
Navigating the complexities of federal student loans can feel overwhelming, especially when faced with multiple loans and varying repayment options. Consolidating your federal student loans offers a potential pathway to simplification, allowing you to combine multiple loans into a single, manageable payment. However, this decision requires careful consideration, as it impacts interest rates, repayment plans, and long-term financial strategies. This guide explores the intricacies of federal student loan consolidation, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your financial future.
We will delve into the process of consolidation, examining its benefits and drawbacks in detail. We’ll analyze the impact on interest rates, explore various repayment plans, and discuss the eligibility criteria for loan forgiveness programs. Furthermore, we’ll address potential risks and considerations, comparing consolidation to refinancing options, and providing practical tips for managing your consolidated loans effectively. Our goal is to empower you with the information needed to navigate this crucial financial step with confidence.
Understanding Federal Student Loan Consolidation

Consolidating your federal student loans can simplify your repayment process by combining multiple loans into a single, new loan. This can lead to a more manageable monthly payment and potentially streamline your communication with your loan servicer. However, it’s crucial to understand both the advantages and disadvantages before making a decision.
The Process of Consolidating Federal Student Loans
The process of consolidating federal student loans involves applying through the Federal Student Aid website. You’ll need to gather information about your existing loans, including the loan servicer, loan amounts, and interest rates. The application itself requires providing personal information and details about your loans. Once submitted, the application is processed, and a new loan is created, encompassing all your eligible federal student loans. The new loan will have a new interest rate, calculated as a weighted average of your existing loans’ interest rates, and a new repayment schedule.
Benefits of Federal Student Loan Consolidation
Consolidation offers several potential benefits. A simplified repayment plan with a single monthly payment can improve organization and reduce the risk of missed payments. A potentially lower monthly payment, although with a potentially longer repayment term, can make managing your debt more manageable. Furthermore, consolidation can offer access to different repayment plans, such as income-driven repayment options, which can be beneficial for borrowers experiencing financial hardship. Finally, consolidation can simplify communication with a single loan servicer, eliminating the need to coordinate with multiple servicers.
Drawbacks of Federal Student Loan Consolidation
While consolidation offers advantages, it also has potential drawbacks. A longer repayment period, resulting from a lower monthly payment, can lead to paying more in total interest over the life of the loan. The weighted average interest rate may be higher than some of your existing loan rates, particularly if you have loans with low interest rates. Additionally, consolidation may mean losing certain benefits associated with specific loan programs, such as loan forgiveness programs tied to specific professions or public service. Finally, the process of consolidating can take some time, and you might experience a temporary delay in receiving your payments.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying for Consolidation
Applying for federal student loan consolidation is a straightforward process. First, gather all necessary information about your existing federal student loans. This includes loan amounts, interest rates, and loan servicers. Second, visit the Federal Student Aid website (StudentAid.gov) and locate the Direct Consolidation Loan application. Third, complete the application accurately and thoroughly, providing all required information. Fourth, submit your application and wait for processing, which typically takes several weeks. Finally, once approved, you’ll receive information about your new consolidated loan, including your new interest rate, monthly payment, and loan servicer.
Comparison of Federal Student Loan Consolidation Programs
While the primary federal student loan consolidation program is the Direct Consolidation Loan, it’s important to understand that there aren’t significantly different programs. The core process and terms remain consistent. The variations usually stem from the types of loans being consolidated (e.g., including Perkins loans or Federal Family Education Loans). The key differences are reflected in the interest rate calculation and eligibility requirements, which are primarily based on the types of loans included in the consolidation.
| Program | Interest Rate | Repayment Plans | Eligibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Consolidation Loan | Weighted average of existing loans | Various income-driven and standard plans | Eligible federal student loans |
Managing Your Consolidated Loans
Consolidating your federal student loans simplifies your repayment process by combining multiple loans into a single monthly payment. However, effective management is crucial to avoid delinquency and achieve timely repayment. This section will Artikel strategies for budgeting, preventing late payments, and maintaining open communication with your loan servicer.
Effective Budgeting and Loan Payment Management
Creating a realistic budget is paramount to successful student loan repayment. This involves tracking your income and expenses to determine how much you can comfortably allocate towards your loan payments each month. Consider using budgeting apps or spreadsheets to monitor your finances. Prioritize essential expenses like housing, food, and transportation before allocating funds to discretionary spending and loan payments. Building an emergency fund is also advisable to cover unexpected costs and prevent loan payment disruptions.
