Navigating the complex world of student loan interest rates can feel overwhelming, especially with the constant fluctuations and variations between federal and private loans. Understanding these rates is crucial for responsible borrowing and financial planning, impacting your monthly payments and overall repayment burden significantly. This guide aims to demystify the process, providing clarity on current rates, influencing factors, and resources to help you make informed decisions.
From subsidized and unsubsidized federal loans to the intricacies of private loan interest calculations, we’ll explore the key differences and how various factors, such as credit score and loan type, affect the interest you’ll pay. We’ll also illustrate the long-term implications of interest rate changes, showcasing how even small variations can accumulate into substantial differences in your total repayment amount over time. By understanding these dynamics, you can better manage your debt and plan for a financially secure future.
Understanding the Basics of Student Loan Interest Rates
Student loan interest rates are a crucial factor influencing the overall cost of your education. Understanding how these rates are determined and what factors affect them is essential for responsible borrowing and financial planning. This section will break down the complexities of federal student loan interest rates, providing clarity on the different loan types and their associated costs.
Federal Student Loan Types and Interest Rates
The federal government offers several types of student loans, each with its own interest rate structure. These rates are generally lower than private loan rates, making federal loans a more attractive option for many students. The interest rate for a particular loan depends on several factors, including the loan type and the loan disbursement date. It’s important to note that these rates are subject to change annually.
Interest Rate Determination for Federal Student Loans
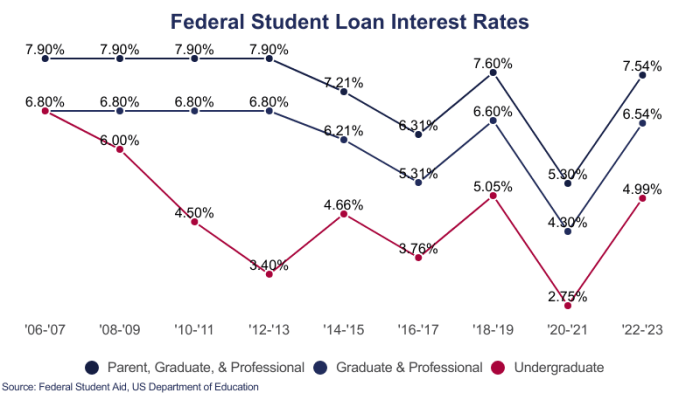
Interest rates for federal student loans are not fixed; they fluctuate. For subsidized and unsubsidized Stafford Loans, the interest rate is set annually by Congress. This rate is usually tied to the 10-year Treasury note yield, plus a fixed margin. This means that the rate is influenced by prevailing economic conditions and the government’s borrowing costs. For other federal loan programs, like PLUS loans, the interest rate is also determined annually but might follow a different index or have a different margin added. The interest rate is fixed for the life of the loan, meaning it won’t change after the loan is disbursed.
Factors Influencing Student Loan Interest Rates
Several factors influence the interest rate you’ll receive on a federal student loan. The most significant factor is the type of loan itself. Subsidized Stafford Loans, for instance, typically have lower interest rates than unsubsidized Stafford Loans or PLUS loans. The timing of the loan disbursement also plays a role, as the interest rate is set for each academic year. A student’s credit history is not a factor for federal student loans, unlike private loans, where a good credit score often leads to lower interest rates.
Comparison of Federal Student Loan Interest Rates
The following table provides a comparison of interest rates for various federal student loan programs. Remember that these rates are subject to change and should be verified with the official government sources before making any borrowing decisions. The table illustrates a range because the specific interest rate can vary slightly depending on the disbursement year.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate Range (Example – Subject to Change) | Repayment Plan Options | Additional Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidized Stafford Loan | 3.73% – 5.28% | Standard, Graduated, Extended, Income-Driven | None |
| Unsubsidized Stafford Loan | 4.23% – 6.54% | Standard, Graduated, Extended, Income-Driven | None |
| PLUS Loan (Graduate/Professional) | 7.54% – 8.05% | Standard, Extended, Income-Driven | Origination Fee |
| PLUS Loan (Parent) | 7.54% – 8.05% | Standard, Extended | Origination Fee |
Current Interest Rates for Federal Student Loans
Understanding the current interest rates for federal student loans is crucial for borrowers to effectively manage their debt. These rates directly impact the total amount repaid over the life of the loan, making it essential to know how they’re determined and where to find the most current information. Federal student loan interest rates are not fixed; they fluctuate annually, influenced by market conditions.
Federal student loan interest rates are set annually by the government. The process involves several factors, including market-based indices and Congressional action. While the exact mechanics are complex, the core principle is to establish rates that reflect the cost of borrowing for the government while remaining manageable for students. The rates are typically announced in the spring for the upcoming academic year.
Federal Student Loan Interest Rates
The interest rates for federal student loans vary depending on the loan type and the loan’s disbursement date. It’s important to note that these rates are subject to change annually. The following information reflects the rates for the 2023-2024 academic year, but it is crucial to consult official government sources for the most current rates.
