
Navigating the complexities of student loans can feel overwhelming, especially within the specific context of a state like Missouri. This guide offers a clear and concise overview of Missouri’s student loan landscape, covering various programs, repayment options, and the overall impact on the state’s economy. We’ll explore the financial realities facing Missouri graduates and provide practical resources to help borrowers manage their debt effectively.
From understanding eligibility criteria for state-sponsored programs to comparing interest rates and repayment plans, we aim to demystify the process. We’ll also delve into the broader economic implications of student loan debt in Missouri, examining its influence on individual financial well-being and the state’s overall economic growth. This comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for current students, recent graduates, and anyone seeking a better understanding of student loans in the Show-Me State.
Repayment Options and Forgiveness Programs

Navigating student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, but understanding the available options and potential forgiveness programs is crucial for Missouri borrowers. This section Artikels the various repayment plans and forgiveness opportunities to help you manage your student loan debt effectively. Careful consideration of your individual financial circumstances is key to selecting the most suitable plan.
Standard Repayment Plan
The standard repayment plan is a fixed monthly payment spread over 10 years. This plan offers predictable payments but may result in higher total interest paid compared to other plans. It’s a good option for borrowers who can comfortably afford the higher monthly payments and want to pay off their loans quickly.
Extended Repayment Plan
For borrowers who find the standard 10-year plan too burdensome, the extended repayment plan offers longer repayment periods, typically up to 25 years. This lowers monthly payments but increases the total interest paid over the life of the loan. It’s beneficial for those with lower incomes or higher loan balances.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans in Missouri
Missouri borrowers have access to several income-driven repayment (IDR) plans designed to make monthly payments more manageable based on income and family size. These plans typically recalculate payments annually. Specific plans offered may include Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR). The terms and eligibility requirements vary slightly between these plans. Choosing the right IDR plan requires careful comparison of the long-term implications, including potential forgiveness after a set period of payments.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program
The PSLF program offers complete loan forgiveness for borrowers working full-time in qualifying public service jobs, such as government or non-profit organizations, after making 120 qualifying monthly payments under an IDR plan. This program requires diligent tracking of payments and employment verification. Borrowers must ensure their loans are eligible and that their payments consistently meet the program’s criteria. A common pitfall is having loans not consolidated under the Direct Loan program.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program
This program offers forgiveness for teachers who meet specific requirements, including teaching full-time for five consecutive academic years in a low-income school or educational service agency. The amount of forgiveness is dependent on the type and amount of loans. Eligibility criteria include teaching in a designated low-income school or educational service agency and maintaining full-time employment status.
Application Process for Loan Forgiveness Programs
The application process for loan forgiveness programs generally involves submitting documentation to verify employment, income, and loan details. It’s crucial to carefully review the specific requirements for each program and maintain accurate records throughout the repayment period. Incomplete or inaccurate applications can significantly delay the forgiveness process. It is strongly recommended to thoroughly understand the requirements and deadlines for each program to ensure timely application and eligibility.
Student Loan Debt in Missouri
Understanding the landscape of student loan debt in Missouri is crucial for prospective students and graduates alike. This section provides a statistical overview of student loan debt in the state, comparing it to national trends and offering insights into the financial burden faced by Missourians. The data presented here is intended to inform and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their educational financing.
Missouri, like many other states, faces significant challenges related to student loan debt. The rising cost of higher education, coupled with limited financial aid options, contributes to a growing number of graduates burdened by substantial debt. This section will delve into the specific details of this issue within the state.
Average Student Loan Debt for Missouri Graduates
Precise figures on the average student loan debt for Missouri graduates fluctuate slightly depending on the source and methodology used, and data collection lags. However, consistent reports indicate that Missouri graduates typically carry a debt load comparable to or slightly below the national average. While precise numbers are hard to pinpoint without specifying the year and institution type, a reasonable estimate would place the average debt somewhere between $25,000 and $35,000 for recent graduates. This range reflects the variability across different institutions and degree programs.
