Navigating the complexities of student loan interest rates can feel overwhelming. Understanding why your rate increased is crucial for effectively managing your debt. This guide explores the various factors that can influence your student loan interest rate, from market fluctuations to your personal credit history. We’ll provide clear explanations and practical steps to help you understand your loan agreement and take control of your financial future.
From fixed versus variable rates to the impact of missed payments, we’ll examine the key elements that contribute to interest rate changes. We’ll also offer strategies for managing higher interest rates, including exploring repayment options and the possibility of refinancing. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of your situation and the tools to address it confidently.
Understanding Student Loan Interest Rate Calculations
Understanding how your student loan interest rate is determined is crucial for managing your debt effectively. Several factors influence this rate, and knowing these components allows for better financial planning and informed decision-making regarding your loans. This section will break down the key elements involved in calculating your interest rate and explore how different loan types and terms affect the overall cost.
Components of a Student Loan Interest Rate
Several key factors contribute to your final student loan interest rate. These include your credit history (if applicable), the type of loan, the lender, and prevailing market interest rates. For federal student loans, your credit history typically doesn’t play a role, but for private student loans, a strong credit history often leads to lower interest rates. The type of loan (e.g., subsidized vs. unsubsidized, federal vs. private) significantly impacts the interest rate, with subsidized loans often having lower rates than unsubsidized ones. The lender’s own policies and risk assessment also affect the rate they offer. Finally, general economic conditions and market interest rates play a major role in determining the rates offered by lenders. A period of higher interest rates across the board will generally result in higher student loan rates.
Types of Student Loans and Interest Rate Ranges
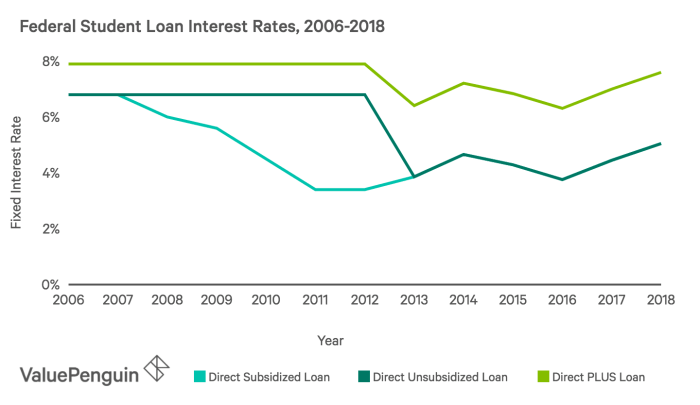
Student loans fall into two main categories: federal and private. Federal loans are offered by the government and generally have more favorable terms and lower interest rates than private loans. Federal student loans include subsidized and unsubsidized loans, with subsidized loans offering the lowest rates as interest does not accrue while the student is in school (under certain eligibility requirements). Unsubsidized loans, conversely, accrue interest throughout the loan’s life. Private student loans, offered by banks and credit unions, typically have higher interest rates, reflecting the lender’s higher risk. The interest rates for these loans are highly variable depending on factors such as the borrower’s creditworthiness, the loan amount, and the repayment terms. Generally, expect interest rates on private loans to range from a few percentage points above federal loan rates to significantly higher depending on the borrower’s profile.
Impact of Loan Terms on Total Interest Paid
The length of your repayment period significantly impacts the total interest you pay over the life of the loan. A longer repayment period results in lower monthly payments, but you will pay significantly more interest overall because the interest is calculated over a longer period. Conversely, a shorter repayment period means higher monthly payments, but you’ll pay less interest in the long run. For example, a $20,000 loan at 5% interest with a 10-year repayment plan will have significantly lower total interest paid compared to the same loan with a 20-year repayment plan. The longer you take to pay, the more interest you accrue.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
| Feature | Fixed Interest Rate | Variable Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Rate | Stays the same throughout the loan term | Fluctuates based on market conditions |
| Predictability | Highly predictable monthly payments | Monthly payments can change |
| Advantages | Budget stability; you know exactly how much you’ll pay each month. | Potentially lower initial payments if market rates are low. |
| Disadvantages | May have a higher initial interest rate compared to a variable rate if market rates are low. | Risk of higher payments if market interest rates rise; less predictable budgeting. |
Factors Influencing Interest Rate Changes

Several factors can cause a student loan’s interest rate to increase, particularly for variable-rate loans. Understanding these factors is crucial for borrowers to manage their loan repayment effectively and avoid unexpected increases in their monthly payments. This section will explore the key influences on student loan interest rate fluctuations.
