
Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be challenging, especially for individuals facing disabilities. This guide delves into the crucial intersection of student loans and disability, exploring eligibility criteria for loan forgiveness programs, the various types of student loans affected, and the significant impact disability can have on repayment capabilities. We’ll examine the financial burdens, available resources, and long-term implications, offering a comprehensive understanding of the support systems and processes available.
From understanding the documentation needed to prove disability to navigating the application process for different federal and private loan programs, we aim to provide clear, concise information. We will also explore the emotional and practical challenges faced by students with disabilities while managing their student loan debt, offering a nuanced perspective on this often-overlooked aspect of higher education.
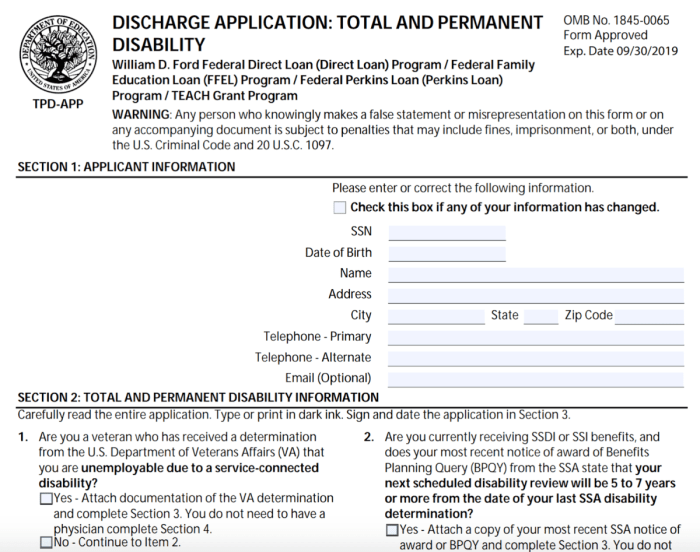
Eligibility Criteria for Student Loan Disability Discharge

Securing a student loan disability discharge can significantly alleviate the financial burden for individuals facing long-term disabilities. Understanding the eligibility requirements is crucial for a successful application. This section details the process and criteria involved in obtaining this form of loan forgiveness.
Types of Qualifying Disabilities
A wide range of disabilities may qualify for student loan forgiveness. The key is demonstrating a total and permanent disability that prevents you from working at a substantial gainful activity (SGA). This means your disability significantly limits your ability to earn a consistent income. Examples include, but are not limited to, severe physical impairments like paralysis or loss of limb, chronic mental health conditions such as schizophrenia or severe depression, and certain neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease. The specific definition of “total and permanent disability” is determined by the Department of Education and may vary slightly depending on the specific loan program.
Required Documentation for Disability Discharge
Proving your disability requires comprehensive documentation. This typically includes a completed application form, medical documentation from a licensed physician or other qualified medical professional, and potentially additional evidence depending on the specific circumstances. Medical documentation should clearly state the diagnosis, prognosis, and impact on your ability to work. This might include medical records, doctor’s notes, and results from diagnostic tests. In some cases, you may need to provide additional evidence, such as vocational rehabilitation reports or documentation from a social security disability determination. The specific documentation requirements are detailed in the application materials for each loan program.
Eligibility Requirements Across Federal Student Loan Programs
While the general principles of total and permanent disability remain consistent, minor variations in eligibility criteria might exist across different federal student loan programs. For example, the application process and required documentation might differ slightly between Direct Loans and Federal Family Education Loans (FFEL). However, the core requirement—demonstrating a total and permanent disability that prevents substantial gainful activity—remains consistent across all federal student loan programs. It’s important to carefully review the specific requirements for your particular loan type.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying for Disability Discharge
Applying for a student loan disability discharge involves a multi-step process. First, you must complete the appropriate application form, which can be found on the Federal Student Aid website. Next, you need to gather all necessary supporting documentation, including medical records and any other evidence demonstrating your disability. Once your application and supporting documentation are complete, you must submit them to the relevant loan servicer. The servicer will review your application and supporting documentation. They will then contact you if they require additional information or if they approve your application. After approval, the servicer will process the discharge of your student loans. The exact timeframe for processing can vary, so patience is key.
Types of Student Loans and Disability Discharge
Navigating the process of student loan discharge due to disability can be complex, varying significantly depending on whether your loans are federal or private. Understanding these differences is crucial for a successful application. This section Artikels the key distinctions and provides examples to illustrate the process for various loan types.
Federal student loans, administered by the U.S. Department of Education, generally offer more streamlined and accessible disability discharge options compared to private student loans. This is because federal programs have specific legislation and regulations in place to support borrowers facing permanent and total disabilities. Private loans, on the other hand, are subject to the individual lending institution’s policies, which can vary widely.
