable), and your driver’s license or state identification. Additional documentation might be requested depending on your individual circumstances, such as proof of citizenship or residency.
Potential Challenges During the Application Process
Several challenges can arise during the application process. One common issue is incomplete or inaccurate information on the FAFSA, leading to delays or rejection. Technical difficulties with the StudentAid.gov website are another potential problem. Errors in providing financial information or misunderstanding the terms and conditions of the loan can also cause delays or complications. Finally, students may encounter challenges navigating the complex terminology and procedures involved in the application process. For example, a student might struggle to understand the difference between subsidized and unsubsidized loans, leading to an ill-informed borrowing decision.
Flowchart Illustrating the Application Process
Imagine a flowchart with the following steps:
1. Start: The process begins with the decision to apply for federal student loans.
2. Complete the FAFSA: This involves gathering the necessary financial information and submitting the form online.
3. Receive the SAR: The Student Aid Report summarizes your information and eligibility.
4. Review Loan Offer: You review the offered loan amount and terms.
5. Accept Loan Offer and Sign MPN: You accept the loan offer and sign the Master Promissory Note.
6. School Certification: Your school certifies your loan amount.
7. Loan Disbursement: The funds are disbursed to your student account.
8. End: The application process is complete.
Each step connects to the next in a linear fashion, representing the sequential nature of the application. A “No” branch could be added to step 4 (Review Loan Offer) leading back to step 2 if the applicant decides to make changes to their FAFSA or explore other financial aid options. Similarly, a “No” branch could exist at step 5 (Accept Loan Offer and Sign MPN) if the student decides against accepting the loan. These “No” branches represent potential deviations from the standard process.
Understanding Interest Rates and Fees
Understanding the interest rates and fees associated with your federal student loans is crucial for effectively managing your debt. This section will clarify how these costs are determined and their impact on your overall repayment. Knowing this information empowers you to make informed decisions about your borrowing and repayment strategy.
Student loan interest rates are determined by a combination of factors. For federal student loans, the interest rate is typically fixed for the life of the loan and is set by Congress annually. The rate varies depending on the loan type (e.g., subsidized, unsubsidized, PLUS loans), the loan’s disbursement date, and sometimes the borrower’s creditworthiness (for PLUS loans). For example, a subsidized Stafford loan might have a lower interest rate than an unsubsidized Stafford loan or a PLUS loan because of the government’s interest subsidy during certain periods. The specific rate for each loan type is published annually by the Department of Education and is available on the studentloans.gov website.
Federal Student Loan Fees
Several fees may be associated with federal student loans. These fees are typically a percentage of the loan amount and are deducted from the loan disbursement. Understanding these fees is essential for accurately calculating your total borrowing costs.
One common fee is the loan origination fee. This fee helps cover the administrative costs of processing your loan application and disbursing the funds. The percentage of this fee varies depending on the loan type and the year the loan is disbursed. For instance, in a given year, the origination fee might be 1.057% for a subsidized Stafford loan and 1.057% for an unsubsidized Stafford loan, while a PLUS loan might have a slightly higher origination fee. This fee is paid upfront and reduces the amount of money you actually receive.
Impact of Interest Rates and Fees on Total Loan Cost
Interest rates and fees significantly influence the total cost of your student loan. Even seemingly small differences in interest rates can accumulate substantial additional costs over the loan’s repayment period. Consider this example:
Let’s say you borrow $10,000 with a 5% interest rate and a 1% origination fee. The origination fee would be $100 ($10,000 * 0.01), leaving you with $9,900. Over a 10-year repayment period, the total interest paid would be approximately $2,700. This means your total repayment would be around $12,600 ($9,900 + $2,700). However, if the interest rate were 7%, the total interest paid would increase to approximately $3,800, resulting in a total repayment of around $13,700. A seemingly small 2% difference in interest rate leads to an extra $1,100 in interest paid.
Calculating Total Loan Cost
Calculating the total cost of a loan involves adding the principal loan amount, interest accrued, and any fees. While complex amortization schedules are used to calculate the precise monthly payment and total interest, a simplified calculation can help you understand the overall impact.
Total Loan Cost = Principal Loan Amount + Total Interest Paid + Total Fees
To accurately determine your total interest paid and total loan cost, you can use online loan calculators or contact your loan servicer. These tools will consider the loan amount, interest rate, repayment term, and any fees to provide a precise estimate of your total repayment amount.
Resources and Support

Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be challenging. Fortunately, StudentAid.gov offers a comprehensive suite of resources and support services designed to guide borrowers through every step of the process, from understanding repayment options to managing their debt effectively. These resources are designed to empower borrowers with the knowledge and tools they need to make informed decisions and achieve their financial goals.
StudentAid.gov provides several avenues for accessing assistance and information. These include direct contact with customer service representatives, access to a wealth of online educational materials, and a frequently asked questions section addressing common borrower concerns. The goal is to provide a user-friendly and supportive experience for all borrowers.
Customer Support and Technical Assistance
StudentAid.gov offers multiple ways to contact customer support. Borrowers can access help through a dedicated phone line, email, or live chat. The website also provides detailed FAQs and troubleshooting guides to address common technical issues. Contact information is readily available on the StudentAid.gov website, typically found under a “Contact Us” or “Help” section. These resources are available during standard business hours, and extended hours may be offered during peak periods.