Strategies for Avoiding Late Payments and Penalties
Late payments can result in significant penalties, including increased interest charges and negative impacts on your credit score. To prevent this, set up automatic payments directly from your bank account. This ensures timely payments without manual intervention. Alternatively, you can set reminders on your phone or calendar to ensure you make your payment on time. Consider exploring options like income-driven repayment plans if you’re facing financial hardship, as these plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income.
Maintaining Communication with Your Loan Servicer
Regular communication with your loan servicer is essential for proactive loan management. Contact them immediately if you anticipate difficulties making a payment or if you have questions about your loan terms or repayment options. They can provide guidance on available repayment plans, deferment or forbearance options, and other assistance programs. Keeping your contact information updated with your servicer is also crucial to ensure you receive important notices and updates.
Sample Student Loan Repayment Budget
The following table illustrates a sample budget, demonstrating how to allocate funds for student loan repayment alongside other essential expenses. Remember, this is just an example, and your individual budget will vary based on your income, expenses, and loan amount.
| Category | Amount | Category | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Housing | $1000 | Student Loan Payment | $500 |
| Food | $400 | Transportation | $200 |
| Utilities | $200 | Savings/Emergency Fund | $100 |
| Healthcare | $150 | Other Expenses | $250 |
Navigating the Application Process

Consolidating your federal student loans can simplify your repayment, but understanding the application process is key to a smooth experience. This section details the steps involved, required documentation, common issues, and how to track your application’s progress.
The federal student loan consolidation application is primarily completed online through the Federal Student Aid website (StudentAid.gov). The process is designed to be straightforward, but careful attention to detail is crucial to avoid delays.
Application Steps
The application process generally involves several key steps. First, you’ll need to gather all necessary information about your existing federal student loans, including loan numbers, lenders, and outstanding balances. Next, you’ll create or log in to your FSA ID account, a username and password used to access federal student aid websites. Then, you’ll complete the online application form, providing accurate information about yourself and your loans. Finally, you’ll review your application and electronically submit it. After submission, you’ll receive a confirmation number, which is essential for tracking your application’s status.
Required Documentation and Verification
To successfully complete the application, you’ll need to provide certain documentation. This typically includes your Social Security number, driver’s license or state-issued ID, and information about your existing federal student loans. The system will likely cross-reference your information with the National Student Loan Data System (NSLDS) to verify your loan details. In some cases, additional documentation may be requested, such as proof of income or identity verification if discrepancies are found. Be prepared to provide this information promptly to avoid delays in processing your application.
Resolving Common Application Issues
While the application process is generally user-friendly, some common issues can arise. For example, inaccurate information provided on the application may lead to delays or rejection. Incorrect loan information or missing documentation are frequent causes of delays. If you encounter any problems, the Federal Student Aid website provides a comprehensive FAQ section and contact information for assistance. Contacting the Federal Student Aid helpline directly is recommended for issues that cannot be resolved through the website’s resources. Proactive attention to detail during the application process can minimize the likelihood of encountering these issues.
Tracking Application Status
Once you submit your application, you can track its progress online. Using your FSA ID, you can log in to the Federal Student Aid website and access your application status. The website usually provides updates on the processing stages, such as when your application has been received, when your loans have been verified, and when your consolidation loan is expected to be disbursed. Regularly checking your application status allows you to stay informed and address any potential delays promptly. This proactive approach can ensure a smoother and more efficient consolidation process.
Impact on Future Borrowing
Consolidating your federal student loans can have a significant impact on your ability to borrow money in the future. While it simplifies your repayment, understanding the potential effects on your credit and borrowing capacity is crucial before proceeding. This section will explore how loan consolidation might influence your future financial decisions.
Consolidation affects future borrowing primarily through its influence on your credit report and the overall picture it presents to potential lenders. Your credit score is a key factor in determining interest rates and loan approval. The changes resulting from consolidation—such as a change in your credit utilization ratio or the age of your credit accounts—can impact your score, which then influences your eligibility for future loans, including graduate school funding or mortgages.