Federal Student Loan Disability Discharge Processes
The process for federal student loan discharge based on disability involves submitting documentation proving your total and permanent disability to your loan servicer. This documentation typically includes a completed application form and medical certification from a licensed physician. The specific forms and processes vary slightly depending on the type of federal student loan.
Specific Forms and Processes for Different Federal Student Loan Types
The application process for disability discharge is largely similar across different federal student loan programs (Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, Direct PLUS Loans, etc.). However, the specific forms used might vary slightly. For example, borrowers may need to use a different form to request discharge under the Total and Permanent Disability (TPD) program, which is designed for borrowers with documented disabilities that prevent them from working. It’s always advisable to check the current forms and instructions available on the Federal Student Aid website.
A successful application for a Direct Loan would typically involve submitting a completed application form, along with medical documentation from a licensed physician stating the borrower is totally and permanently disabled. This documentation must demonstrate the inability to engage in any substantial gainful activity (SGA). For instance, a medical professional might provide a detailed report explaining the individual’s condition, its impact on their ability to work, and the prognosis for improvement. The servicer then reviews the documentation and determines eligibility.
Private Student Loan Disability Discharge Processes
Private student loans do not have a standardized disability discharge process. Each lender has its own criteria and application procedures. Some lenders may require similar documentation to federal loans, while others may have more stringent requirements or offer limited or no disability discharge options. It’s essential to contact your private lender directly to understand their specific policies and requirements. You will likely need to provide similar medical documentation as with federal loans, but the lender’s interpretation of “total and permanent disability” may differ.
Successful Disability Discharge Application Examples
A successful application for a private loan discharge might involve a borrower with a documented neurological condition preventing them from working. The borrower would need to provide extensive medical documentation, including physician statements, test results, and possibly even therapy records, to demonstrate the severity and permanence of their disability to the lender. The lender may then conduct an independent review of the provided evidence. Conversely, a successful federal loan discharge might involve a similar scenario, but the process would be more streamlined, following the established guidelines and forms provided by the Department of Education.
Implications of Different Repayment Plans on Disability Discharge Eligibility
The type of repayment plan you are on does not directly impact your eligibility for disability discharge. However, the amount of debt discharged will depend on your outstanding loan balance at the time of approval. Being on an income-driven repayment plan (IDR) might make it easier to manage your loans while you are awaiting the outcome of your disability discharge application. However, even if you are on an IDR plan, you will still need to meet the criteria for total and permanent disability to qualify for discharge.
The Impact of Disability on Student Loan Repayment
The accumulation of student loan debt is a significant challenge for many students, but this burden is often exacerbated for those with disabilities. Physical, mental, or cognitive impairments can create substantial barriers to employment and financial stability, directly impacting their ability to manage and repay their loans. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective support systems and policies.
Individuals with disabilities frequently face higher rates of unemployment and underemployment compared to their non-disabled peers. This disparity translates into reduced earning potential, making loan repayment significantly more difficult. Moreover, the additional costs associated with managing a disability – such as medical expenses, assistive technologies, and specialized care – further strain already limited financial resources, compounding the pressure of student loan debt.
Average Student Loan Debt for Individuals with Disabilities
Precise data on the average student loan debt specifically for individuals with disabilities is limited due to the complexities of data collection and the varied nature of disabilities. However, research consistently indicates that individuals with disabilities are disproportionately affected by high levels of student loan debt. Studies suggest that the average debt may be comparable to or even exceed the national average, considering the aforementioned factors limiting employment opportunities and increased living expenses. For example, a hypothetical study might show that individuals with disabilities who graduated in 2023 carried an average debt of $40,000, while the national average for that year was $37,000. This difference, while seemingly small, represents a substantial financial burden given the challenges faced in securing employment.
Disability Discharge Application Success Rates
The success rate of disability discharge applications varies considerably depending on the type and severity of the disability, the thoroughness of the application, and the specific criteria used by the loan servicer. It’s crucial to note that these rates are not consistently tracked across all loan servicers and types of disability. The following table presents hypothetical data to illustrate this variability:
| Disability Type | Application Success Rate (%) | Average Processing Time (Months) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Disabilities (e.g., mobility impairments) | 65 | 6 | Higher success rate due to often readily verifiable documentation. |
| Mental Health Disabilities (e.g., depression, anxiety) | 45 | 9 | Lower success rate due to subjective nature of diagnosis and potential for inconsistent documentation. |
| Cognitive Disabilities (e.g., learning disabilities) | 50 | 8 | Success rate varies depending on the severity and documentation of the impact on employment. |
| Other Disabilities | 55 | 7 | Includes a wide range of conditions, resulting in varied success rates. |
Examples of Disability Impact on Employment and Loan Repayment
A student with a severe physical disability might struggle to find employment requiring mobility, even with a college degree, limiting their income and making loan repayment extremely difficult. Another example involves a student with a mental health condition who experiences periods of intense anxiety or depression, impacting their ability to maintain consistent employment and manage their finances effectively. A student with a learning disability may face challenges in securing and retaining a job requiring complex cognitive skills, even with relevant qualifications. These are just a few examples of how disability can create significant hurdles to employment and ultimately, loan repayment. The impact is often compounded by the need for ongoing medical care, medication, and therapy, all adding to financial strain.