Market Interest Rate Fluctuations
Variable-rate student loans are directly tied to market interest rates, such as the prime rate or a specific benchmark index like LIBOR (although LIBOR is being phased out). When these market rates rise, so too will the interest rate on your variable-rate loan. This is because the lender’s cost of borrowing money increases, and they pass that cost onto borrowers. The magnitude of the increase in your loan’s interest rate will depend on the specific terms of your loan agreement, which will Artikel how your interest rate is calculated relative to the underlying market index. For example, if your loan’s rate is pegged to the prime rate plus 2%, and the prime rate increases by 0.5%, your loan’s interest rate will also increase by 0.5%.
Impact of Borrower Credit Score
While less common for existing student loans, a borrower’s credit score can sometimes influence interest rate changes, especially during the loan application process or loan refinancing. Lenders use credit scores to assess risk. A lower credit score signals a higher risk of default, leading lenders to offer higher interest rates to compensate for that increased risk. Conversely, borrowers with excellent credit scores may qualify for lower interest rates. For example, a borrower with a credit score below 650 might face a significantly higher interest rate than a borrower with a score above 750. It’s important to note that this factor is usually more relevant when initially obtaining a loan or refinancing, rather than affecting an already established loan.
Unexpected Interest Rate Increases
In some cases, a student loan’s interest rate might increase unexpectedly due to factors outside the borrower’s direct control or clearly stated in the loan agreement. For instance, some lenders may have clauses allowing for interest rate adjustments based on unforeseen economic events or changes in their internal risk assessment models. While this is less frequent, it highlights the importance of carefully reviewing the loan agreement’s fine print before signing. A specific example could be a lender adjusting rates due to significant and unforeseen changes in regulatory requirements. This is an uncommon scenario but represents a potential reason for an unexpected increase. Another possibility, though less likely, is a change in the lender’s internal risk assessment model, potentially leading to an adjustment in the interest rate for a subset of borrowers.
Review of Loan Documents and Agreements
Understanding your student loan agreement is crucial for managing your debt effectively. A thorough review can help you identify the reasons behind any interest rate fluctuations and ensure you’re not paying more than necessary. Failing to understand these terms could lead to unexpected costs and financial difficulties.
Your student loan agreement is a legally binding contract outlining the terms and conditions of your loan. It details all aspects of your repayment, including the interest rate, payment schedule, and any potential fees. Careful examination of this document is essential to prevent misunderstandings and protect your financial well-being.
Checklist for Reviewing Student Loan Agreements Regarding Interest Rate Adjustments
Before reviewing your loan documents, it’s helpful to have a checklist to guide your search. This structured approach will ensure you don’t miss any critical information regarding interest rate changes.
- Initial Interest Rate: Note the interest rate stated at the loan’s origination.
- Interest Rate Type: Identify whether your loan has a fixed or variable interest rate. Fixed rates remain constant throughout the loan term, while variable rates can fluctuate.
- Index and Margin (for Variable Rate Loans): If your loan has a variable rate, find the specific index used (e.g., LIBOR, SOFR) and the margin added to that index to determine your interest rate.
- Interest Rate Adjustment Frequency: Determine how often the interest rate can be adjusted (e.g., annually, semiannually). This information is crucial for variable rate loans.
- Rate Caps (for Variable Rate Loans): Check for any maximum or minimum interest rate limits. These caps prevent excessively high or low interest rates.
- Notification of Rate Changes: Confirm how and when you will be notified of any interest rate changes. The agreement should specify the method of notification (e.g., mail, email) and the timeframe.
- Grace Period (if applicable): Identify if there is a grace period before interest begins to accrue.
- Payment Calculation Method: Understand how your monthly payment is calculated, including the interest component.
Locating and Interpreting Information on Interest Rate Adjustments
Finding the relevant information within your loan documents may require careful searching. The specific location of this information can vary depending on the lender and loan type.
- Review the Loan Agreement: The primary source of information will be your original loan agreement or promissory note. Look for sections titled “Interest Rate,” “Variable Interest Rate,” or similar headings.
- Search for Key Terms: Use s like “index,” “margin,” “adjustment,” “rate change,” or “rate cap” to quickly locate relevant sections.
- Contact Your Lender: If you have difficulty finding the information, don’t hesitate to contact your loan servicer. They can provide clarification on your interest rate terms.
- Understand the Language: Loan agreements often use technical jargon. If any terms are unclear, seek professional advice or use online resources to understand the definitions.
Potential Clauses Describing Interest Rate Changes
Several clauses within a loan agreement can describe how your interest rate may change. Understanding these clauses is essential to managing your loan effectively.
- Variable Rate Clause: This clause Artikels the mechanics of a variable interest rate, including the index used, margin, and frequency of adjustments.