Credit Report Implications
Consolidating your federal student loans will create a new loan entry on your credit report, replacing your individual student loan entries. While this simplifies your credit profile visually, it can also affect your credit score in both positive and negative ways. A longer credit history, for example, generally results in a better score. Conversely, if your consolidation results in a higher debt-to-income ratio, it could lower your score. The impact is highly individualized and depends on your existing credit history and the terms of your consolidated loan. For example, if you had multiple loans with varying interest rates and consolidated into a single loan with a lower rate, your credit utilization ratio might improve, leading to a better score. However, if your new loan has a higher balance than the sum of your individual loans, your credit utilization could increase negatively impacting your score.
Impact on Graduate School or Other Loans
Your ability to secure future loans, particularly for graduate school, can be affected by your consolidated loan. Lenders will review your credit report and consider your debt-to-income ratio. A lower credit score due to consolidation, or a higher debt-to-income ratio resulting from a larger consolidated loan, could lead to higher interest rates or even loan rejection. Conversely, if consolidation improves your credit score by reducing your credit utilization or simplifying your credit history, it could improve your chances of securing future loans at favorable terms. For instance, a student with several smaller loans with high interest rates might see their credit score increase after consolidating into a single loan with a lower interest rate, thereby improving their chances of securing a graduate school loan.
Long-Term Effects of Consolidation
Understanding the potential long-term consequences is vital. The following points summarize the key impacts:
- Credit Score Fluctuation: Consolidation can either improve or worsen your credit score, depending on your specific circumstances and how the consolidation affects your credit utilization and debt-to-income ratio.
- Interest Rate Changes: While consolidation might offer a lower interest rate initially, this is not guaranteed. The new interest rate will depend on your creditworthiness at the time of consolidation.
- Debt Management: Consolidation simplifies repayment, making it easier to manage your debt. However, if you don’t manage your finances carefully, you might accumulate more debt in the future.
- Future Borrowing Capacity: Your ability to secure future loans (such as mortgages or auto loans) may be influenced by your credit score and debt-to-income ratio after consolidation.
Comparing Consolidation to Refinancing
Choosing between federal student loan consolidation and private student loan refinancing is a significant decision that can impact your repayment strategy and overall financial health. Both options aim to simplify your loan payments, but they operate under different mechanisms and carry distinct advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these key differences is crucial for making an informed choice.
Federal student loan consolidation combines multiple federal student loans into a single, new federal loan. Private student loan refinancing, on the other hand, involves replacing your existing federal or private student loans with a new private loan from a lender. While both streamline payments, the implications for interest rates, repayment terms, and access to federal benefits differ considerably.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Federal Student Loan Consolidation
Federal consolidation offers several advantages. Primarily, it simplifies repayment by reducing the number of monthly payments and potentially lowering your monthly payment amount through an extended repayment plan. Furthermore, it maintains access to federal loan forgiveness programs and income-driven repayment plans, which can be crucial for borrowers facing financial hardship. However, consolidation doesn’t lower your interest rate; instead, it calculates a weighted average of your existing loan interest rates, resulting in a fixed interest rate for the consolidated loan. This means you might not save money on interest in the long run. Additionally, the consolidation process can take several weeks or months to complete.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private Student Loan Refinancing
Private refinancing offers the potential for lower interest rates, especially for borrowers with strong credit scores and stable incomes. This can lead to significant savings on interest payments over the life of the loan. Refinancing can also simplify payments by consolidating multiple loans into one. However, refinancing your federal student loans means losing access to federal benefits like income-driven repayment plans and potential forgiveness programs. Furthermore, the refinancing process is subject to credit checks and approval from a private lender, potentially excluding borrowers with less-than-perfect credit history. Finally, the terms and conditions of private loans can vary significantly between lenders, requiring careful comparison and consideration.
Scenarios Favoring Consolidation or Refinancing
Consolidation is generally preferable for borrowers who prioritize maintaining access to federal benefits like income-driven repayment and forgiveness programs, even if it means a slightly higher interest rate. This is particularly true for borrowers who anticipate potential financial difficulties or who work in public service fields eligible for loan forgiveness.
Refinancing is a better option for borrowers with excellent credit scores and stable incomes who are confident in their ability to make consistent payments and who are willing to forgo federal benefits in exchange for potentially lower interest rates. This strategy works best when you are certain about your future financial stability and repayment capabilities. For example, a borrower with a high income and a strong credit history could significantly reduce their interest payments by refinancing, outweighing the loss of federal benefits.
