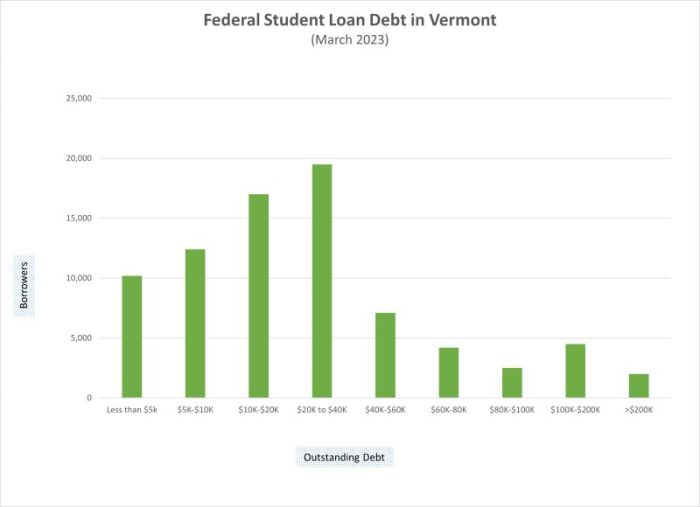
Securing a higher education is a significant investment, and understanding the landscape of student loan options is crucial for Vermont students. This guide delves into the intricacies of Vermont student loan programs, providing a clear overview of available options, eligibility requirements, and repayment strategies. We’ll explore both state-specific and federal loan programs, highlighting their unique benefits and drawbacks to help you make informed decisions about financing your education.
From understanding eligibility criteria and interest rates to navigating loan forgiveness programs and managing debt effectively, this resource aims to empower Vermont students with the knowledge they need to successfully navigate the complexities of student loan financing. We’ll examine various repayment plans, discuss strategies for avoiding loan default, and provide links to valuable resources that can offer further assistance.
Vermont Student Loan Programs

Securing funding for higher education is a crucial step for many aspiring Vermonters. Understanding the various student loan programs available within the state is essential for making informed financial decisions. This section details the key Vermont-based student loan programs, their eligibility requirements, and associated benefits. It’s important to note that program details are subject to change, so always verify information directly with the relevant lending institution or government agency.
Vermont Student Assistance Corporation (VSAC) Programs
The Vermont Student Assistance Corporation (VSAC) is the primary source of student financial aid in Vermont. They offer a range of loan programs designed to help Vermonters finance their education. These programs vary in their eligibility criteria and terms. While VSAC doesn’t directly lend all its programs, it serves as a central resource and often facilitates access to various loan options.
Eligibility Criteria for VSAC Programs
Eligibility requirements for VSAC-administered programs vary widely depending on the specific program and the student’s circumstances. General criteria often include Vermont residency, enrollment in an eligible educational institution, and demonstration of financial need (for need-based programs). Specific GPA requirements are not usually a factor in loan eligibility but may influence eligibility for certain scholarships or grants that might accompany a loan. Income limitations are often considered for need-based aid.
Interest Rates, Repayment Options, and Forgiveness Programs
Interest rates for VSAC-administered loans fluctuate based on market conditions and the type of loan. Repayment options generally include standard repayment plans, graduated repayment plans (where payments increase over time), and income-driven repayment plans (where payments are tied to a percentage of the borrower’s income). Some programs may offer loan forgiveness options under specific circumstances, such as working in public service or teaching in underserved areas. Specific details are available on the VSAC website.
| Program Name | Eligibility Criteria | Interest Rate | Repayment Options | Forgiveness Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSAC Direct Loan (Example) | Vermont residency, enrollment in eligible institution, demonstrated financial need | Variable, based on market conditions | Standard, graduated, income-driven | Potential for public service loan forgiveness (PSLF) eligibility |
| VSAC Private Loan (Example) | Creditworthiness, enrollment in eligible institution | Variable, based on credit score and market conditions | Standard, graduated | Generally no federal forgiveness programs |
State-Specific Loan Forgiveness Programs
Vermont offers several loan forgiveness programs designed to incentivize graduates to remain in the state and contribute to vital sectors. These programs aim to alleviate student loan debt burdens while addressing workforce needs in critical fields like education and healthcare. Eligibility criteria vary depending on the specific program and often involve a commitment to working in a designated profession within Vermont for a specified period.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program
This program provides partial or full loan forgiveness for teachers who work in Vermont public schools. To qualify, applicants must have a Vermont student loan, teach in a Vermont public school for a minimum of five consecutive years, and meet certain income requirements. The amount of forgiveness is directly related to the number of years of service. For example, a teacher who works for five years might receive 25% loan forgiveness, while ten years of service could lead to 100% forgiveness. While specific examples of individuals benefiting from this program are not publicly available due to privacy concerns, anecdotal evidence from the Vermont Student Assistance Corporation (VSAC) suggests that many teachers have significantly reduced their loan debt through this program.
- Confirm eligibility based on loan type and employment.
- Gather required documentation, including employment verification and loan details.