Educational Materials on Financial Literacy and Loan Management
StudentAid.gov provides a variety of educational resources to help borrowers understand and manage their student loans effectively. These materials cover topics such as budgeting, credit management, and understanding different repayment plans. The resources are presented in various formats, including articles, videos, and interactive tools, catering to diverse learning styles. This commitment to financial literacy aims to equip borrowers with the skills necessary to make sound financial decisions and avoid potential pitfalls. For example, there may be videos explaining the differences between income-driven repayment plans and standard repayment plans, with clear examples of how each plan might affect a borrower’s monthly payment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding common concerns is crucial for effective support. The following are some frequently asked questions and their corresponding answers. These answers are simplified for clarity and may not encompass every possible scenario. It’s always advisable to consult the official StudentAid.gov website for the most up-to-date and comprehensive information.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How can I find my loan servicer? | Your loan servicer information is accessible through your StudentAid.gov account. |
| What are my repayment options? | Several repayment plans are available, including standard, graduated, extended, and income-driven repayment. The best option depends on your individual financial situation. |
| What is loan forgiveness? | Loan forgiveness programs, such as Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), may eliminate remaining loan balances under specific conditions, such as working in public service for a qualifying period. |
| How do I consolidate my loans? | Loan consolidation combines multiple federal student loans into a single loan with a new repayment plan. The process is managed through StudentAid.gov. |
| What happens if I miss a payment? | Missing payments can result in late fees, damage to your credit score, and potential loan default. Contact your loan servicer immediately if you anticipate difficulties making a payment. |
Potential Issues and Scams
Navigating the student loan system can present challenges, and unfortunately, borrowers are sometimes targeted by fraudulent activities. Understanding potential problems and recognizing scams is crucial for protecting your financial well-being. This section will Artikel common issues, explain how to identify and avoid scams, and detail the steps to take if you suspect fraudulent activity.
Common Issues Borrowers Face Using StudentLoans.gov
StudentLoans.gov, while a valuable resource, isn’t immune to technical glitches or user-related difficulties. For example, website outages can temporarily prevent access to account information. Incorrect or incomplete information provided during the application process can lead to delays in loan disbursement or processing. Difficulty understanding complex loan terms and repayment options is another common issue. Finally, changes in personal circumstances, such as job loss or unexpected medical expenses, can impact a borrower’s ability to make timely payments.
Recognizing and Avoiding Student Loan Scams
Scammers often prey on borrowers’ anxieties about student loan debt, using deceptive tactics to steal personal information or money. They may falsely claim to be affiliated with the Department of Education or other government agencies. They might offer loan consolidation services at unreasonably low rates or promise loan forgiveness without meeting the eligibility requirements. Be wary of unsolicited emails, phone calls, or text messages offering loan modification or debt relief services. Legitimate communication from the Department of Education or your loan servicer will typically be initiated by you or through official channels.
Examples of Fraudulent Activities
Several fraudulent activities target student loan borrowers. One common tactic involves phishing emails that appear to be from a legitimate source, but contain links to malicious websites designed to steal login credentials. Another scam involves fraudulent companies offering loan forgiveness or consolidation services for a fee, often promising results that are impossible to deliver. Some scammers create fake websites mimicking the official StudentLoans.gov site to trick borrowers into providing sensitive information. Finally, there are instances of individuals posing as loan servicers to obtain personal and financial details.
Steps to Take if You Suspect a Scam
If you suspect you are a victim of a student loan scam, take immediate action. First, do not respond to any suspicious communications. Second, report the incident to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at ftc.gov. Third, change your passwords for all online accounts, especially those related to your student loans. Fourth, contact your loan servicer directly through official channels to verify any communication you’ve received. Fifth, monitor your credit report for any unauthorized activity. Finally, consider filing a police report, particularly if you’ve suffered financial loss.
Final Review
Successfully managing your federal student loans requires proactive engagement and a thorough understanding of the available resources. Studentloans.gov provides a comprehensive platform to access crucial information, manage your account, and explore various repayment options. By utilizing the tools and resources discussed, you can take control of your student loan debt and pave the way for a financially secure future. Remember to regularly check the website for updates and utilize the available support services to address any questions or concerns you may encounter along the way.
Essential Questionnaire
What happens if I miss a student loan payment?
Missing payments can lead to delinquency, negatively impacting your credit score and potentially resulting in fees and collection actions. Contact your loan servicer immediately if you anticipate difficulties making a payment to explore options like forbearance or deferment.
How do I consolidate my student loans?
Studentloans.gov offers a direct consolidation loan program that combines multiple federal student loans into a single loan with a new repayment plan. The process involves applying online through the website.
Can I change my repayment plan?
Yes, you can often switch between repayment plans. Studentloans.gov provides information on available plans and the process for changing your plan. Factors such as income and loan type may influence eligibility.
Where can I find my loan servicer’s contact information?
Your loan servicer’s contact information is typically available on your studentloans.gov account dashboard.