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans: The interest rate for subsidized Stafford loans disbursed during the 2023-2024 academic year is 5.0%. This rate is fixed for the life of the loan. Subsidized loans are awarded based on financial need and the government pays the interest while the borrower is in school at least half-time, during grace periods, and during deferment periods.
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans: The interest rate for unsubsidized Stafford loans disbursed during the 2023-2024 academic year is 5.0%. This rate is fixed for the life of the loan. Unsubsidized loans are available to students regardless of financial need, and interest begins accruing immediately.
- Federal PLUS Loans: The interest rate for Federal PLUS Loans disbursed during the 2023-2024 academic year is 7.5%. This rate is fixed for the life of the loan. PLUS loans are available to graduate and professional students, as well as parents of undergraduate students.
Finding the Most Up-to-Date Interest Rate Information
To find the most current interest rates for federal student loans, it is recommended to consult official government sources. The most reliable source is the official website of the Federal Student Aid (FSA) office, part of the U.S. Department of Education. This website provides detailed information on current interest rates, loan types, and repayment plans. Searching “Federal Student Aid” on a search engine will easily lead you to the official site. Always verify information from unofficial sources by cross-referencing it with data from the FSA website.
Private Student Loan Interest Rates

Private student loans, unlike federal loans, are offered by private lenders such as banks and credit unions. These loans are subject to variable interest rates, meaning the rate can fluctuate over the life of the loan, unlike some federal loan options. Understanding these rates is crucial for responsible borrowing.
Private student loan interest rates are significantly influenced by a borrower’s creditworthiness. This differs substantially from federal student loan programs, which typically base eligibility and interest rates on factors other than credit history, such as demonstrated financial need.
Comparison of Private and Federal Student Loan Interest Rates
Federal student loans generally offer lower interest rates than private student loans. This is because the government subsidizes these loans, reducing the risk for lenders. Private lenders, on the other hand, assess risk based on the individual borrower’s credit profile, leading to potentially higher rates for those with less-than-stellar credit. The difference in interest rates can be substantial, potentially adding thousands of dollars to the total cost of borrowing over the loan’s lifetime. For example, a federal student loan might have a fixed interest rate of 5%, while a comparable private loan could have a variable rate starting at 7% and potentially rising higher.
Factors Affecting Private Student Loan Interest Rates
Several key factors determine the interest rate a borrower receives on a private student loan. A strong credit history is paramount. A higher credit score indicates lower risk to the lender, resulting in a more favorable interest rate. The presence of a creditworthy co-signer can also significantly reduce the interest rate, as the co-signer assumes responsibility for repayment should the primary borrower default. The loan amount itself also plays a role; larger loan amounts may be associated with slightly higher interest rates due to increased risk for the lender. Finally, the type of loan (e.g., undergraduate vs. graduate) and the lender’s own pricing policies influence the final interest rate.
Impact of Credit Score on Private Student Loan Interest Rates
A borrower’s credit score directly impacts the interest rate offered on a private student loan. Lenders use credit scores to assess risk. For example, a borrower with an excellent credit score (750 or higher) might qualify for an interest rate of 6%, while a borrower with a fair credit score (650-699) might face an interest rate of 9% or higher. A borrower with a poor credit score (below 650) may struggle to secure a private student loan at all, or face extremely high interest rates, making repayment incredibly difficult. These differences highlight the importance of building and maintaining a good credit history before applying for private student loans.
Risks and Benefits of Private Student Loans
Private student loans offer flexibility in terms of loan amounts and repayment options, but they also carry significant risks. The higher interest rates compared to federal loans can lead to substantial increases in the total cost of borrowing. The lack of federal protections, such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs, also poses a considerable risk for borrowers. However, a benefit might be the potential for higher loan amounts, which can be crucial for students who exhaust their federal loan eligibility. Careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits is essential before taking out a private student loan.
Interest Rate Changes and Their Impact
Student loan interest rates are not static; they fluctuate based on various economic factors. Understanding how these changes impact your overall loan cost is crucial for effective financial planning. Even small shifts in interest rates can significantly alter the total amount you repay over the life of your loan.
Interest rate changes directly affect the total cost of a student loan. A higher interest rate means you’ll pay more in interest over the life of the loan, increasing your total repayment amount. Conversely, a lower interest rate results in lower overall interest payments and a smaller total repayment. This impact is amplified by the length of the repayment period; longer repayment terms expose borrowers to greater cumulative interest charges.
The Implications of Interest Rate Fluctuations for Borrowers
Increases in interest rates lead to higher monthly payments and a greater total repayment amount. This can strain borrowers’ budgets, particularly those with limited income or unexpected financial challenges. Conversely, decreases in interest rates can provide some financial relief, lowering monthly payments and reducing the overall loan burden. Borrowers should actively monitor interest rate changes and consider refinancing options if rates fall significantly. Refinancing allows borrowers to potentially secure a lower interest rate and reduce their monthly payments. However, it’s crucial to carefully compare offers and ensure the refinancing terms are favorable before making a decision.