Percentage of Missouri Students with Student Loan Debt
A substantial percentage of Missouri students rely on loans to finance their education. While the exact figure varies year to year, it’s safe to say that a majority of college graduates in Missouri have some level of student loan debt. This high percentage underscores the need for comprehensive financial literacy programs and readily available resources to help students manage their debt effectively. Again, precise percentages are difficult to pinpoint without specifying the year and source, but a reasonable estimate places the percentage well above 50%.
Comparison of Missouri Student Loan Debt to National Averages
The student loan debt burden in Missouri generally mirrors national trends, although specific figures vary depending on the year and data source. Over the past decade, both Missouri and the nation have seen increases in average student loan debt. While Missouri may not consistently rank significantly above or below the national average, it’s important to note that the overall trend of increasing debt affects both the state and the country as a whole. A direct comparison requires accessing and analyzing specific yearly data from reliable sources like the Department of Education and other relevant research institutions.
Trends in Missouri Student Loan Debt Over Time
Analyzing trends in Missouri student loan debt over time requires consulting multiple data sources and accounting for changes in data collection methodologies. The following table provides a simplified representation of potential trends, emphasizing the general upward movement in debt levels. Note that these figures are illustrative and should not be considered precise due to the complexities of data collection and reporting.
| Year | Average Debt (Estimate) | Percentage of Graduates with Debt (Estimate) | National Average Debt (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | $28,000 | 60% | $29,000 |
| 2015 | $30,000 | 65% | $31,000 |
| 2018 | $33,000 | 70% | $34,000 |
| 2021 | $35,000 | 75% | $37,000 |
Resources and Assistance for Borrowers
Navigating student loan debt can be challenging, but Missouri offers various resources and support systems to help borrowers manage their finances and explore repayment options. Understanding these resources is crucial for ensuring long-term financial well-being. This section Artikels available assistance programs and provides contact information for relevant organizations.
Available Resources for Missouri Student Loan Borrowers
Missouri provides several avenues for assistance to students and borrowers struggling with student loan debt. These resources offer guidance, counseling, and potentially debt management strategies. Effective utilization of these resources can significantly impact a borrower’s ability to successfully repay their loans.
- Missouri Attorney General’s Office: This office provides information and resources on consumer protection, including guidance on student loan scams and predatory lending practices. They can also help borrowers navigate complaints against lenders. Contact information can be found on their official website.
- Consumer Credit Counseling Services (CCCS): Non-profit organizations like CCCS offer free or low-cost credit counseling services, including assistance with developing a debt management plan and negotiating with lenders. They can help borrowers create a budget and explore options like debt consolidation or repayment plans.
- The United States Department of Education (USDOE): The federal government offers several resources and programs for student loan borrowers, including income-driven repayment plans, loan forgiveness programs, and deferment options. The USDOE website is a comprehensive source of information on federal student loans.
- Student Loan Servicing Companies: Your specific loan servicer can provide personalized information about your loan terms, repayment options, and available assistance programs. Contact information for your servicer is typically found on your monthly loan statement.
Contact Information for Relevant Organizations
Accessing the right resources is key to effectively managing student loan debt. Below is a list of important contact details: Remember to always verify contact information on the organization’s official website.
| Organization | Website (Example – replace with actual URLs) | Phone Number (Example – replace with actual numbers) |
|---|---|---|
| Missouri Attorney General’s Office | www.ago.mo.gov | (573) 751-3321 |
| National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC) (Example – find a Missouri-based CCCS) | www.nfcc.org | (800) 388-2227 |
| Federal Student Aid (USDOE) | studentaid.gov | (800) 433-3243 |
Steps to Effectively Manage Student Loan Debt
A proactive approach is vital for successful student loan repayment. Following a structured plan can significantly reduce stress and improve financial outcomes.
- Understand Your Loans: Gather all loan documents and understand the interest rates, repayment terms, and any applicable fees.
- Create a Budget: Track your income and expenses to identify areas where you can reduce spending and allocate funds towards loan repayment.