- Interest Rate Adjustment Clause: This clause details the process for adjusting the interest rate, including notification procedures and any applicable limitations.
- Default Rate Clause: This clause specifies a higher interest rate that may be applied if you default on your loan payments.
- Late Payment Fee Clause: This clause explains any additional fees charged for late payments, which can indirectly increase the overall cost of your loan.
Contacting the Loan Servicer
Understanding why your student loan interest rate increased requires direct communication with your loan servicer. They are the company responsible for managing your loan, and they possess the information needed to clarify any changes to your interest rate. This process involves several steps, from choosing the best method of contact to meticulously documenting all interactions.
It’s crucial to approach your loan servicer in a proactive and organized manner. This ensures a smoother process and helps you obtain the necessary information to address the interest rate increase effectively. Remember to keep a record of all communication to safeguard your rights and facilitate future reference.
Methods for Contacting the Loan Servicer
Several avenues exist for contacting your loan servicer. Choosing the best method depends on your preference and the urgency of your inquiry. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, influencing the speed and efficiency of communication.
- Phone: Calling your loan servicer directly often provides the quickest resolution. You can usually find their phone number on your loan documents or their website. Be prepared to provide your loan details for verification purposes. Expect potential hold times, particularly during peak hours.
- Email: Email allows for a documented record of your inquiry and response. Ensure you use a secure email address and include all relevant loan information in your message. Response times can vary, depending on the servicer’s workload.
- Mail: Sending a letter via mail is the least efficient method but provides a formal paper trail. Include your loan information, a clear explanation of your inquiry, and a return address. Allow ample time for delivery and response.
Examples of Questions to Ask the Loan Servicer
Preparing specific questions beforehand streamlines the communication process and ensures you receive the information you need. Focusing on clear and concise inquiries helps maintain a productive conversation. The following examples illustrate the type of questions you should ask.
- “What is the reason for the increase in my student loan interest rate?”
- “Can you provide me with documentation detailing the interest rate change, including the effective date?”
- “Is this interest rate increase consistent with my loan agreement?”
- “Are there any options available to lower my interest rate?”
- “What are the steps I need to take to appeal this interest rate increase, if applicable?”
Documenting Communication with the Loan Servicer
Maintaining a comprehensive record of all communications is essential for protecting your interests. This record serves as proof of your inquiries and the servicer’s responses. It’s also beneficial should you need to escalate the issue or pursue further action.
Effective documentation includes:
- Date and time of contact: Note the exact date and time of each phone call, email, or letter sent.
- Method of contact: Specify whether you contacted the servicer by phone, email, or mail.
- Summary of conversation or correspondence: Briefly describe the content of your communication and the servicer’s response. Include any specific details, such as reference numbers or dates mentioned.
- Copies of all correspondence: Keep copies of any emails, letters, or notes you receive from the servicer.
- Name and contact information of the representative: Record the name and contact information of the loan servicer representative you spoke with.
Exploring Options for Managing Higher Interest Rates
Facing a higher student loan interest rate can be daunting, but understanding your options for managing this increase is crucial for minimizing long-term costs. Several strategies can help you navigate this challenge and potentially reduce the overall amount you pay. This section explores different repayment plans, interest reduction strategies, and the potential of refinancing.
Student Loan Repayment Plans and Their Impact on Interest Costs
Different repayment plans significantly affect the total interest paid over the life of your loan. The standard repayment plan involves fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period. While this minimizes the total repayment time, it results in higher monthly payments. Extended repayment plans, conversely, stretch payments over a longer period (up to 25 years), lowering monthly payments but increasing the total interest paid due to the extended repayment timeline. Income-driven repayment plans (IDR) adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. These plans often result in lower monthly payments but may extend the repayment period significantly, leading to higher overall interest costs. Finally, graduated repayment plans start with lower monthly payments that gradually increase over time. This approach offers manageable initial payments but can lead to substantially higher payments later in the repayment period. The choice depends on your current financial situation and long-term financial goals. For example, someone with a stable income might prefer the standard plan to minimize interest, while someone with fluctuating income might benefit from an IDR plan.
Strategies to Reduce Total Interest Paid
Several strategies can help reduce the total interest paid on your student loans. Making extra principal payments, even small amounts, can significantly reduce the overall interest paid and shorten the loan’s repayment term. For instance, an extra $100 payment per month can substantially decrease the total interest over the loan’s lifespan. Another effective strategy is to consolidate multiple loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate, simplifying payments and potentially lowering your monthly payment. Careful budgeting and prioritizing loan repayment over other expenses are also crucial. By dedicating more of your income towards loan repayment, you can accelerate the payoff process and reduce interest accumulation.