Loan Capitalization and Its Effect on Total Interest Paid
Loan capitalization is the process of adding accumulated interest to the principal loan balance. This occurs when a borrower enters into a grace period or defers payments. The capitalized interest then accrues interest itself, leading to a snowball effect that significantly increases the total interest paid over the life of the loan. For example, if a borrower has $10,000 in unpaid interest capitalized, that $10,000 is added to the principal, and future interest calculations are based on the increased principal balance. This compounding effect can dramatically increase the overall cost of borrowing.
Illustrative Scenario: Total Repayment with Varying Interest Rates
The following table demonstrates the impact of different interest rates on a $20,000 student loan with a 10-year repayment period. Note that these are simplified examples and do not include any potential fees. Actual repayment amounts will vary based on loan type, lender, and individual repayment plan.
| Interest Rate | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid | Total Repayment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4% | $200 | $2,700 | $22,700 |
| 6% | $222 | $4,000 | $24,000 |
| 8% | $244 | $5,600 | $25,600 |
| 10% | $267 | $7,200 | $27,200 |
Resources for Finding Current Interest Rate Information
Locating precise and current information on student loan interest rates requires utilizing reliable sources. Understanding where to find this information and how to verify its accuracy is crucial for making informed financial decisions. This section Artikels reliable sources, navigation strategies, and verification techniques.
Knowing where to look for the most up-to-date student loan interest rates is essential for borrowers. Several government and private websites provide this information, but it’s vital to understand how to navigate these resources effectively and confirm the authenticity of the data presented.
Reliable Sources for Student Loan Interest Rate Information
The most reliable sources for student loan interest rates are official government websites and established financial institutions. Relying on unofficial or less reputable sources can lead to inaccurate or misleading information.
- Federal Student Aid (FSA): The official website of the U.S. Department of Education’s Federal Student Aid office (studentaid.gov) provides comprehensive information on federal student loan programs, including current interest rates for various loan types (subsidized and unsubsidized Stafford Loans, PLUS Loans, etc.). The site often includes rate tables, explanations of how rates are determined, and details on potential rate changes.
- National Education Association (NEA): The NEA often publishes articles and resources related to student loan debt and interest rates. While not a primary source for rate data, their analysis can provide context and interpretation of the information found on official government websites.
- Individual Lenders (for Private Loans): If you have private student loans, check the websites of the lenders directly. These websites usually provide details about your loan terms, including the interest rate, in your account dashboard or loan documents.
Navigating Sources to Find Interest Rate Information
Finding the relevant information on these websites usually involves searching for terms like “student loan interest rates,” “current interest rates,” or “loan rates.” Many sites organize this information within sections dedicated to loan programs or financial aid. Look for tables or charts that clearly display the interest rates for different loan types and periods. Pay close attention to the effective date of the rates, as these can change periodically. For federal loans, the information will typically be displayed by loan type and year. For private loans, the information is usually found within your personal loan account summary.
Verifying the Authenticity of Interest Rate Information
Always verify information from unofficial sources by cross-referencing it with official government websites or your lender’s statements. Be wary of websites that lack clear contact information or that appear to be promoting specific financial products without disclosing potential conflicts of interest. Look for sites with “.gov” (government) or “.edu” (educational institution) domains, as these typically indicate higher reliability. Information found on credible news sources that cite official government data can also be considered trustworthy.
Information Typically Found on Official Websites
Official websites, such as studentaid.gov, usually provide detailed information including:
- Current interest rates: Rates are often presented in tables, specifying the interest rate for each loan type (e.g., subsidized and unsubsidized Stafford Loans, PLUS Loans).
- Interest rate calculation methods: Explanations of how the interest rates are determined, including the index used (if applicable) and the calculation methodology.
- Effective dates: The dates when the listed interest rates became effective and any future changes that are expected or planned.
- Loan terms and conditions: Details about repayment plans, deferment options, and other important aspects of the loan agreement.
- Contact information: Ways to contact the relevant authorities or customer service representatives for further assistance.
Outcome Summary
Securing a higher education often involves taking on student loan debt, making a thorough understanding of interest rates paramount. This exploration of current student loan interest rates has highlighted the critical distinctions between federal and private loans, emphasizing the factors influencing these rates and their long-term financial consequences. By actively utilizing the provided resources and remaining informed about rate changes, borrowers can navigate the complexities of loan repayment effectively and confidently plan for their financial well-being.
FAQs
What is the difference between subsidized and unsubsidized federal student loans?
Subsidized loans don’t accrue interest while you’re in school (at least half-time), during grace periods, and during deferment. Unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed.
Can I refinance my student loans to get a lower interest rate?
Yes, refinancing can potentially lower your interest rate, but it often involves switching from federal to private loans, which may eliminate certain borrower protections.
How often do student loan interest rates change?
Federal student loan interest rates are typically set annually, while private loan rates can change more frequently based on market conditions.
What is loan capitalization?
Loan capitalization is when accrued interest is added to the principal loan balance, increasing the amount you owe and subsequently increasing future interest payments.