- Explore Repayment Options: Research different repayment plans offered by your lender or the federal government, such as income-driven repayment or extended repayment plans.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are struggling to manage your debt, consider seeking guidance from a credit counselor or financial advisor.
- Prioritize Payments: Make timely payments to avoid late fees and damage to your credit score.
Impact of Student Loans on Missouri’s Economy

Student loan debt significantly impacts Missouri’s economy, affecting both individual financial well-being and broader economic growth. The substantial amount of debt held by Missourians influences consumer spending, investment in businesses, and overall economic activity. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing effective economic policies and support systems within the state.
The relationship between student loan debt and economic growth in Missouri is complex and multifaceted. High levels of student loan debt can hinder economic expansion by reducing disposable income among young adults, a demographic crucial for driving economic activity. This reduced spending power can negatively impact various sectors, from retail and hospitality to the housing market. Conversely, a highly educated workforce, even with debt, can contribute positively to innovation, productivity, and economic competitiveness. The net effect, therefore, depends on a variety of factors, including the size of the debt burden, the availability of high-paying jobs for graduates, and the overall health of the state’s economy.
Student Loan Debt’s Influence on Individual Financial Decisions
High student loan debt burdens significantly restrict individual financial decisions. Many young Missourians postpone major life milestones like homeownership, starting a family, or starting a business due to loan repayments. This delayed entry into these significant economic activities reduces overall economic activity. For example, a young couple might delay buying a house, thereby reducing demand in the housing market and slowing related economic growth. Similarly, entrepreneurs may delay launching their businesses due to the financial constraints imposed by loan repayments, potentially missing out on opportunities for job creation and economic expansion within the state. The ripple effect of these individual decisions contributes to a broader economic impact.
Economic Impacts of Student Loan Debt in Missouri
The following points illustrate the positive and negative economic impacts of student loan debt in Missouri:
- Negative Impacts:
- Reduced consumer spending: High loan repayments limit disposable income, decreasing consumer demand and slowing economic growth.
- Delayed major life purchases: Homeownership, starting a family, and business ventures are often delayed, hindering economic activity in various sectors.
- Increased financial stress and reduced economic mobility: High debt levels can lead to financial instability, hindering upward economic mobility for individuals and families.
- Potential for decreased entrepreneurial activity: The financial burden can discourage young people from starting businesses, reducing job creation and economic innovation.
- Positive Impacts:
- Increased human capital: Higher education leads to a more skilled and productive workforce, boosting long-term economic growth.
- Potential for higher earning potential: Individuals with higher education often earn more, contributing to higher tax revenues for the state.
- Economic contributions from educated workforce: A highly educated workforce drives innovation and productivity, leading to economic competitiveness.
Comparison with Other States
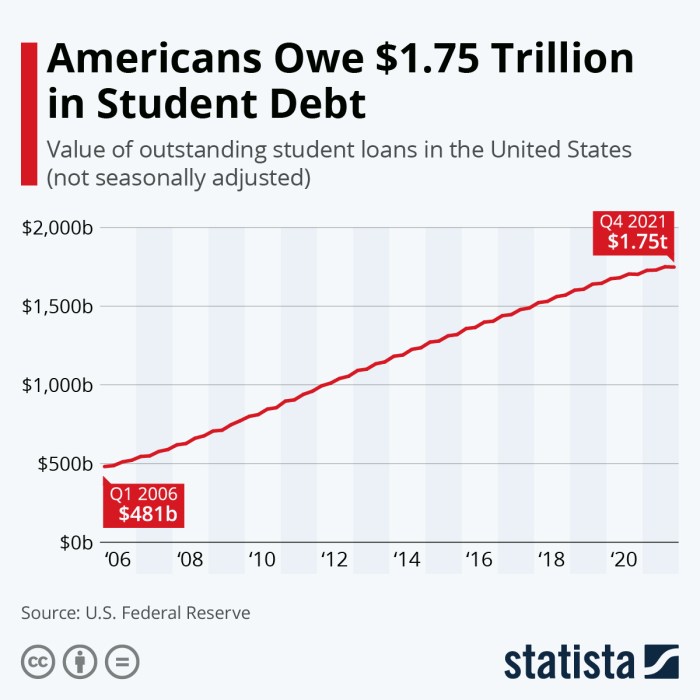
Understanding Missouri’s student loan landscape requires comparing it to neighboring states. Significant variations exist in eligibility criteria, interest rates, and repayment options, stemming from differing state priorities and economic conditions. This comparison highlights the nuances of state-level student loan policies and their impact on borrowers.