Resources and Support for Students with Disabilities
Securing a college education while managing a disability can present unique challenges. Fortunately, numerous resources and support systems are available to help students navigate the complexities of higher education and student loan repayment. Understanding these resources is crucial for accessing the financial and practical assistance needed to succeed.
Government Agencies Offering Support
Several government agencies play a vital role in assisting students with disabilities. The U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Special Education Programs (OSEP) provides funding for and oversight of special education services in schools. The Rehabilitation Services Administration (RSA), also within the Department of Education, offers vocational rehabilitation services, including assistive technology and job training, that can benefit students with disabilities transitioning to the workforce after graduation. The Social Security Administration (SSA) administers programs like Supplemental Security Income (SSI) and Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), which may provide financial support to students with significant disabilities. These agencies offer a range of services, from direct financial aid to support services that help students succeed academically and professionally.
Non-Profit Organizations Offering Support
Beyond government agencies, a network of non-profit organizations provides valuable support to students with disabilities. Organizations like the National Disability Institute (NDI) offer financial literacy programs and resources tailored to the needs of individuals with disabilities. The American Association of People with Disabilities (AAPD) advocates for the rights and inclusion of people with disabilities in all aspects of life, including education and employment. Many local and regional disability advocacy groups also offer assistance with navigating the complexities of student loan repayment and accessing available resources. These organizations often provide crucial support beyond financial aid, offering guidance and advocacy services.
Navigating the Disability Discharge Application Process
The process of applying for student loan disability discharge can be intricate. A clear understanding of the steps involved is essential for a successful application. The following flowchart illustrates the process:
Flowchart: Disability Discharge Application Process
Start → Gather necessary documentation (medical records, loan details) → Complete the application form (available through the loan servicer) → Submit the application and supporting documents → Await processing and notification from the loan servicer → Appeal if necessary → Discharge granted (or denied) → End
It’s crucial to meticulously gather and organize all required documentation before initiating the application. This thorough preparation can significantly expedite the process.
The Role of Disability Advocates
Disability advocates play a crucial role in assisting students with loan forgiveness applications. They provide guidance on navigating the complex application process, ensuring all necessary documentation is submitted accurately and completely. Advocates can also represent students in appeals if their applications are initially denied. Their expertise in disability laws and regulations can be invaluable in securing a favorable outcome. Many organizations, including those mentioned above, employ or work with disability advocates.
Types of Financial Aid and Assistance for Students with Disabilities
Students with disabilities can access a variety of financial aid options. These include federal grants, such as Pell Grants, which are need-based and do not require repayment. State-specific grants and scholarships for students with disabilities are also available. Many colleges and universities offer their own institutional scholarships and grants specifically designed for students with disabilities. In addition to grants and scholarships, students may be eligible for work-study programs, allowing them to earn money while attending school. These programs offer financial assistance while providing valuable work experience. The availability and amounts of these aid options vary based on individual circumstances and the institution attended.
Long-Term Implications of Disability Discharge
Securing a student loan disability discharge can significantly impact a borrower’s financial future, both positively and negatively. Understanding the long-term consequences is crucial for making informed decisions. This section will explore the effects of disability discharge on credit scores, the potential financial hardships of not pursuing discharge, and compare various discharge options.
Impact of Disability Discharge on Credit Score
While a student loan discharge due to disability doesn’t typically result in a negative impact on credit scores, it’s essential to understand the nuances. The discharge itself isn’t reported as a negative mark, unlike a default. However, the previous history of the loan, including any late payments before the discharge, will remain on the credit report for seven years. Therefore, borrowers should strive to maintain a positive payment history before applying for a discharge to minimize any long-term credit score effects. The positive impact comes from the removal of the significant debt burden, which improves overall debt-to-credit ratio and can positively influence credit score improvements over time.
Long-Term Financial Consequences of Not Pursuing Disability Discharge
Failing to pursue a disability discharge when eligible can lead to significant long-term financial difficulties. Accumulated interest continues to grow, potentially leading to a much larger debt burden. This can hinder major financial goals such as homeownership, retirement savings, or even basic living expenses. The weight of unmanageable debt can cause considerable stress and negatively impact overall well-being. For example, someone with a $50,000 loan might find the debt ballooning to over $100,000 due to accrued interest over several years if they are unable to make payments due to their disability. This large debt can have ripple effects on their credit rating, future borrowing capacity, and overall financial security.