Key Differences Between Consolidation and Refinancing
| Feature | Federal Consolidation | Private Refinancing |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Type | Federal | Private |
| Interest Rate | Weighted average of existing rates (fixed) | Variable or fixed, potentially lower than existing rates |
| Federal Benefits | Retained | Lost |
| Credit Check | Not required | Required |
End of Discussion
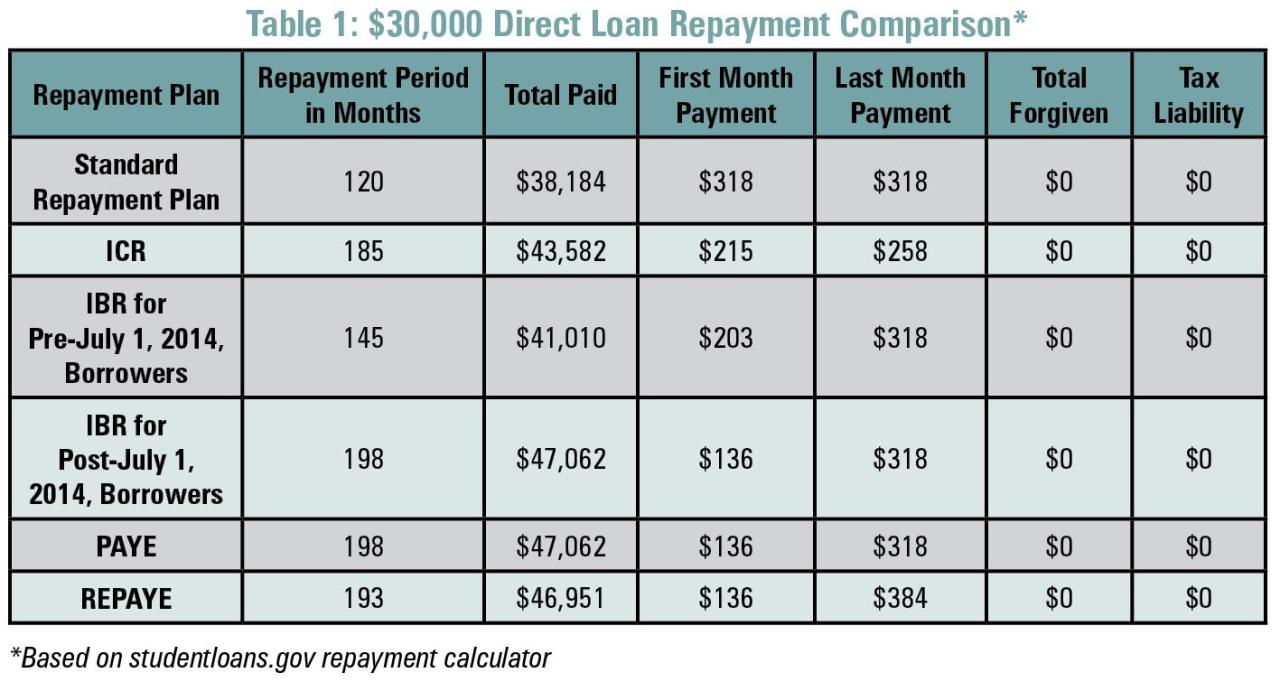
Ultimately, the decision to consolidate federal student loans is a personal one, requiring a thorough understanding of your individual financial circumstances and long-term goals. While consolidation can simplify repayment and potentially access loan forgiveness programs, it’s crucial to weigh the potential drawbacks, such as increased overall interest paid. By carefully considering the information presented in this guide, you can approach the consolidation process with clarity and make a well-informed choice that aligns with your financial aspirations. Remember to always consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between consolidation and refinancing?
Consolidation combines multiple federal loans into one, while refinancing replaces federal loans with a new private loan. Refinancing offers potentially lower interest rates but loses federal protections.
Can I consolidate private student loans with federal loans?
No, federal student loan consolidation only applies to federal loans. Private loans must be refinanced separately.
What happens to my loan forgiveness eligibility after consolidation?
Consolidation may affect eligibility for certain forgiveness programs; check eligibility requirements for each program before consolidating.
How long does the consolidation process take?
The processing time varies, but generally takes several weeks. Check the status of your application regularly.