Key Differences in Student Loan Programs Across States
Neighboring states like Illinois, Kansas, Kentucky, and Arkansas exhibit notable differences in their student loan programs compared to Missouri. These variations affect accessibility, affordability, and the overall borrowing experience for students. The following table summarizes key distinctions.
| State | Eligibility Criteria | Average Interest Rates (Example: for a 10-year fixed loan) | Repayment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Missouri | Generally aligned with federal programs, potentially with state-specific scholarships or grants. | Variable, depending on the lender and loan type; reflects national trends. Assume an example average of 6.5% for illustration. | Standard federal repayment plans (e.g., Standard, Extended, Graduated), potentially supplemented by state-specific programs (if any). |
| Illinois | May have more robust state-specific grant programs or eligibility requirements for in-state students. | Potentially slightly lower due to state-sponsored initiatives or competitive market pressures; assume an example average of 6.0% for illustration. | May offer state-specific income-driven repayment plans or other assistance programs. |
| Kansas | May have a focus on specific industries or skill sets for grant eligibility. | Could be comparable to Missouri, or slightly higher depending on market conditions; assume an example average of 7.0% for illustration. | Likely aligns with standard federal repayment plans. |
| Kentucky | Similar to Missouri, largely relying on federal programs for base eligibility. | Comparable to Missouri, influenced by market factors; assume an example average of 6.8% for illustration. | Primarily standard federal repayment options. |
| Arkansas | May have specific grant programs targeting underrepresented groups or rural students. | Potentially higher due to economic factors or lower competition; assume an example average of 7.2% for illustration. | Likely standard federal repayment plans, possibly with limited state-specific options. |
Note: The interest rate examples provided are for illustrative purposes only and are not guaranteed rates. Actual interest rates vary depending on numerous factors, including creditworthiness, loan type, and market conditions. Specific details should be obtained from official state and lender resources.
Reasons for Variations in Student Loan Policies
State-level variations in student loan policies are influenced by several factors. State budgets, economic priorities, and political landscapes all play a role. States with stronger economies might invest more in student financial aid, resulting in lower interest rates or more generous repayment options. Conversely, states facing budgetary constraints may have limited resources for such initiatives. Furthermore, differing political priorities might lead to variations in the types of students prioritized for assistance (e.g., in-state versus out-of-state students, students pursuing specific fields of study). The level of state-level involvement also differs; some states have extensive programs, while others primarily rely on federal programs.
Outcome Summary
Successfully managing student loan debt requires proactive planning and a thorough understanding of available resources. This guide has provided a framework for navigating the complexities of student loans in Missouri, from exploring diverse program options and repayment plans to understanding the broader economic implications. By utilizing the resources Artikeld and seeking personalized guidance when needed, Missouri students and borrowers can effectively manage their debt and build a secure financial future. Remember, informed decisions are key to achieving financial stability.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the average student loan debt for Missouri graduates?
The average student loan debt for Missouri graduates varies depending on the year and institution attended. Specific data can be found through the Missouri Higher Education Loan Authority (MOHELA) and the National Center for Education Statistics.
Are there any state-specific grants available to help with student loan repayment in Missouri?
Missouri offers several grant programs, but they are typically for current students rather than repayment assistance. It’s advisable to check with MOHELA and the Missouri Department of Higher Education for the most current information on available grants.
What happens if I can’t make my student loan payments?
Contact your loan servicer immediately. They can discuss options like deferment, forbearance, or income-driven repayment plans to help you manage your payments. Failing to make payments can lead to serious consequences, including damage to your credit score.