Refinancing Student Loans: Benefits and Drawbacks
Refinancing your student loans involves replacing your existing loans with a new loan from a different lender, often at a lower interest rate. This can lead to significant savings in interest paid over the life of the loan, potentially lowering your monthly payments and shortening the repayment period. However, refinancing has drawbacks. You might lose benefits associated with federal student loans, such as income-driven repayment plans or deferment options. Additionally, refinancing typically requires a good credit score, and the new loan’s terms may not be as favorable if your credit score is low. For example, a borrower with excellent credit might secure a significantly lower interest rate, whereas someone with a poor credit history may not qualify or receive a favorable rate.
Resources for Borrowers Struggling with High Interest Rates
Before listing resources, it’s important to note that seeking help is crucial when facing financial difficulties related to student loan debt. Many organizations offer support and guidance to navigate this challenge.
- Your loan servicer: They can provide information about repayment plans and options available to you.
- The National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC): Offers free and low-cost credit counseling services.
- The Student Loan Borrower Assistance Project (SLBAP): Provides free legal assistance to student loan borrowers.
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): Offers resources and information on managing student loan debt.
- Your school’s financial aid office: May offer guidance and support.
Illustrative Scenarios
Understanding how various factors can impact your student loan interest rate is crucial for effective financial planning. The following scenarios illustrate different situations that can lead to interest rate changes, both positive and negative.
Interest Rate Increase Due to Market Conditions
Rising interest rates in the broader economy often translate to higher rates on variable-rate student loans. Imagine Sarah, who has a variable-rate federal student loan with an initial interest rate of 5%. Due to inflation and Federal Reserve actions to combat it, the benchmark interest rate used to calculate her loan rate increases to 7%. This means Sarah’s monthly payment will increase, and she will pay significantly more in interest over the life of her loan. The impact on Sarah is a higher total repayment cost and a potentially tighter budget. She might need to adjust her spending or explore options like loan consolidation to mitigate the effects.
Interest Rate Increase Due to Missed Payment
Late or missed payments can severely impact your credit score and often trigger penalty interest rates. Consider John, who has a federal student loan with a fixed interest rate of 6%. He misses a payment, resulting in a late payment fee and an increase in his interest rate to 8%. This penalty interest rate is applied to his outstanding balance, significantly increasing his total repayment cost. Furthermore, his credit score takes a hit, potentially impacting his ability to secure future loans or credit at favorable rates. The consequences for John are not only a higher cost of borrowing but also potential long-term financial repercussions.
Successful Negotiation of a Lower Interest Rate
Negotiating a lower interest rate is possible, although not always guaranteed. Let’s say Maria has a private student loan with a high interest rate of 9%. She researches her loan servicer’s policies and discovers they offer interest rate reductions for borrowers who demonstrate financial hardship or consistently make on-time payments. Maria meticulously documents her financial situation and contacts her loan servicer. After providing evidence of her improved financial stability and consistent payment history, she successfully negotiates a reduction to 7.5%, saving her a substantial amount over the life of the loan. This success was achieved through proactive communication, documentation, and a clear understanding of her loan terms.
Successful Loan Refinancing for a Lower Interest Rate
Refinancing can be a powerful tool to lower your interest rate. Suppose David has several federal student loans with varying interest rates, averaging around 7%. He has a good credit score and stable income. He researches various private lenders and finds one offering a refinancing option with a lower fixed interest rate of 5%. After carefully comparing terms and fees, David decides to refinance his loans. This consolidation simplifies his payments and significantly reduces his overall interest payments, allowing him to pay off his debt faster. The key to David’s success was thorough research, a strong credit profile, and a clear understanding of the refinancing process.
Conclusion
Ultimately, understanding why your student loan interest rate increased empowers you to make informed decisions. By carefully reviewing your loan documents, proactively communicating with your loan servicer, and exploring available options, you can navigate this challenge and work towards a more manageable debt repayment plan. Remember, seeking professional financial advice can provide additional support and guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Expert Answers
What if my interest rate increased without notification?
Immediately contact your loan servicer. A lack of notification may indicate an error or a violation of your loan agreement. Document all communication.
Can I negotiate a lower interest rate?
While not always possible, it’s worth attempting. Contact your servicer and present your case, highlighting factors like improved credit or financial hardship. Be prepared to negotiate.
How do I find my loan’s interest rate details?
Your loan documents (typically online through your servicer’s portal) will specify the interest rate, its type (fixed or variable), and any conditions for changes. Review these carefully.
What are the consequences of missing a student loan payment?
Missing payments can significantly impact your credit score and may lead to increased interest rates (often through penalties) and potential collection actions.