- Complete and submit the application through the VSAC website.
- Maintain continuous employment in a qualifying Vermont public school.
- Regularly update VSAC on employment status.
Healthcare Professional Loan Forgiveness Program
Vermont also offers loan forgiveness opportunities for healthcare professionals, particularly those working in underserved areas. This program targets professionals such as nurses, physicians, and physician assistants who commit to practicing in designated rural or underserved communities within Vermont. Requirements include a specific number of years of service (often five or more), employment in a qualifying healthcare facility, and meeting certain income thresholds. The forgiveness amount is typically based on the length of service and the level of need in the designated area. One example could be a nurse practitioner who served in a rural Vermont clinic for ten years receiving substantial loan forgiveness, enabling them to focus on patient care rather than significant debt repayment.
- Determine eligibility based on profession, location, and loan type.
- Identify a qualifying healthcare facility in an underserved area.
- Gather necessary documentation, including employment verification and loan information.
- Submit the application to the designated agency (likely VSAC).
- Maintain employment and report annually to the relevant agency.
Federal Student Loan Options in Vermont
Vermont residents have access to the full range of federal student loan programs, offering a valuable supplement or even alternative to state-based options. These federal programs provide a consistent and nationally recognized framework for financing higher education, regardless of individual circumstances or the specific institution attended. Understanding the nuances of both federal and state programs is crucial for maximizing financial aid.
Federal student loans are administered through the U.S. Department of Education and offer several advantages, including various repayment plans and potential for loan forgiveness programs depending on career path. However, it’s important to weigh these benefits against potential drawbacks such as interest rates that may fluctuate and overall loan amounts that could potentially be higher than some state-based programs.
Comparison of Federal and Vermont Student Loan Programs
The key differences between federal and Vermont state-based student loan programs lie primarily in interest rates, repayment plans, and deferment options. Choosing the right loan type often involves balancing the immediate cost with long-term financial implications.
- Interest Rates: Federal loan interest rates are typically set annually by Congress and can vary depending on the loan type (e.g., subsidized vs. unsubsidized). Vermont state-based programs may offer interest rates that are fixed or variable, potentially lower than the federal rates in certain years, but this can fluctuate. A comparison of current interest rates from the respective lenders would be necessary to determine the most advantageous option in a given year.
- Repayment Plans: Federal loans provide a wider array of repayment plans, including income-driven repayment (IDR) options that adjust monthly payments based on income and family size. Vermont state-based programs may offer standard repayment plans, but the flexibility and options may be less extensive. For example, a graduate pursuing a low-income career might find an IDR plan particularly beneficial under a federal loan.
- Deferment Options: Both federal and Vermont state loans may offer deferment options, allowing borrowers to temporarily postpone payments under specific circumstances (e.g., unemployment or enrollment in graduate school). However, the eligibility criteria and duration of deferment may differ. A student facing unexpected unemployment could utilize deferment under either program, but understanding the specific requirements of each is vital.
Combining Federal and Vermont Loan Programs
Strategic combination of federal and state loan programs can significantly optimize financial aid. For instance, a student might utilize Vermont’s state-based programs to cover a portion of their tuition, then supplement with federal loans to cover the remaining costs. This approach can help minimize the overall amount borrowed and potentially reduce the long-term financial burden. A student aiming for a specific amount of financial aid could strategically use a combination of state grants, state loans and federal loans to reach their desired goal. For example, a student needing $20,000 could receive $5,000 in state grants, $5,000 in state loans and $10,000 in federal loans.
Managing Vermont Student Loan Debt
Navigating student loan repayment can feel overwhelming, but understanding your options and proactively managing your debt is crucial for your financial future. This section Artikels strategies to effectively manage your Vermont student loans, address potential challenges, and access available resources.
Repayment Strategies for Vermont Student Loan Borrowers
Several repayment strategies are available to Vermont student loan borrowers, allowing flexibility based on individual financial circumstances. These include standard repayment plans, graduated repayment plans, extended repayment plans, and income-driven repayment (IDR) plans. Standard plans involve fixed monthly payments over a set period (typically 10 years). Graduated plans start with lower payments that gradually increase, while extended plans spread payments over a longer period (up to 25 years), resulting in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest. IDR plans, such as the Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) plans, tie your monthly payment to your income and family size. These plans may result in lower monthly payments, but often lead to higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. It’s important to carefully compare the long-term costs of each plan before making a decision. Contact your loan servicer to explore your options and determine which plan best suits your financial situation.
Consequences of Loan Default and Steps to Avoid Default
Defaulting on your student loans has serious consequences, including damage to your credit score, wage garnishment, tax refund offset, and potential legal action. A damaged credit score can make it difficult to obtain loans, rent an apartment, or even secure certain jobs. To avoid default, consistently make your loan payments on time. If you anticipate difficulty making a payment, contact your loan servicer immediately to discuss options such as deferment or forbearance. These programs temporarily postpone or reduce your payments, but interest may still accrue during these periods. Open communication with your loan servicer is key to preventing default.