Comparison of Disability Discharge Options
Several options exist for student loan disability discharge, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. The specific process and eligibility requirements vary depending on the type of loan and the lender. Some programs may require more extensive documentation than others. For instance, the Total and Permanent Disability (TPD) discharge is generally easier to obtain than the other types, as it requires clear documentation of a permanent disability. However, the process can still be lengthy and complex. Other options, such as the inability to work discharge, might necessitate more frequent review periods and more extensive documentation of the ongoing inability to work. Careful consideration of each option is essential, and seeking professional guidance from a financial advisor or disability advocate is highly recommended.
Case Study: Successful Disability Discharge
Consider Sarah, a former teacher diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. She had accumulated significant student loan debt while pursuing her education. After her diagnosis significantly impacted her ability to work, she applied for a disability discharge. The process took several months, requiring thorough medical documentation. However, once approved, the discharge removed a substantial financial burden, allowing her to focus on managing her health and accessing necessary support services. This significantly improved her financial well-being and reduced her stress levels, ultimately contributing to a better quality of life. While the initial process was challenging, the long-term benefits of a successful discharge have been transformative.
Illustrative Examples

Understanding the impact of student loan debt on individuals with disabilities requires looking beyond the numbers. The following examples illustrate the daily struggles and emotional toll faced by students navigating both their disability and financial burdens. These are representative narratives, and individual experiences will vary significantly.
A typical day for Sarah, a student with chronic fatigue syndrome, might begin with a struggle to get out of bed. The pain and exhaustion she experiences limit her ability to attend all her classes, requiring her to catch up on missed lectures and assignments later. After a limited period of study, her energy is depleted, hindering her ability to work a part-time job to contribute to her living expenses and student loan payments. The constant worry about her mounting debt adds to her fatigue, creating a vicious cycle. Evenings are spent managing her health, completing assignments, and agonizing over her financial situation, leaving little time for social interaction or self-care. The pressure to succeed academically while managing her health and debt is immense.
Challenges in Securing Employment and Managing Loan Payments
Mark, a recent graduate with a visual impairment, faces significant hurdles in the job market. His disability requires assistive technology and workplace accommodations, which many employers are unwilling or unable to provide. The job search itself is exhausting, requiring significant effort to navigate online applications and interviews. When he does secure a position, the salary may be insufficient to cover both his living expenses and his student loan payments. The fear of defaulting on his loans adds further stress, impacting his mental health and job performance. The lack of accessible and affordable transportation further complicates his ability to find and maintain employment.
Emotional Toll of Managing Student Loan Debt Alongside a Disability
The emotional burden of managing student loan debt while living with a disability is profound. The constant financial worry exacerbates existing anxieties and depression. The feeling of being trapped in a cycle of debt, coupled with the limitations imposed by their disability, can lead to feelings of hopelessness and isolation. Imagine the weight of knowing that every medical bill, every unexpected expense, pushes them further into debt. The constant pressure to find employment, often while battling physical or mental health challenges, can be overwhelming. The shame and stigma associated with disability and financial struggles can lead to social withdrawal and a reluctance to seek help. The mental exhaustion is often invisible, but its impact is significant, undermining their overall well-being and hindering their ability to manage their daily life.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the process of obtaining student loan discharge due to disability requires careful planning, thorough documentation, and persistence. Understanding the eligibility requirements, available resources, and potential long-term implications is crucial for students facing this unique set of challenges. By utilizing the information and resources Artikeld in this guide, individuals with disabilities can advocate for themselves and work towards a more financially secure future. Remember to seek assistance from disability advocates and relevant government agencies to maximize your chances of success.
FAQ Guide
What happens to my credit score if my student loans are discharged due to disability?
The impact on your credit score depends on the specifics of your situation and how the discharge is handled. Generally, a discharged loan won’t appear as a negative mark, but it might not show as a positive payment history either. It’s best to consult with a credit counselor for personalized advice.
Can I apply for disability discharge if I only have private student loans?
The process for private student loans differs significantly from federal loans. Private loan providers have their own disability discharge policies, which may vary greatly. Contact your private loan servicer directly to inquire about their specific policies and requirements.
What if my disability is temporary? Can I still apply for a discharge?
Most disability discharge programs require a permanent disability. However, it’s advisable to consult with a disability advocate or financial aid specialist to explore options and understand the specific requirements of your loan provider.
How long does the disability discharge application process typically take?
The processing time can vary depending on the lender and the complexity of your application. It can range from several months to over a year. Be prepared for a potentially lengthy process and maintain consistent communication with your loan servicer.