Resources for Vermont Students Struggling with Student Loan Debt
Vermont offers several resources to assist students struggling with student loan debt. The Vermont Student Assistance Corporation (VSAC) provides comprehensive counseling and guidance on managing student loan debt. They offer personalized assistance in exploring repayment options, budgeting strategies, and consolidating loans. Additionally, several non-profit credit counseling agencies throughout Vermont offer free or low-cost credit counseling services. These agencies can help you create a budget, develop a debt management plan, and negotiate with your creditors. These services can be invaluable in navigating challenging financial situations and preventing default.
Consolidating Multiple Vermont Student Loans
Consolidating multiple student loans into a single loan can simplify repayment by combining several monthly payments into one. This can make tracking payments easier and potentially lower your monthly payment amount, depending on the chosen repayment plan. However, it’s crucial to understand that consolidation may not always lower the total interest paid over the life of the loan. The interest rate on your consolidated loan will be a weighted average of your existing loan interest rates. To consolidate your Vermont student loans, you’ll need to gather information about your existing loans, including loan amounts, interest rates, and loan servicers. You can then apply for a Direct Consolidation Loan through the federal government or explore private consolidation options. Carefully compare the terms and conditions of different consolidation options before making a decision. Contact VSAC for guidance on the consolidation process.
Visual Representation of Loan Repayment
Understanding the long-term financial implications of different student loan repayment plans is crucial for effective debt management. A clear visual representation can significantly aid this understanding by comparing total repayment amounts and timelines across various plans. This allows borrowers to make informed decisions aligned with their financial capabilities and long-term goals.
Visualizing repayment plans effectively requires a graph that clearly displays the relationship between time and total repayment cost. A line graph is particularly well-suited for this purpose, allowing for a direct comparison of multiple repayment scenarios.
Line Graph Illustrating Repayment Plan Comparisons
The graph will use a standard Cartesian coordinate system. The x-axis will represent the repayment period, measured in years, starting from zero and extending to the maximum repayment duration under consideration (e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years). The y-axis will represent the cumulative total amount repaid, expressed in dollars. Each repayment plan (e.g., Standard, Extended, Income-Driven) will be represented by a separate line on the graph. Data points will be plotted at regular intervals (e.g., annually) along the x-axis, representing the cumulative amount repaid at each point in time under each plan. These points will then be connected to form lines representing the cumulative repayment trajectory for each plan.
For example, let’s consider three hypothetical repayment plans for a $30,000 loan:
* Standard Repayment: A 10-year plan with a fixed monthly payment, resulting in a total repayment of approximately $36,000 (including interest). The line for this plan will show a steady, upward trajectory, reaching $36,000 at the 10-year mark.
* Extended Repayment: A 20-year plan, resulting in a total repayment of approximately $48,000 (due to increased interest accumulation). This line will show a less steep, but still upward, trajectory, reaching $48,000 at the 20-year mark.
* Income-Driven Repayment: A plan with variable monthly payments adjusted based on income, potentially extending over 20-25 years. The total repayment amount will depend on income fluctuations and the specific plan parameters, but it could range from $45,000 to $60,000. This line might show a less predictable trajectory, potentially with slight variations in the slope due to income-based payment adjustments.
The graph should include a clear legend identifying each line corresponding to a specific repayment plan. Annotations can be added to highlight key data points, such as the total amount repaid for each plan and the duration of each repayment plan. For instance, a small text box could be placed near the endpoint of each line, clearly stating the total amount repaid and the repayment period for that particular plan. This visual representation allows for a direct comparison of the total cost and time commitment associated with each repayment plan, enabling borrowers to make a well-informed decision.
Final Summary

Successfully managing Vermont student loans requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of the available resources. By carefully considering the options presented in this guide—from exploring state-specific programs and federal loan options to implementing effective repayment strategies—Vermont students can make informed decisions that align with their individual financial goals. Remember to utilize the available resources and seek professional guidance when needed to ensure a smooth and successful journey through higher education and beyond.
Key Questions Answered
What is the Vermont Student Assistance Corporation (VSAC)?
VSAC is a non-profit organization that provides financial aid assistance and resources to Vermont students, including information and application support for various student loan programs.
Can I consolidate my Vermont student loans?
Yes, it’s possible to consolidate multiple student loans into a single loan, potentially simplifying repayment. Check with VSAC or your loan servicer for details on consolidation options.
What happens if I default on my Vermont student loans?
Loan default can lead to serious consequences, including damage to your credit score, wage garnishment, and potential legal action. Contact your loan servicer immediately if you’re struggling to make payments.
Are there income-driven repayment plans for Vermont student loans?
Yes, several income-driven repayment plans are available for federal student loans, and some state programs may offer similar options. Check with your loan servicer or VSAC to explore your choices.
Where can I find additional resources for managing my student loan debt?
VSAC provides comprehensive resources and guidance. Additionally, you can explore federal government websites and non-profit credit counseling agencies for further assistance.
